Cell Structure and Functions Class 8 Science Extra Questions and Answers
Cell Structure and Functions Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Extra Questions and Answers are provided here. We prepared these extra questions based on the latest NCERT Class 8 Science Book. CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions Extra Questions will help you to properly understand a particular concept of the chapter.
Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions Extra Questions
Very Short Answer Type Question
Question 1: Where are genes located?
Answer: Genes are located on chromosomes.
Question 2: What is the basic living unit of an organism?
Answer: Cell is the basic living unit of an organism.
Question 3: What do chloroplasts contain?
Answer: Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll.
Question 4: Name the instrument used to study cells.
Answer: Microscope is used to study cells.
Question 5: Do animal cells have a cell wall?
Answer: No, animal cells do not have a cell wall.
Question 6: What is a nucleolus?
Answer: A smaller spherical body in the nucleus is called the nucleolus.
Question 7: Name the scientist who coined the term cell.
Answer: Robert Hooke coined the term ‘cell’.
Question 8: Name one cell in human body which is spherical in shape.
Or
Give an example of spherical cell.
Answer: Spherical red blood cells
Question 9: Which part of a cell controls all the activities of the cell?
Answer: Nucleus acts as control centre of the activities of the cell.
Question 10: Name the outermost layer of an animal cell.
Answer: Cell membrane is the outermost layer of an animal cell.
Question 11: What are the units of inheritance in living organisms?
Answer: Chromosomes are the units of inheritance in living organisms.
Question 12: What is nucleus?
Answer: The central dense round body in the centre is called the nucleus.
Question 13: Which is the largest floating body generally in the centre of a cell?
Answer: Nucleus is the largest floating body generally in the centre of a cell.
Question 14: What is vacuole?
Answer: Any blank-looking structure in the cytoplasm is called vacuole.
Question 15: What is tissue?
Answer: A tissue is a group of similar cells performing a specific function.
Question 16: Which cell receives and transfers messages?
Answer: The nerve cell (or a neuron) receives and transfers messages.
Question 17: Name the spindle shaped cells present in the human body.
Answer: Spindle shaped muscle cells
Question 18: What is the basic similarity among all the living organisms (plants and animals)?
Answer: All the living things (plants and animals) are made from cells.
Question 19: What are prokaryotic cells?
Answer: Cells without well organised nucleus, i.e. lacking nuclear membrane, are called prokaryotic cells.
Question 20: What is the layer outside the cell membrane of a plant cell called?
Answer: In addition to the cell membrane, there is an outer thick layer in cells of plants called cell wall.
Question 21: Name the organelle of a plant cell where photosynthesis takes place.
Answer: In plants, photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts, which contain the chlorophyll.
Question 22: How are the vacuoles in animal and plant cells different?
Answer: Plant cell has a big central vacuole unlike a number of small vacuoles in animal cells.
Question 23: What is the function of nucleus in a cell?
Answer: Nucleus, in addition to its role in inheritance, acts as control centre of the activities of the cell.
Question 24: Name the animal cell which is long and has thread like branches.
Answer: Nerve cell (a neuron) is the only animal cell which is long and has thread like branches.
Question 25: A hen’s egg can be seen easily. Is it a cell or a group of cells?
Answer: The egg of a hen represents a single cell and is big enough to be seen by the unaided eye.
Question 26: Name one cell which can be seen by unaided eye.
Answer: Some cells are big enough to be seen with the unaided eye. Hen’s egg is an example.
Question 27: Name a single cell present in the human body which can change its shape.
Answer: A white blood cell (WBC) in human blood is another example of a single cell which can change its shape.
Question 28: Name one organism which has no definite shape, and keeps on changing its shape.
Or
Which unicellular organism has no definite shape?
Or
Name an organism that changes its shape frequently.
Answer: Amoeba has no definite shape, unlike other organisms. It keeps on changing its shape.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1: What is an organ?
Answer: An organ is a collection of different tissues which work together to perform a particular function in the body of an organism.
Question 2: Why nerve cells are long and have branches?
Answer: Nerve cells are long and have branches so that it can receive and transfer messages.
Question 3: What regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell?
Answer: The plasma membrane is porous and allows the movement of substances or materials both inward and outward.
Question 4: Name the smallest and largest cell in the world.
Answer: The smallest cell is 0.1 to 0.5 micrometre in bacteria. The largest cell measuring 170 mm ×130 mm, is the egg of an ostrich.
Question 5: What is cell wall? What is its function?
