Microorganisms Friend and Foe Class 8 Important Questions and Answers
Important questions of Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms Friend and Foe is given below. These important questions will help students while preparing for the exam. Practising these important questions will analyse their performance and work on their weak points. Score well in exam of Class 8 Science by going through these important questions. Students of Class 8 can download important questions of Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms Friend and Foe PDF by clicking the link provided below.
Important Questions of Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms Friend and Foe
Here you can get Class 8 Important Questions Science based on NCERT Text book for Class 8. Science Class 8 Important Questions are very helpful to score high marks in board exams. Here we have covered Important Questions on Microorganisms Friend and Foe for Class 8 Science subject.
Very Short Answer Questions
1. What are microorganisms or microbes?
Answer: The organisms which are not seen with our naked eyes are called microorganisms.
2. Give two examples of microorganisms.
Answer: Bacteria and Fungi.
3. What are the four major groups of microorganisms?
Answer: (i) Bacteria (ii) Fungi
(iii) Protozoa (iv) Algae.
4. Name two habitats of microorganisms.
Answer: (i) Soil
(ii) Water.
5. What are viruses?
Answer: Very tiny microscopic organisms which reproduce only inside the cells of host organisms are called viruses.
6. Write the names of some diseases caused by virus.
Answer: Influenza (Flu), Polio and Chicken Pox are some diseases caused by viruses.
7. Name some diseases caused by Protozoans.
Answer: Dysentery and Malaria.
8. Mention some diseases caused by bacteria.
Answer: Typhoid and Tuberculosis (TB) are the bacterial diseases.
9. Name two single-celled microorganisms.
Answer: (i) Bacteria (ii) Some algae.
10. Name two multicellular microorganisms.
Answer: (i) Fungi (ii) Algae.
11. Mention two groups of microorganisms which live in colonies.
Answer: (i) Bacteria (ii) Fungi
12. What are the two types of microorganisms on the basis of their functions?
Answer: (i) Useful microorganisms. (ii) Harmful microorganisms.
13. Name the microorganisms which promote the formation of curd.
Answer: Bacterium Lactobacillus promotes the formation of curd.
14. What is the main ingredient of rava idlis and bhaturas?
Answer: Curd.
15. What is fermentation?
Answer: The process of conversion of sugar into alcohol is known as fermentation.
16. Name the scientist who discovered fermentation.
Answer: Louis Pasteur discovered fermentation in 1857.
17. What are antibiotics?
Answer: The medicines which kill or stop the growth of the disease‑causing microorganisms are called antibiotics.
18. Who discovered antibiotics?
Answer: Alexander Fleming in 1929.
19. Name some antibiotics.
Answer: Streptomycin, Tetracycline and Erythromycin are some antibiotics.
20. What do you mean by the antibodies?
Answer: When a disease carrying microbe enters in the body, the body produces a substance to fight the invader, these are called antibodies.
21. What is vaccine?
Answer: The medicine used to protect the children from several diseases is called vaccine.
22. What do you mean by vaccination?
Answer: The process of providing vaccine is called vaccination.
23. Name a popular vaccination programme.
Answer: Pulse Polio Programme.
24. Who discovered the vaccine for Small Pox?
Answer: Edward Jenner in 1798.
25. What do you mean by nitrogen fixation?
Answer: The process by which atmospheric nitrogen is converted into nitrates by the action of microorganisms is called nitrogen fixation.
26. What are pathogens?
Answer: The disease‑causing microorganisms are called pathogens.
27. How do pathogens enter in our body?
Answer: The pathogens enter in our body through air, water and food.
28. Name two communicable diseases.
Answer: Cholera and Chicken Pox.
29. What are carriers of disease-causing microbes?
Answer: The insects and animals which help in the transmission of the pathogens from source to the persons are called carriers of disease‑causing microbes.
30. Which is the carrier of dengue virus?
Answer: Female Aedes mosquito.
31. Why should we not let water collect anywhere?
Answer: All mosquitoes breed in water. Hence we should not let water collect anywhere.
32. Name a disease which is common in human and other animals.
Answer: Anthrax.
33. Name the pathogen of anthrax.
Answer: Bacillus anthracis.
34. Write the name of viral disease in cattles.
Answer: Foot and Mouth disease.
35. What do you mean by food preservation?
Answer: Process to prevent food material from spoilage by the action of microbes is called preservation.
36. What are preservatives?
Answer: The chemicals which are used to check the growth of microorganisms are called preservatives.
