Extra Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Force and Laws of Motion
Extra questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 9 Force and Laws of Motion with answers is given below. Our subject expert prepared these solutions as per the latest NCERT textbook. These questions will be helpful to revise the all topics and concepts. CBSE Class 9 extra questions are the most simple and conceptual questions that are prepared by subject experts for the students to study well for the final exams. By solving these extra questions, students can be very efficient in their exam preparations.
Force and Laws of Motion Class 9 Science Extra Questions and Answers
Very Short Answer Questions
1: Define force.
Answer: It is a push or pull on an object that produces acceleration in the body on which it acts.
2: What is S.I. unit of force?
Answer: S.I. unit of force is Newton.
3: Define one Newton.
Answer: A force of one Newton produces an acceleration of 1 m/s2 on an object of mass 1 kg. .
1 N = 1 kg m/s2
4: What is balanced force?
Answer: When forces acting on a body from the opposite direction do not change the state of rest or of motion of an object, such forces are called balanced forces.
5: What is frictional force?
Answer: The force that always opposes the motion of object is called force of friction.
6: What is inertia?
Answer: The natural tendency of an object to resist a change in their state of rest or of uniform motion is called inertia.
7: State Newton’s first law of motion.
Answer: An object remains in a state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an external unbalanced force.
8: State Newton’s second law of motion.
Answer: The rate of change of momentum of an object is proportional to the applied unbalanced force in the direction of the force.
9: What is momentum?
Answer: The momentum of an object is the product of its mass and velocity and has the same direction as that of the velocity. The S. I. unit is kg m/s. (p = mv)
10: State Newton’s III law of motion.
Answer: To every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction and they act on two different bodies.
11: Which will have more inertia a body of mass 10 kg or a body of mass 20 kg?
Answer: A body of mass 20 kg will have more inertia.
12: Name the factor on which the inertia of the body depends.
Answer: Inertia of a body depends upon the mass of the body.
13: Name two factors which determine the momentum of a body.
Answer: Two factors on which momentum of a body depend is mass and velocity. Momentum is directly proportional to the mass and velocity of the body.
14: What decides the rate of change of momentum of an object?
Answer: The rate of change of momentum of an object is proportional to the applied unbalanced force in the direction of force.
15: The diagram shows a moving truck. Forces A, B,
C and D are acting on the truck.
Name the type of forces acting on a truck.
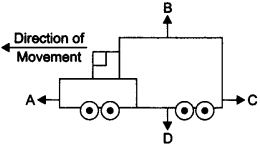
Answer: The forces A, B, C and D acting on the truck are:
A → driving force
B → reacting force
C → frictional force
D → weight/gravitational force
Short Answer Type Questions
1: State the difference in balanced and unbalanced force.
Answer:
| Balanced force | Unbalanced force |
| Forces acting on a body from the opposite directions are same. | Forces acting on a body from two opposite directions are not same. |
| It does not change the state of rest or of motion of an object. | It change the state of rest or of motion of an object. |
2: What change will force bring in a body?
Answer: Force can bring following changes in the body:
- It can change the speed of a body.
- It can change the direction of motion of a body,
- It can change the shape of the body.
3: When a motorcar makes a sharp turn at a high speed, we tend to get thrown to one side. Explain why?
Answer: It is due to law of inertia. When we are sitting in car moving in straight line, we tend to continue in our straight-line motion. But when an unbalanced force is applied by the engine to change the direction of motion of the motorcar. We slip to one side of the seat due to the inertia of our body.
4: Explain why it is dangerous to jump out of a moving bus.
Answer: While moving in a bus our body is in motion. On jumping out of a moving bus our feet touches the ground and come to rest. While the upper part of our body stays in motion and moves forward due to inertia of motion and hence we can fall in forward direction.
Hence, to avoid this we need to run forward in the direction of bus.
5: Why do fielders pull their hand gradually with the moving ball while holding a catch?