Answer: Cell wall is an additional covering over the cell membrane in plant cells. It gives shape and rigidity to these cells.
Question 6: What advantage does Amoeba derive by changing shape?
Answer: The change in shape is due to formation of pseudopodia which facilitates movement and help in capturing food.
Question 7: How do scientists observe and study the living cells?
Answer: They use microscopes which magnify objects. Stains (dyes) are used to colour parts of the cell to study the detailed structure.
Question 8: What is plastid? What is the name of green plastids present in plant cells?
Answer: Coloured bodies called plastids are found in the plant cells only. Green plastids containing chlorophyll are called chloroplasts.
Question 9: What are the three main parts of the cell?
Answer: The cell has three main parts, (i) the cell membrane, (ii) cytoplasm which contains smaller components called organelles, and (iii) the nucleus.
Question 10: Name two plant organs.
Answer: Roots – They help in the absorption of water and minerals.
Leaves – They are responsible for synthesis of food.
Question 11: What are unicellular organisms? Give two examples.
Answer: The single-celled organisms are called unicellular (uni : one; cellular : cell). Example: amoeba and paramecium.
Question 13: What are pseudopodia in amoeba? What are the functions of pseudopodia?
Answer: Pseudopodia is a temporary arm-like projection. Pseudopodia facilitate movement and help in capturing food.
Question 14: What is a gene? What is its function?
Answer: Gene is a unit of inheritance in living organisms. It controls the transfer of a hereditary characteristic from parents to offspring.
Question 15: What is protoplasm?
Answer: The entire content of a living cell is known as protoplasm. It includes the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Protoplasm is called the living substance of the cell.
Question 16: What are multicellular organisms? Give two examples.
Answer: Organisms made of more than one cell are called multicellular (multi: many; cellular: cell) organisms. Most of the plants and animals around us are multicellular organisms. Example: a mango tree, a deer, etc.
Question 17: Why are plant and animal specimens usually stained with dyes before observing them through a microscope? Name one stain used for this purpose.
Answer: Stains (dyes) are used to colour parts of the cell to study the detailed structure. Methylene blue solution stain is used in the study of structure of cell.
Question 18: Which part of the cell contains organelles?
Answer: Cytoplasm is a part of the cell that contains organelles such as mitochondria, golgi bodies, ribosomes, etc. It is the jelly-like substance present between the cell membrane and the nucleus.
Question 19: Where are chromosomes found in a cell? State their function.
Answer: Nucleus contains thread-like structures called chromosomes. These carry genes and help in inheritance or transfer of characters from the parents to the offspring.
Question 20: What is nuclear membrane? State its function.
Answer: Nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a membrane called the nuclear membrane. This membrane is also porous and allows the movement of materials between the cytoplasm and the inside of the nucleus.
Question 21: What are the different shapes of cells?
Answer: Generally, cells are round, spherical or elongated. Some cells are long and pointed at both ends. They exhibit spindle shape. Cells sometimes are quite long. Some are branched like the nerve cell or a neuron.
Question 22: Are the cells in an elephant larger than the cells in a rat?
Answer: The size of the cells has no relation with the size of the body of the animal or plant. It is not necessary that the cells in the elephant be much bigger than those in a rat. The size of the cell is related to its function.
Question 23: Explain why chloroplasts are found only in plant cells?
Answer: Green coloured plastids are called chloroplasts. They provide green colour to the leaves. Chlorophyll in the chloroplasts of leaves is essential for photosynthesis. As only plants can perform photosynthesis, so chloroplasts are found only in plant cells.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1: What is the difference between amoeba and white blood cell?
Answer: The difference between amoeba and white blood cell is that while amoeba cell is a full-fledged organism capable of independent existence, white blood cell is merely a cell of human blood which is not a full-fledged organism and hence cannot exist independently.
Question 2: Which part of the cell gives it shape?
Answer: Components of the cell are enclosed in a membrane. This membrane provides shape to the cells of plants and animals. Cell wall is an additional covering over the cell membrane in plant cells. It gives shape and rigidity to these cells. Bacterial cell also has a cell wall.
Question 3: ‘Cells are the basic structural units of living organisms’. Explain.
Answer: Both, bricks in a building and cells in the living organisms, are basic structural units. The buildings, though built of similar bricks, have different designs, shapes and sizes. Similarly, in the living world, organisms differ from one another but all are made up of cells. Cells in the living organisms are complex living structures unlike non-living bricks.