37. Name some preservatives.
Answer: Sugar, salt, oils and vinegar are some common preservatives.
38. Which microorganism are called nitrogen fixing bacteria?
Answer: Rhizobium bacteria.
39. Where do Rhizobium bacteria commonly live?
Answer: Rhizobium bacteria live in the root nodules of leguminous plants
40. What do you mean by symbiotic relationship?
Answer: The relationship between two organisms in which both the organisms are benefitted is called symbiotic relationship.
41. Mention the amount of nitrogen gas in atmosphere.
Answer: 78%
Short Answer Type Questions
1: Write short notes on
(a) Bacteria
(b) Viruses
Answer: Bacteria: Bacteria are single celled microorganisms. They can survive under all types of environment, ranging from ice cold climate to hot springs and deserts to marshy lands. Bacteria can be seen under microscope which enlarges their image from a hundred to thousand times. They are of spiral shape or rod shape.
Viruses: Viruses are microscopic infectious agent that acts as non-living outside host cell and inside host cell becomes living and show reproduction. It can affect all kinds of an organism including animals, plants and bacteria. Common ailments like cold, coughs and influenza (flu) are caused by viruses; serious diseases like chicken pox and polio are also caused by viruses.
2: Write short notes on
(a) Protozoa
(b) Algae
Answer: Protozoa: Protozoa are unicellular animals. Some are free-living, others are parasites. Several parasitic protozoans cause diseases in human beings, domestic animals and plants. For example, Plasmodium, a protozoan, causes malaria.
Algae: Algae are green substances floating on the surface of a pond, lake, river, stagnant water, moist soil, stones. They tend to grow on wet surfaces. Therefore, they can synthesize their own food. They are found in water or in very moist places.
3: What do you mean by friendly microbes?
Answer: Microorganisms are beneficial to us in various ways; they not only prepare curd, bread, cake, wine and medicines for us but also used to increase soil fertility by fixing atmospheric nitrogen. Thus, we called them as friendly microbes.
4: How curd is formed?
Answer: Milk is turned into curd by bacteria. Curd contains several micro-organism including Lactobacilli bacteria.It promotes the formation of curd from milk. When a little of pre-made curd is added to warm milk,then Lactobacilli bacteria present in curd multiply in milk and convert the lactose sugar into lactic acid. This lactic acid then converts milk into curd.
5: Why yeast is used in the baking industry for making bread, cakes and pastries?
Answer: Yeast reproduces rapidly and produces carbon dioxide during respiration. Bubbles of gas fill the dough (mixture of atta or maida and some sugar and water) and increase its volume. This is the basic of using yeast in baking industry.
6: Define the process of fermentation and its application.
Answer: Fermentation is the process of food processing in which sugar is converted into alcohol by the action of microorganisms. This process is used to produce alcoholic beverages such as wine, beer, and cider. For this purpose yeast is grown on natural sugars present in grains like barley, wheat, rice, crushed fruit juices etc.
7: How antibiotics are related to microorganisms?
Answer: Antibiotics are medicines that kill or stop the growth of disease causing microorganisms and they are prepared from microorganisms. For e.g. Streptomycin, tetracycline and penicillin are some of the antibiotics prepared from microorganisms like fungi and bacteria.
8: Why vaccines are important?
Answer: Vaccines produces antibodies in our body to fight against disease causing microbes entering our body. Diseases like cholera, tuberculosis, smallpox and hepatitis can be prevented by vaccination, polio drop given to children is also a vaccine.
9: What is the main motto of pulse polio program?
Answer: The main motto of pulse polio program is to protect children from polio, by providing them with polio drops.
10: Write short notes on medicinal use of microorganisms.
Answer: Antibiotics are medicines that kill or stop the growth of disease causing microorganisms and they are prepared from microorganisms. For e.g. streptomycin, tetracycline and penicillin are some of the antibiotics prepared from microorganisms like fungi and bacteria.
11: Write short notes on increasing soil fertility by the action of microorganisms.
Answer: Some bacteria and blue green algae are able to fix atmospheric nitrogen into nitrates and nitrates are an important constituent to increase soil fertility. These microbes are generally called biological nitrogen fixers.
12: How do microbes clean our environment?
Answer: Microbes decompose the dead organic wastes of plants and animals converting them into simple substances. These substances are again used by other plants and animals. Thus microbes degrade the harmful and smelly substances and clean up the environment.
13: Why some microorganisms are considered as harmful?