Answer: While catching a. fast moving cricket ball, a fielder on the ground gradually pulls his hands backwards with the moving ball. This is done so that the fielder increases the time during which the high velocity of the moving ball decreases to zero. Thus, the acceleration of the ball is decreased and therefore the impact of catching the fast moving ball is reduced.
6: In a high jump athletic event, why are athletes made to fall either on a cushioned bed or on a sand bed?
Answer: In a high jump athletic event, athletes are made to fall either on a cushioned bed or on a sand bed so as to increase the time of the athlete’s fall to stop after making the jump. This decreases the rate of change of momentum and hence the force.
7: How does a karate player breaks a slab of ice with a single blow?
Answer: A karate player applied the blow with large velocity in a very short interval of time on the ice slab which therefore exerts large amount of force on it and suddenly breaks the ice slab.
8: What is law of conservation of momentum?
Answer: Momentum of two bodies before collision is equal to the momentum after collision.
In an isolated system, the total momentum remain conserved.
9. Why are roads on mountains inclined inwards at turns?
Answer: A vehicle moving on mountains is in the inertia of motion. At a sudden turn there is a tendency of vehicle to fall off the road due to sudden change in the line of motion hence the roads are inclined inwards so that the vehicle does not fall down the mountain.
10: For an athletic races why do athletes have a special posture with their right foot resting on a solid supporter?
Answer: Athletes have to run the heats and they rest their foot on a solid supports before start so that during the start of the race the athlete pushes the support with lot of force and this support gives him equal and opposite push to start the race and get a good start to compete for the race.
11:Why do you think it is necessary to fasten your seat belts while travelling in your vehicle?
Or
How are safety belts helpful in preventing any accidents?
Answer: While we are travelling in a moving car, our body remains in the state of rest with respect to the seat. But when driver applies sudden breaks or stops the car our body tends to continue in the same state of motion because of its inertia. Therefore, this sudden break may cause injury to us by impact or collision. Hence, safety belt exerts a force on our body to make the forward motion slower.
12: Explain how momentum gets conserved in collision of two bodies.
Answer: Consider two bodies i.e., balls A and B, the mass and initial velocities are mAuA and mBuB respectively before collision. The two bodies collide and force is exerted by each body. There is change in their velocities due to collision.
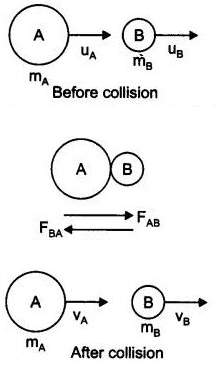
The momentum of ball A before collision is mAuA and final momentum is mAvA.
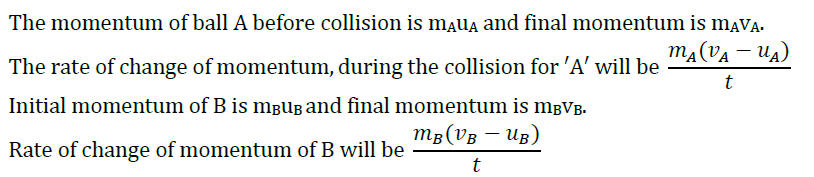
According to the third law of motion, the force fAB exerted by ball A on ball B and the force fBA exerted by the ball B on ball A must be equal and opposite to each other.
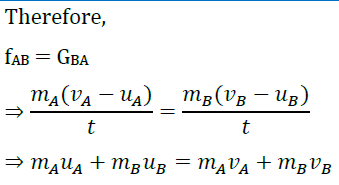
∴ (mAuA +mBuB) is the total momentum of the two balls A and B before collision and (mAvA + mBvB) is their total momentum after collision.
∴ The total momentum of the two balls remains unchanged or conserved provided no other external force acts.
13: When you kick a football it flies away but when you kick a stone you get huh why?
Answer: This is because stone is heavier than football and heavier objects offer larger inertia.