Question 4: Does the number of cells in an organism affect its functioning? Explain.
Answer: The number of cells being less in smaller organisms does not, in any way, affect the functioning of the organisms. A single-celled organism performs all the necessary functions that multicellular organisms perform. An organism with billions of cells begins life as a single cell which is the fertilized egg. The fertilised egg cell multiplies and the number of cells increases as development proceeds.
Question 5: Why plant cells need cell walls?
Or
What is the function of cell wall in a plant cell?
Answer: Cell membrane gives shape to the cell. In addition to the cell membrane, there is an outer thick layer in cells of plants called cell wall. This additional layer surrounding the cell membrane is required by the plants for protection. Plant cells need protection against variations in temperature, high wind speed, atmospheric moisture, etc. They are exposed to these variations because they cannot move.
Question 6: What are the functions of the cell membrane?
Answer: Functions of the cell membrane are as follows
- The cytoplasm and nucleus are enclosed within the cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane.
- The membrane separates cells from one another and also the cell from the surrounding medium.
- The plasma membrane is porous and allows the movement of substances or materials both inward and outward.
Question 7: State the difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
Answer:
| Eukaryotes | Prokaryotes |
| 1. The cells, like onion cells and cheek cells having well organised nucleus with a nuclear membrane are designated as eukaryotic cells. All organisms other than bacteria and blue green algae are called eukaryotes. | 1. The cells having nuclear material without nuclear membrane are termed prokaryotic cells. The organisms with these kinds of cells are called prokaryotes. |
| 2. Examples are plant and animal cells. | 2. Examples are bacteria and blue green algae. |
Question 8: Make a sketch of the human nerve cell. What function do nerve cells perform?
Answer:
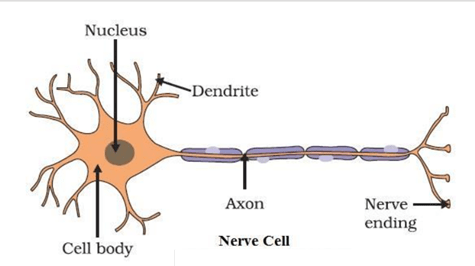
The nerve cell receives and transfers messages, thereby helping to control and coordinate the working of different parts of the body.
Question 9: Write short notes on the following:
(a) Cytoplasm
(b) Nucleus of a cell
Answer: (a) Cytoplasm: It is the jelly-like substance present between the cell membrane and the nucleus. Various other components, or organelles, of cells are present in the cytoplasm. These are mitochondria, golgi bodies, ribosomes, etc.
(b) Nucleus of a cell – It is generally spherical and located in the centre of the cell. It is composed of the following components:
- Nuclear membrane – Nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a membrane called the nuclear membrane. This membrane is also porous and allows the movement of materials between the cytoplasm and the inside of the nucleus.
- Nucleolus – A smaller spherical body in the nucleus is called the nucleolus.
- Chromosomes – nucleus contains thread-like structures called chromosomes. These carry genes and help in inheritance or transfer of characters from the parents to the offspring. The chromosomes can be seen only when the cell divides.
Question 10: Make sketches of animal and plant cells. State three differences between them.
Answer: Figure (a) – Plant Cell
Figure (b) – Animal Cell
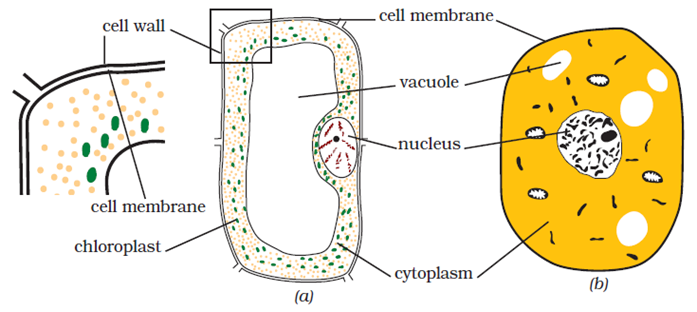
| Animal Cell | Plant Cell |
| 1. They are generally small in size. | 1. They are usually larger than animal cells. |
| 2. Cell wall is absent. | 2. Cell wall is present. |
| 3. Vacuoles are smaller in size. | 3. Vacuoles are larger in size. |
At Study Path, you can also learn more about Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Cell Structure and Functions by accessing the free exhaustive list of study materials and resources related to the chapter such as NCERT Solutions, Notes, Important Questions, and MCQ.