Combustion and Flame Class 8 Important Questions and Answers
Important questions of Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame is given below. These important questions will help students while preparing for the exam. Practising these important questions will analyse their performance and work on their weak points. Score well in exam of Class 8 Science by going through these important questions. Students of Class 8 can download important questions of Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame PDF by clicking the link provided below.
Important Questions of Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame
Here you can get Class 8 Important Questions Science based on NCERT Text book for Class 8. Science Class 8 Important Questions are very helpful to score high marks in board exams. Here we have covered Important Questions on Combustion and Flame for Class 8 Science subject.
Very Short Answer Questions
1. What are fuels?
Answer: The substances which provide heat and light are called fuels.
2. Name two fuels that are used in your homes.
Answer: (i) L.P.G (ii) Kerosene.
3. What fuels are used for running automobiles?
Answer: Petrol, diesel and CNG.
4. What is the full form of CNG?
Answer: CNG stands for Compressed Natural Gas.
5. What is the difference between burning of a candle and burning of coal?
Answer: A candle burns with a flame whereas coal does not.
6. Classify the fuels.
Answer: The fuels are classified into solid, liquid and gas.
7. What are combustible substances?
Answer: The substances that undergo combustion are called combustible substances.
8. Do all the fuels burn with a flame?
Answer: No, all the fuels do not burn with a flame.
9. What are the products of combustion?
Answer: Carbon dioxide, water vapour, heat and light.
10. Name some combustible substances.
Answer: Wood, paper, kerosene oil, charcoal etc.
11. Write the names of some non-combustible substances.
Answer: Mud, stone, glass etc.
12. On the basis of the combustion classify the substances.
Answer: These are two types of substances: (i) Combustible (ii) Non‑combustible
13. What is the source of heat and light in the sun?
Answer: In the sun, heat and light are produced by nuclear reactions.
14. What do you mean by an ignition temperature?
Answer: The lowest temperature at which any substance catches fire is called its ignition temperature.
15. Do all the substances catch fire at the same temperature?
Answer: No, all the substances do not catch fire at the same temperature. Different substances catch fire at different temperature.
16. What are inflammable substances?
Answer: The substances which have very low ignition temperature and can catch fire easily with a flame are called inflammable substances.
17. Mention some examples of inflammable substances.
Answer: Petrol, alcohol and LPG etc.
18. Name the substances used to extinguish fire.
Answer: Water, sand and fire extinguishers.
19. Are these substances used to extinguish all the types of fire?
Answer: No.
20. What substances are used to extinguish fire in case of electric short circuit?
Answer: Sand or soil and CO2.
21. Does your city/town have a fire brigade station?
Answer: Yes, there is a fire brigade station in my city.
22. What are the essential requirements for producing fire?
Answer: There are three requirements to produce fire:
(i) Fuel
(ii) Air to supply oxygen
(iii) Ignition temperature.
23. What is the principle to extinguish fire?
Answer: Fire can be controlled by removing one or more of the requirements—air, fuel or heat.
24. Which is the most common fire extinguisher?
Answer: Water is the most common fire extinguisher.
25. Write the name of different types of fire extinguisher.
Answer: (i) Soda‑acid (contains baking soda and acid) fire extinguisher.
(ii) Fire extinguisher cylinders having CO2 stored at high pressure
26. How many types of combustion are there?
Answer: There are three types of combustion:
(i) Rapid combustion
(ii) Spontaneous combustion and
(iii) Explosion.
27. What is flame?
Answer: The burning of vapours forms flame.
28. What is the colour of LPG flame?
Answer: Blue colour.
29. What is the colour of candle flame?
Answer: Yellow flame.
30. What type of substances produce flame?
Answer: The substances which vapourise during burning give flame.
31. Give examples of the substances which give flame.
Answer: Kerosene oil and molten wax.
32. Why does charcoal not produce flame?
Answer: Charcoal does not vapourise, so it does not produce a flame.
33. What are the different zones of flame?
Answer: There are three zones of flame:
(i) Non‑luminous zone
(ii) Luminous zone and
(iii) Dark zone.
34. Which zone of flame has highest temperature?
Answer: Non‑luminous zone.
35. What do you mean by deforestation?
Answer: The cutting of trees is called deforestation.