When we kick a football its mass is less and inertia is also less so force applied by our kick acts on it and hence it shows larger displacement but in case of stone, it has larger mass and offers larger inertia. When we kick (action) the stone it exerts an equal and opposite force (reaction) and hence it hurts the foot.
14: If a person jumps from a height on a concrete surface he gets hurt. Explain.
Answer: When a person jumps from a height he is in state of inertia of motion. When he suddenly touches the ground he comes to rest in a very short time and hence the force exerted by the hard concrete surface on his body is very high, and the person gets hurt.
15: What is the relation between Newton’s three laws of motion?
Answer: Newton’s first law explains about the unbalanced force required to bring change in the position of the body.
Second law states/explains about the amount of force required to produce a given acceleration.
And Newton’s third law explains how these forces acting on a body are interrelated.
16: Give any three examples in daily life which are based on Newton’s third law of motion.
Answer: Three examples based on Newton’s third law are :
(i) Swimming: We push the water backward to move forward.
action – water is pushed behind
reaction – water pushes the swimmer ahead
(ii) Firing gun: A bullet fired from a gun and the gun recoils.
action – gun exerts force on the bullet
reaction – bullet exerts an equal and opposite force on the gun
(ii) Launching of rocket: action – hot gases from the rocket are released reaction – the gases exert upward push to the rocket
17: A bullet of mass 20 g is horizontally fired with a velocity 150 m/s from a pistol of mass 2 kg. What is the recoil velocity of the pistol?
Answer:
For Bullet
m1 = 20g = 0.02 kg
u1 = 0
v1 = +150 m/s
Pistol
m2 = 2kg
u2 = 0
v2 = ?
Total momentum of the pistol and bullet before firing, when the gun is at rest
= m1u1 + m2u2
= (0.02 × 0) + (2 × 0)
= 0 kg m/s
Total momentum of the pistol and bullet after it is fired
= m1v1 + m2v2
= (0.02 × 150) + (2 × v)
= 3 + 2v
∴ Total momentum after firing = Total momentum before firing
⇒ 3 + 2v = 0
⇒ v = – 3/2
⇒ v = – 1.5 m/s
18: Negative sign indicates that the direction in which the pistol would recoil is opposite to that of bullet.
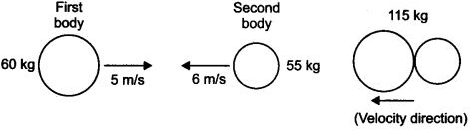
Two bodies as shown in the figure collide with each other and join thereafter. With what velocity will they move after combining together?
Answer:
m1 = 60 kg
u1 = +5 m/s
v = ?
Pistol
m2 = 2kg
u2 = – 6 m/s
v = ?
Total momentum of two bodies before collision
= m1u1 +m2u2
= 60 × 5 + 55 × -6
= -30 kg m/s
If v is the velocity of two joined bodies. After collision, the total momentum will be
= m1v1 + m2v2 (∴ v1 = v2)
= (m1 + m2)v
= (60 + 55)v
= 115 v
∴ According to law of conservation of momentum
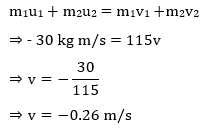
∴ Two bodies will move with velocity 0.26 m/s in the direction of the second body.
Long Answer Type Questions
1: Explain Newton’s second law of motion and with the-help of an example show how it is used in sports.
Answer: Newton’s second law of motion: The rate of change of momentum of an object is proportional to the applied unbalanced force in the direction of the force.
Let us assume: Object of mass m, is moving along a straight line with an initial velocity ‘u’, It is uniformly accelerated to velocity v in time ‘t by the application of force,
F throughout the time ‘t’.