Answer: Some microorganisms cause diseases in human beings, plants and animals, like some species of bacteria causes tuberculosis and typhoid, some species of virus causes common cold and influenza. Some microorganisms also cause spoilage of food, clothing and leather items. Thus we consider some microorganisms are harmful.
14: List all possible ways by which pathogens can enter our body.
Answer: Diseases causing microorganisms can enter our body through the air we breathe, water we drink and the food we eat. They can also get transmitted by direct contact through an infected person or carried through an animal.
15: Define communicable diseases with examples.
Answer: There are some microbial diseases that can spread from an infected person to a healthy person through air, water, food or physical contact. Such kind of diseases is called communicable disease.
For example: Cholera, Chicken pox, Tuberculosis.
16: Why we should keep a handkerchief on the nose and mouth while sneezing?
Answer: When a person suffering from common cold sneezes, the fine droplets of moisture containing thousands of viruses are spread in the air, these viruses may enter the body of healthy person while breathing, thus we should keep handkerchief on the mouth and nose while sneezing so that viruses may not spread In the air and enter into a healthy person’s body to make him sick.
17: How does housefly spread diseases?
Answer: Houseflies sit on the garbage and animal excreta where pathogens stick to their bodies and these pathogens get transferred to uncovered food when these flies sit on uncovered food items and the person consuming these food fall sick.
18: What are the advantages of sealed air tight packing for storage of food items?
Answer: Sealed air tight packets prevent the attack of microbes and protect the food items inside it from getting spoiled and toxic.
19: Write short notes on diseases causing microorganisms in animals.
Answer: There are some microorganisms that cause disease in animals also like anthrax is a very dangerous human and cattle disease caused by a bacterium. Foot and mouth disease of cattle is caused by a virus.
20: Write short notes on diseases causing microorganisms in plants.
Answer: There are some microorganisms that cause disease in plants like wheat, sugarcane, rice, potatoes, oranges, and apples. Like citrus canker disease caused by bacteria in plant, rust of wheat disease in wheat plant caused by fungi. These diseases reduce the yield of crops and can be controlled by using certain chemicals that kill microbes.
21: Neha went to a party and she ate a variety of foodstuff there, on reaching home she started vomiting and had stomach ache. What do you think why it is so?
Answer: It is because of food poisoning. Food poisoning could be due to the consumption of food spoiled by some microorganisms.
22: How do we preserve cooked food at home?
Answer: We preserve cooked food at home by using preservatives like salt, sugar and edible oil. Common salt has been used to preserve meat and fish. It is also used to preserve amla, raw mangoes, tamarind, etc. Jams, jellies and squashes are preserved by using sugar. Vegetables, fruits, pickles are often preserved by oil and vinegar.
23: Why a mango gets spoilt and rotten after few days but a mango pickle does not spoil for a long period of time?
Answer: A mango gets spoilt and rotten after few days but a mango pickle does not spoil for a long period of time because mango pickles contains salt which acts as preservatives and prevent the growth of microorganisms in it.
24: What are preservatives and their importance?
Answer: Preservatives are naturally occurring or synthetically produced substance that are generally used to check the growth of microorganisms.
Example: Salt and sugar acts as preservatives in pickles to prevent the growth of microorganisms. Sodium benzoate and sodium metabisulphite are common preservatives.
25: Why milk is boiled before storage or consuming?
Answer: Boiling kills many microorganisms, thus milk is boiled before storing or consuming. Boiling of milk at about 70°C for 15 to 30 seconds and then suddenly chilling and its storage destroy all of its microorganisms and prevent further growth of the microorganisms.
26. What are viruses? Name some common diseases in human caused by virus.
Answer: Viruses are microscopic organisms. They however reproduce only inside the cells of host organism, which may be a bacterium plant or animal. Some diseases like cold, influenza (flu), polio and chicken pox are caused by viruses.
27. How do microorganisms survive under adverse conditions?
Answer: Under unfavourable conditions of temperature and water, they generally form a hard and tough covering called cyst. This protects them. When favourable conditions come they emerge from their shell, multiply and go through their life cycles.
28. How do microorganisms act as a cleaning agent of nature?
Answer: Microorganisms are also used in cleaning up of the environment. The organic wastes like vegetable peels and remains of animals are broken down into harmless and usable substances by the action of microorganisms. In agriculture they are used to increase soil fertility by fixing nitrogen and by making manure.
29. Explain the commercial use of microorganisms.
Answer: Microorganisms are used for large scale production of alcohol, wine and acetic acid (vinegar). Yeast is used for commercial production of alcohol and wine. For this purpose yeast is grown on natural sugar present in grains. Yeast converts the sugar into alcohol. This process is called fermentation. Microorganisms are also used to prepare medicines like antibiotics.