Short Answer Type Questions
1: State the difference between burning of a candle and burning of a fuel like coal
Answer: Candle burns with a flame but coal does not burn with a flame also coal is a carbon product and its burning is harmful for environment but candle is made from wax its burning is not as much harmful as burning of coal.
2: Explain combustion and combustible along with examples.
Answer: The chemical process in which a substance reacts with oxygen to give off heat is called combustion. In combustion the release of heat can result in the production of light in the form of either glowing or a flame. The substance which undergoes combustion is called combustible or fuel. Fuel may be solid, liquid or gas.
Example: Burning of a coal shows the process of combustion and coal here is combustible or fuel.
3: Food is a fuel for the body. Justify this statement.
Answer: Food is a fuel for our body because inside our body food is broken down into simpler form by reaction with oxygen and with the release of heat and energy.
4: Identify the materials in which combustion can take place Wood, paper, kerosene oil, iron nails, brick, stone, charcoal.
Answer: Wood, paper, kerosene oil, charcoal
5: On putting glass over a lighted candle, the candle flame flickers and produce smoke, why so?
Answer: Take two lighted candle A and B, and place them on a table, now put a transparent glass over candle B and see what happens to the candle B, we will observe that candle flame flickers and produces smoke and finally it goes off, this is because on putting glass over it, the air supply was cut off and candle was unable to burn in the absence of air.
6: What is acid rain? Write its effects.
Answer: The oxides of sulphur and nitrogen dissolve in rain water to form acids.
Such rain containing acids is called acid rain. It is very harmful for crops, buildings and soil.
7: When the clothes of a person catch fire, the person is covered with a blanket to extinguish fire, explain why?
Answer: To cut off the air supply of the fire, so that the fire gets off and the person could be saved from fire.
8: What is forest fire?
Answer: A forest fire is a natural disaster consisting of a fire which destroys a forested area, and is dangerous for the people living in forest area as well as for the wildlife. During extreme heat of summer, at some places dry grass catches fire, the fire gets spread from grass to tree, and very soon whole forest catches fire. It is very difficult to control such fires.
9: What do you mean by ignition temperature? Why a matchstick dose not catch fire on its own at room temperature?
Answer: The lowest temperature at which a substance catches fire or the lowest temperature at which combustion begins and continues in a substance is called its ignition temperature.
Match Stick cannot catch fire on its own at room temperature because it can catch fire only at its ignition temperature not at room temperature.
10: Why does the matchstick start burning on rubbing it on the side of matchbox?
Answer: The striking surface of the matchbox contains red phosphorus and the head of the matchstick contains potassium chlorate. So when the matchstick is rubbed on the matchbox, some of the red phosphorus is converted to white phosphorus, a chemical i.e. so volatile that it ignites in air.
11: Why does kerosene oil catch fire faster than wood?
Answer: This is because the specific heat capacity of the wood is more than the kerosene oil. So, the wood takes time to burn but burns for longer period than the kerosene oil.
12: Why we should store kerosene oil with proper care?
Answer: Because kerosene oil can catch fire very easily as its ignition temperature is lower than other combustible material.
13: Explain why inflammable substance can easily set on fire?
Answer: Inflammable substances have very low ignition temperature and thus they can easily catch fire with a flame, example: diesel, kerosene oil, alcohol, Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) etc.
14: How do we control fire?
Answer: As we know there are three essential requirements for producing fire these are fuel, air and heat. Fire can be controlled by removing one or more of these requirements that is either by cutting of the air supply, or by bring down the temperature of the fuel or both.
15: How a fireman extinguishes fire?
Answer: Fireman through water with pressure on fire, water helps in cooling down of the combustible material so that its temperature is brought below its ignition temperature and fire does not get spread. A part from this combustible material is surrounded by water vapour which helps in cutting of the air supply and finally fire is extinguished.
16: Write short note on fire extinguisher.
Answer: The most commonly used fire extinguisher is water, it works when wood and paper are on fire, but if electrical equipment is on fire water may conduct electricity and may harm those trying to douse the fire, also water is not suitable for fires involving oil and petrol, since water is heavier than oil it sinks below the oil and oil keeps burning on the top. So if electrical equipment and inflammable materials are on fire Carbon dioxide is the best extinguisher. Since it is heavier than oxygen it covers the fire so that the contact between fuel and oxygen is cut off and the fire is controlled, it also bring s down the temperature of the fuel. For this purpose carbon dioxide is stored at high pressure as a liquid in cylinders.