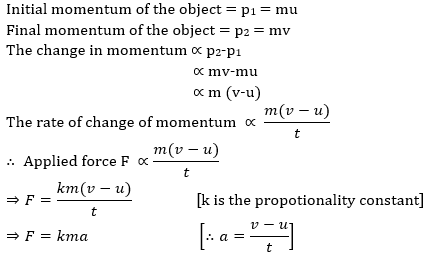
Use of second law of motion in sports:
In cricket field, the fielder gradually pulls his hands backward while catching a ball. The fielder catches the ball and gives swing to his hand to increase the time during which the high velocity of the moving ball decreases to zero. The acceleration of the ball is decreased and therefore the impact of catching the fast moving balls reduced.
If not done so, then the fast moving ball will exert large force and may hurt the fielder.
2: State all 3 Newton’s law of motion. Explain inertia and momentum.
Answer: Newton’s 1st law of motion: An object remains in a state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an external unbalanced force.
Newton’s 2nd law of motion: The rate of change of momentum of an object is proportional to the applied unbalanced force in the direction of the-force.
Newton’s 3rd law of motion: To every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction and they act on two different bodies.
Inertia: The natural tendency of an object to resist a change in their state of rest or of uniform motion is called inertia.
Momentum: The momentum of an object is the product of its mass and velocity and has the same direction as that of the velocity. Its S.I. unit is kgm/s. p = m x v
3: Define force. Give its unit and define it. What are different types forces?
Answer: Force: It is a push or pull on an object that produces acceleration in the body on which it acts.
A force can do 3 things on a body
(a) It can change the speed of a body.
(b) It can change the direction of motion of a body.
(c) It can change the shape of the body.
The S.I. unit of force is Newton.
Newton: A force of one Newton produces an acceleration of 1 m/s2 on an object of mass 1 kg.
1N = 1kg m/s2
Types of forces:
(i) Balanced force: When the forces acting on a body from the opposite direction do not change the state of rest or of motion of an object, such forces are called balanced forces.
(ii) Unbalanced force: When two opposite forces acting on a body move a body in the direction of the greater force or change the state of rest, such forces are called as unbalanced force.
(iii) Frictional force: The force that always opposes the motion of object is called force of friction.
4: What is inertia? Explain different types of inertia. Give 3 examples in daily life which shows inertia.
Answer: Inertia: The natural tendency of an object to resist change in their state of rest or of motion is called inertia.
The mass of an object is a measure of its inertia. Its S.I. unit is kg.
Types of inertia:
Inertia of rest: The object at rest will continue to remain at rest unless acted upon by an external unbalanced force.
Inertia of motion: The object in the state of uniform motion will continue to remain in motion with same speed and direction unless it is acted upon by an external unbalanced force. .
Three examples of inertia in daily life are:
1. When we are travelling in a vehicle and sudden brakes are .applied we tend to fall forward.
2. When we shake the branch of a tree vigorously, leaves fall down.
3. If we want to remove the dust from carpet we beat the carpet so that dust fall down.
Value-based Questions
1: Class V students were playing cricket with the cork hall in the school campus. Charu a senior student told them about the accidents that can occur due to cork ball in the campus and also advised them to bring soft cosco ball to play the game.
(a) Why it was safe to play with soft ball and not with hard cork ball?
(b) A player pulls his hands backwards after holding the ball shot at high speed. Why?
(c) What value of Charu is seen in this act?
Answer: (a) The soft ball will have less inertia as compared to the heavy ball and it would not hurt the players.
(b) By pulling the hand backwards it reduces the force exerted by the ball on hands.
(c) Charu showed the value of being responsible and helpful by nature.
2: Saksham saw his karate expert friend breaking a slate. He tried to break the slate but Saksham’s friend stopped him from doing so and told him that it would hurt, one needs lot of practice in doing so.
(a) How can a karate expert break the slate without any injury to his hand?
(b) What is Newton’s third law of motion?
(c) What value of Saksham’s friend, is seen in the above case?
Answer: (a) A karate player applies the blow with large velocity in a very short interval of time on the slate, therefore large force is exerted on the slate and it breaks.
(b) To every action there is an equal and opposite reaction, both act on different bodies.
Saksham’s friend showed the value of being responsible and caring friend.