30. Mention some beneficial effects of bacteria.
Answer: Beneficial effects of bacteria:
(i) They help in fixation of nitrogen to increase soil fertility.
(ii) They are used to make vinegar, curd etc.
(iii) They help in the cleaning of environment by the decomposition of organic wastes.
(iv) They are also used in making medicines like antibiotics.
31. Explain the various types of bacteria.
Answer: The bacteria are classified into three types on the basis of their shape:
(i) Rod shaped (Bacillus): These are long and rod shaped bacteria like Lactobacillus.
(ii) Round shaped (Coccus): They are round shaped like Streptococcus.
(iii) Spiral: These are comma shaped bacteria like Triponema.
32. What are antibiotics? Explain with the help of examples.
Answer: The medicines which are used to kill or stop the growth of the disease-causing microorganisms are called antibiotics. The first antibiotics is Penicillin. It is discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1929. These days a large number of antibiotics are being produced from bacteria and fungi. For example: Streptomycin, Tetracycline and Erythromycin.
33. Explain the discovery of Penicillin.
Answer: In 1929, Alexander Fleming was working on a culture of disease-causing bacteria. Suddenly, he found the spores of a little green mould in one of his culture plates. He observed that the presence of mould killed and stopped the growth of bacteria. From this the mould penicillin was prepared.
34. Explain how does a vaccine work.
Answer: When a disease carrying microbe enters in our body, the body produces antibodies to fight the invader. The body also remembers how to fight the microbe if it enters again. So, if dead or weakened microbes are introduced in the healthy body, the body fights and kills the microbes by producing suitable antibodies. The antibodies remain in the body and we are protected from disease-causing microbes. This is how a vaccine works.
35. Describe the role of blue green algae and bacteria in fertility of soil.
Answer: Some bacteria and blue green algae are able to fix nitrogen from the atmosphere to enrich soil with nitrogen and increase its fertility. These microbes are commonly called biological nitrogen fixers. In this way bacteria and blue green algae increase the soil fertility.
36. Explain the cleaning action of microorganisms.
Answer: The microorganisms are called the cleaning agent of nature. Collect wastes of plants, vegetables and fruits from your nearby surroundings. Put them in a pit meant for waste disposal. After some time, it decomposed and got converted to manure by the action of microorganisms. In this way the waste products are converted into useful manure by the action of microbes. This is the way by which microorganisms act as cleaning agent of nature.
37. How do microorganisms spoil food?
Answer: Microorganisms grow on the food materials and multiply rapidly. They release toxins in the food and make them unfit to consume. They breakdown the food molecules into amines and change the taste, texture and appearance of food.
38. What do you mean by food poisoning?
Answer: Some microorganisms get settled on the food stuff. They release the toxic substances in the food stuff. This makes the food contaminated and unfit for use. This is called food poisoning. If anyone consumes this food, it can produce fatal results. Serious illness is caused and patient get frequent vomiting and loose motion. This physical condition can lead even to death. So it is very important that we preserve food to prevent it from being spoilt.
39. What is pasteurisation of milk?
Answer: Pasteurised milk can be consumed without boiling as it is free from harmful microbes. The milk as heated to about 70ºC for 15 to 30 seconds and then suddenly chilled and stored. By doing so the milk is prevented by the growth of microbes. This process was discovered by Louis Pasteur so it is called Pasteurisation.
Long Answer Type Questions
1: Explain how microbes are useful to us in our day to day life.
Answer: (i) Microorganisms are beneficial to us in various ways; they not only prepare curd, bread, cake, wine and medicines for us but also used to increase soil fertility by fixing atmospheric nitrogen. Thus we called them as friendly.
(ii) Yeast reproduces rapidly and produces carbon dioxide during respiration. Bubbles of gas fill the dough (mixture of atta or maida and some sugar and water) and increase its volume. This is the basis of using yeast in baking industry.
(iii) Fermentation is the process of food processing in which sugar is converted into alcohol by the action of microorganisms. This process is used to produce alcoholic beverages such as wine, beer, and cider. For this purpose yeast is grown on natural sugars present in grains like barley, wheat, rice, crushed fruit juices etc.
(iv) Antibiotics are medicines that kill or stop the growth of disease causing microorganisms and they are prepared from microorganisms. For e.g. streptomycin, tetracycline and penicillin are some of the antibiotics prepared from microorganisms like fungi and bacteria.