17: Explain the essential requirements for producing fire.
Answer: Following are the essential requirements for producing a fire:
- Fuel: It is the combustible material
- Air: Air supplies oxygen which supports combustion and without which it is impossible to set on a fire.
- Heat: Heat is important as it raises the temperature of the fuel beyond the ignition temperature.
18: Why water is not a good fire extinguisher in case of electrical equipment and inflammable materials?
Answer: The most commonly used fire extinguisher is water, it works when wood and paper are on fire, but if electrical equipment is on fire water may conduct electricity and may harm those trying to douse the fire, also water is not suitable for fires involving oil and petrol, since water is heavier than oil it sinks below the oil and oil keeps burning on the top. So if electrical equipment and inflammable materials are on fire Carbon dioxide is the best extinguisher. Since it is heavier than oxygen it covers the fire so that the contact between fuel and oxygen is cut off and the fire is controlled, it also bring s down the temperature of the fuel. For this purpose carbon dioxide is stored at high pressure as a liquid in cylinders.
19: How many types of combustion are there? Name them.
Answer: There are three types of combustion:
- Rapid combustion: Bring a burning matchstick or gas lighter near a gas stove and turn on the knob of gas stove, we will find the gas burns rapidly and produces heat and light, such combustion is called as rapid combustion
- Spontaneous combustion: In this type of combustion a material suddenly bursts into a flame, without the application of any apparent. Eg: spontaneous combustion of coal dust.
- Explosion: When a cracker is ignited a sudden reaction takes place with the evolution of heat, light and sound, this type of combustion is called Explosion.
20: What is flame?
Answer: A flame is the visible, gaseous part of a fire. The substance which vaporise during burning give flames, It is caused by a highly exothermic reaction taking place in a thin zone.
21: Introduce a glass plate into the luminous zone of the steady candle flame and hold it for few seconds, then remove it? What did you observe on the glass plate?
Answer: We will observe a circular blackish ring formed on the glass plate, this indicates the deposition of unburnt carbon particles present in the luminous zone of the flame.
22: State some of the characteristics of a good fuel.
Answer: A good fuel is one which is:
- Readily available
- Ignite easily
- Burn well, not with explosion
- Cheap
- Produces a large amount of heat
- Have low smoke and ash content
- Should be easy to store and transport
23: How calorific value of a fuel is related to amount of heat produced by fuel? Mention calorific value of wood, coal, petrol, CNG and Biogas.
Answer: Calorific value of the fuel is the amount of heat energy produced on complete combustion of 1 kg of fuel. It is expressed in kilojoule per kg.
Calorific value of wood is 17000-22000 kJ/kg
Calorific value of coal is 25000-33000 kJ/kg
Calorific value of CNG is 50000 kJ/kg
Calorific value of biogas is 35000 – 40000 kJ/kg
24: Why we say increasing fuel consumption has harmful effects on environment?
Answer: Increasing fuel consumption has harmful effects on environment because:
- Carbon fuels like wood, coal and petroleum releases unburnt carbon particles that are dangerous pollutants causing diseases like asthma and respiratory disorders
- Incomplete combustion of these fuel releases a very poisonous gas carbon monoxide
- Release of carbon dioxide gas by combustion of fuels is becoming one of the cause of global warming
25: Explain global warming and its causes.
Answer: Global warming is the increase in the average temperature of Earth’s atmosphere and oceans, reason for the same is:
1. Increasing population that leads to increased use of fossil fuels and agriculture, fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide gas which causes global warming.
2. Because of increased population more number of people releases carbon dioxide gas during respiration process and that contributes to global warming.
3. Increased demand of agriculture for our increasing population is also one of the reason of global warming as manures used in agriculture contains methane gas.
26: What are the effects of global warming?
Answer: Global warming is the increase in the average temperature of Earth’s atmosphere and oceans, it results in melting of the glacier of the polar region which leads to rise in sea level, causing flood in coastal areas. Even low lying coastal region may get permanently submerged under water because of global warming.
27: Explain why it is difficult to burn a heap of green leaves but we can easily burn dry leaves?
Answer: A heap of green leaves contains lot of water and has very high ignition temperature, as water is a natural fire extinguisher it do not allow leaves to catch fire easily where as dry leaves contains no water and have low ignition temperature thus they can catch fire easily.
28: In an experiment 3.5 kg of a fuel was completely burnt. The heat produced was measures to be 160,000 kj. Calculate the calorific value of the fuel.
Answer: Calorific value of the fuel = Amount of heat energy produced / weight of fuel burnt
= 160000/3.5 kJ/kg
= 45714.28 kJ/kg
29: What is fuel? Give some examples of a fuel.
Answer: The combustible substances which produce heat and sometimes light on combustion is called fuel. Fuel may be solid, liquid and gas. Wood, charcoal, petrol and kerosene are some of the examples of fuel.
30: What are combustible and non-combustible substances? Explain with examples.
Answer: The substances in which combustion takes place are called combustible substances. For example: wood, paper, coal. The substances in which no combustion takes place are called non‑combustible substances. For example: Glass, iron nail.
31: Why does a matchstick not burn of its own?
Answer: The ignition temperature for the burning of matchstick is more than room temperature. So it does not catch fire on its own. When the stick is rubbed then due to friction it gets its ignition temperature and starts to burn.
32: Can you burn a piece of wood by bringing a lighted matchstick near it?
Answer: The piece of wood cannot burn by bringing a lighted matchstick near it. It is because the heat produced by matchstick is not sufficient to attain the ignition temperature of wood. So we use paper or kerosene oil to start fire in wood piece.
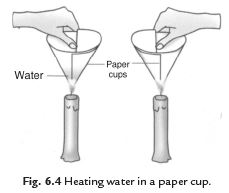
33: We can boil water in a paper cup while paper catches fire easily. Explain the process.
Answer: We take two paper cups. Take some water in one cup and keep the other empty. Heat both the cups. Empty cup starts to burn but the cup containing water does not burn. If we continue heating the water in the cup it starts boiling. The heat supplied to the paper cup is transferred to water by conduction. So in the presence of water the ignition temperature of paper is not reached. Hence, it does not burn.
34: How does fire brigade works to extinguish fire?
Answer: When fire brigade arrives, it pours water on the fire. Water cools the combustible material, so that its temperature is brought below its ignition temperature. This prevents the fire from spreading. Water vapour also surrounds the combustible material, helping in the cutting off the supply of air. So the fire is extinguished.

35: What is the job of a fire extinguisher?
Answer: There are three requirements for producing fire: fuel, air, proper temperature. Fire can be controlled by removing one or more of these requirements.
The job of a fire extinguisher is to cut off the supply of air or to bring down the temperature of the fuel or both. In most of the cases fuel cannot be eliminated.
36: Explain the structure of a flame.
Answer: There are following three parts of a flame:
(i) Outer zone: It is non-luminous and the hottest zone.
(ii) Middle zone: It is less hot and yellow coloured zone.
(iii) Inner zone: It is dark zone and least hot part.
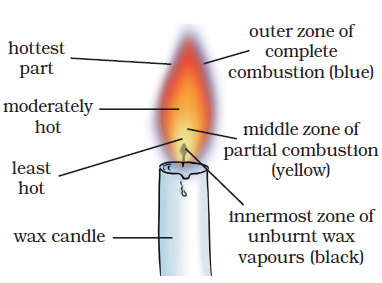
37: Why is the colour of outer zone is blue while middle zone is yellow coloured?
Answer: Outermost zone: It is blue coloured part because complete combustion takes place in this part due to sufficient amount of oxygen. It is the hottest part of the flame.
Middle Zone: The colour of the middle zone is yellow because incomplete combustion takes place in this part for the lack of oxygen. It is less hot part than outer part of the flame.
38: What is calorific value of a fuel?
Answer: The amount of heat energy produced on complete combustion of 1 kg of a fuel is called its calorific value. The calorific value of a fuel is expressed in a unit called kilojoule per kg (kJ/kg).
Long Answer Type Questions
1: What are the advantages of using CNG and LPG as fuels?
Answer: The advantages of using CNG and LPG as fuels are as follows:
- They both are cleanest burning fuels of all fossil fuels.
- They are less polluting, non-corrosive.
- They can be sent through pipes easily.
- These are easily available and have affordable cost.