2: Explain how microbes are harmful to us.
Answer: Microorganisms are harmful in many ways. Some microorganisms cause diseases in human beings, plants and animals. Such disease-causing microorganisms are called pathogens. Some microorganisms spoil food, clothing and leather. Some of the common communicable diseases caused by microorganisms affecting humans are cholera, common cold, chicken pox and tuberculosis. Many microorganisms not only cause diseases in humans and plants but also in animals like anthrax is a dangerous human and cattle disease caused by a bacterium. Disease causing microorganisms in plants like wheat, rice, potato, sugarcane, orange, apple and others reduce the yield of crops. Food poisoning is caused due to the consumption of food spoilt by some microorganisms.
3: What are the major precautions one should follow while taking antibiotics?
Answer: Following precautions must be taken while taking antibiotics:
(i) Antibiotics should be taken only on the advice of a qualified doctor. And one must finish the course prescribed by the doctor.
(ii) Antibiotics must be avoided when not needed or in wrong doses.
(iii) Antibiotics taken unnecessarily may kill the beneficial bacteria in the body.
4: What are the major group of microorganisms explain each group with their harmful and useful effects in our life
Answer: Microorganisms are broadly divided into four major groups namely: Bacteria, virus, fungi and virus.
(i) Bacteria are single-celled microscopic organisms. They can survive under all types of environment, ranging from ice cold climate to hot springs and deserts to marshy lands. Bacteria always live in colonies. They are of spiral shape or rod shape. Bacteria play an important role in our life; some bacteria are useful whereas some others are harmful and cause diseases. Bacteria are involved in making of cheese and pickles. Lactobacillus bacteria promote the formation of curd. Antibiotics are also made from bacteria. Apart from this diseases like tuberculosis and typhoid are caused due to bacteria.
(ii) Viruses are microscopic infectious agent that acts as non-living outside host cell and inside host cell becomes living and show reproduction. It can affect all kinds of an organisms including animals, plants and bacteria. Common ailments like cold, coughs and influenza (flu) are caused by viruses; serious diseases like chicken pox and polio are also caused by viruses.
(iii) Protozoa had been defined as unicellular protists with animal-like behaviour like movement. They move around with whip-like tails called flagella, hair-like structures called cilia, it is responsible for causing diseases like dysentery and malaria in human beings.
(iv) Algae are a very large and diverse group of simple, typically autotrophic organisms, ranging from unicellular to multicellular forms. Most are photosynthetic like plants, and “simple” because their tissues are not organized into many distinct organs found in land plants. The largest and most complex marine forms are called seaweeds.
5. What are carriers of disease-causing microbes? Explain with the help of two examples.
Answer: These are some insects and animals which carry the disease-causing microorganisms like a housefly, mosquitoes. Such insects and animals are called carriers of disease-causing microbes.
Examples:
(i) Housefly: The housefly is a carrier of microorganisms. They sit on the garbage and animal excreta. The pathogens stick to their bodies. When these flies sit on uncovered food, they may transfer the pathogens. Whoever eats the contaminated food is likely to get sick. So, we should not consume uncovered food.
(ii) Female Anopheles Mosquito: It is the carrier of the parasite of malaria. Female Aedes mosquito acts as carrier of dengue virus. We can control malaria by keeping the surroundings clean and dry.
6. Explain causative microorganisms, mode of transmission and preventive measures of the human diseases like Tuberculosis, Measles, Chicken pox, Polio, Cholera, Typhoid, Hepatitis B and Malaria etc.