- LPG and CNG both are easy to store and transport.
- As there calorific value is very high therefore, they are used for cooking purpose.
2: Differentiate between LPG and wood as fuel.
Answer:
| LPG | WOOD |
| It is costly fuel, but readily available and easy to transport in cylinders and tankers | It is cheap fuel but not readily combustible |
| It is more energy efficient | It is less energy |
| Its calorific value is 55000 KJ/kg | Its calorific value is 17000-25000 KJ/kg |
| It causes less air pollution and prevent deforestation by supplementing the fuel. | It causes air pollution and deforestation. |
| It is an exhaustible natural resource. | It is not an exhaustible natural resource as trees can be grown in 5-10 years |
3: Explain working and principles of a fire extinguisher.
Answer: The most commonly used fire extinguisher is water, it works when wood and paper are on fire, but if electrical equipment is on fire water may conduct electricity and may harm those trying to douse the fire, also water is not suitable for fires involving oil and petrol, since water is heavier than oil it sinks below the oil and oil keeps burning on the top. So if electrical equipment and inflammable materials are on fire Carbon dioxide is the best extinguisher. Since it is heavier than oxygen it covers the fire so that the contact between fuel and oxygen is cut off and the fire is controlled, it also bring s down the temperature of the fuel. For this purpose carbon dioxide is stored at high pressure as a liquid in cylinders.
4: Explain why the process of rusting can be called as slow combustion.
Answer: Rusting of iron is a slow oxidation process in which iron using oxygen and water is oxidised and is rusted out, it produces heat at very slow rate. The combustion process is also an oxidation process and is a chemical reaction by which a fuel and an oxidiser react to produce heat and light, thus we can say rusting of iron is a slow combustion process, although combustion is much faster than rusting.
5: What are the essential conditions for combustion? Explain with the help of an activity.
Answer: Take a candle. Light it and fix it on a table. Put a glass chimney over the candle and rest it on wooden blocks in such a way that air can enter the chimney. We see that candle remains lighted. Remove the blocks and let the chimney rest on the table. We see that the flame flickers and produces smoke. Now put a glass plate over the chimney. We see that flame goes off because air is not available. This activity shows that air is essential to burn a fuel at its ignition temperature.
6: Describe the history of the matchstick.
Answer: History of matchstick is about five thousand years old. The modern safety match was developed only about 200 years ago. A mixture of antimony trisulphide, potassium chlorate and white phosphorus with some glue and starch was applied on the head of a match made of suitable wood. When it struck against a rough surface, white phosphorus got ignited and combustion of matchstick started. These days red phosphorus is used in place of white phosphorus.
7: Write three examples of each type of fuel in tabular form.
Answer:
| Solid Fuels | Liquid Fuels | Gaseous Fuels |
| Coal | Kerosene oil | Natural gas |
| Wood | Petrol | L.P.G |
| Dung Cake | Diesel | Gobar Gas |
8: Make a table to show the calorific value of various fuels.
Answer:
| Name of fuel | Calorific Value kJ/kg |
| Cowdung cake | 6000-8000 |
| Wood | 17000-22000 |
| Coal | 25000-33000 |
| Petrol | 45000 |
| Kerosene | 45000 |
| Diesel | 45000 |
| Methane | 50000 |
| CNG | 50000 |
| LPG | 55000 |
| Biogas | 35000-40000 |
| Hydrogen | 150000 |
9: What is deforestation? Write its effect on environment.
Answer: Cutting of trees is called deforestation.
Effects: Deforestation is very harmful to the environment. The following are the effects of deforestation:
1. The annual rainfall is disturbed in that area.
2. The frequent floods come.
3. Balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide is disturbed.
4. It causes respiratory problem.
5. Trees provide us with useful substances which are lost due to deforestation.
10: What are the ill-effects due to the increasing consumption of fuel?
Answer: Harmful effects of using more fuels:
(i) Carbon fuels like wood, coal and petroleum release unburnt carbon particles. These fine particles create respiratory disorders and diseases like asthma.
(ii) Incomplete combustion of these fuels gives carbon monoxide. It is very harmful gas and causes respiratory disorders. It can kill persons sleeping in that room.
(iii) Excessive use of fuels causes global warming.
(iv) They cause acid rain which is harmful for crops, buildings and soil.