Answer: Some of the common diseases affecting humans, their mode of transmission and few general methods of prevention are given in the following table:
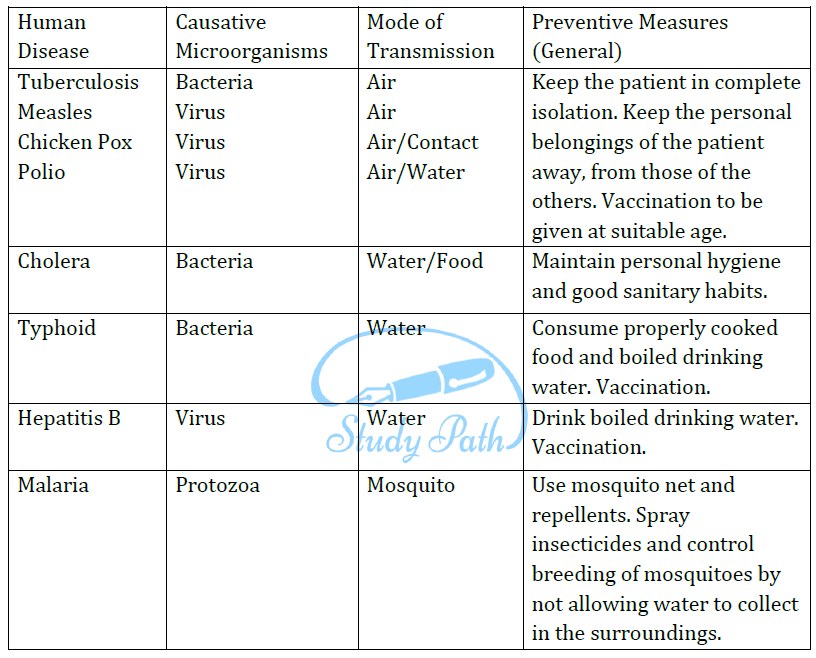
7. What are food preservatives? Explain some common food preservatives.
Answer: The chemical substances which are used to check or stop the growth of harmful microorganisms in food are called food preservatives. These food preservatives keep the edible food materials protected from the invasion of microorganisms which can spoil the food. Some common food preservatives are:
(i) Salt: Common salt is used to preserve meat, fish, amla, raw mangoes and tamarind etc.
(ii) Sugar: Jams, jellies and squashes are preserved by sugar. Sugar reduces the moisture contents which inhibit the growth of bacteria which spoil food.
(iii) Oil: Edible oils are used as preservatives in vegetables and pickles. Oil does not allow the moisture to surface, thus preventing the growth of harmful bacteria.
(iv) Vinegar: It is used to preserve fruits, vegetables, fish, meat and pickles.
8. Explain nitrogen cycle with a schematic diagram.
Answer: Certain bacteria and blue green algae present in the soil fix the atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into compounds of nitrogen. These can be utilised by plants by taking them from the soil through their root system. Nitrogen is then used for the synthesis of the plant proteins and other compounds. Animals use these proteins and other nitrogen compounds as food.
When animals and plants die, bacteria and fungi present in the soil convert these nitrogenous waste into usable nitrogen compounds which are used by plants again. Some other bacteria convert some part of them to free nitrogen gas which goes back into the atmosphere. As the result percentage of nitrogen in the atmosphere remains constant.
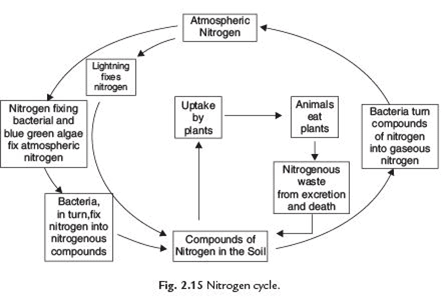
9. Explain the uses of Bacteria, Fungi and Algae.
Answer: (A) Uses of Bacteria:
(i) They are used to increase soil fertility by fixing nitrogen.
(ii) Some bacteria are used to produce antibiotics.
(iii) Lactobacillus bacteria converts milk into curd. It also helps in digestion of food.
(iv) Some bacteria help in many functions of our body.
(B) Uses of Fungi:
(i) Yeast is used to prepare alcohol and vinegar by fermentation.
(ii) Yeast is used to produce bread, cheese, beer, wine etc.
(iii) Mushrooms are eaten as food.
(iv) Yeast is used to produce vitamin B.
(v) Penicillin is an antibiotic formed by a fungus called Penicillium.
(C) Uses of Algae:
(i) Algae are used to make jellies.
(ii) They are used in soups, ice creams, jellies and jams as thickening agent.
(iii) Chlorella is used to obtain proteins.
(iv) Silica from Diatoms are used in toothpastes.
10. Explain some indications which help to detect the spoilage of food.
Answer: Indications to detect spoilage of food:
(i) Odour: The unpleasant and foul smell indicates that food is spoiled.
(ii) Discolouration: The presence of the microorganisms in the food results in discolouration of food black. Some fungi and moulds cause change in original colour.
(iii) Taste: Sometimes the cooked food becomes sour. It is due to the production of acids by the action of certain bacteria.
(iv) Sliminess: Sometimes the food becomes slimy. It is also due to action of certain bacteria, thread like slims also caused due to moulds.
(v) Gas formation: Due to action of bacteria, gases like, carbon dioxide are produced. They also spoil the food by making it swell or become spongy.