NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Geography Chapter 4 Air
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Geography Chapter 4 Air contains the answers to the exercises given in the NCERT History book. These solutions are easy and accurate that help you to answer the questions asked in the examinations. NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Geography Chapter 4 are prepared by our subject experts in very easy language. Practice these solutions regularly to ensure excellent marks in the exams.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Geography Chapter 4
Question 1: Answer the following questions.
(i) What is the atmosphere?
Solution: The blanket of air surrounding the earth is called the atmosphere. The atmosphere primarily comprises nitrogen and oxygen in bulk and other gases like carbon dioxide, helium, ozone, etc in lesser quantities. All living beings on earth depend on the atmosphere for their survival.
(ii) Which two gases make the bulk of the atmosphere?
Solution: The two gases that make the bulk of the atmosphere are:
- Oxygen (21%)
- Nitrogen (78%)
(iii) Which gas creates a greenhouse effect in the atmosphere?
Solution: Carbon dioxide is the gas that creates the greenhouse effect in the atmosphere.
(iv) What is the weather?
Solution: The hour to hour or the day to day condition of the atmosphere is called weather. Weather can change dramatically from day-to-day. It may be classified as hot, dry, cold or wet.
(v) Name three types of rainfall?
Solution: The three types of rainfall are as follows:
- Convectional rainfall
- Orographic rainfall
- Cyclonic rainfall
(vi) What is air pressure?
Solution: Air pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by the weight of air on the earth’s surface. The air pressure decreases as height increases and is the highest at the sea level.
Question 2: Tick the correct answer.
(i) Which of the following gases protects us from harmful sun rays?
(a) Carbon dioxide
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Ozone
Solution: (c) Ozone
(ii) The most important layer of the atmosphere is
(a) Troposphere
(b) Thermosphere
(c) Mesosphere
Solution: (a) Troposphere
(iii) Which of the following layers of the atmosphere is free from clouds?
(a) Troposphere
(b) Stratosphere
(c) Mesosphere
Solution: (b) Stratosphere
(iv) As we go up the layers of the atmosphere, the pressure
(a) Increases
(b) Decreases
(c) Remains the same
Solution: (b) Decreases
(v) When precipitation comes down to the earth in the liquid form, it is called
(a) Cloud
(b) Rain
(c) Snow
Solution: (b) Rain
Question 3: Match the following.
| (i) Trade Winds | (a) Incoming solar energy |
| (ii) Loo | (b) Seasonal wind |
| (iii) Monsoon | (c) The horizontal movement of Air |
| (iv) Wind | (d) A layer of ozone gas |
| (e) Permanent wind | |
| (f) Local wind |
Solution:
| (i) Trade Winds | (e) Permanent wind |
| (ii) Loo | (f) Local wind |
| (iii) Monsoon | (b) Seasonal wind |
| (iv) Wind | (c) The horizontal movement of Air |
Question 4: Give reasons.
(i) Wet clothes take longer time to dry on a humid day?
Solution: Wet clothes take longer time to dry on a humid day because the amount of water in the air is more on a humid day than on a sunny day. Due to which, the rate of evaporation decreases and air soaks in less water from the clothes.
(ii) Amount of insolation decreases from the equator towards poles?
Solution: Insolation is the incoming solar energy intercepted by the earth. Amount of insolation decreases from the equator toward poles, because sun rays fall vertically on the equator and slant on the poles.
Extra Questions
Very Short Answer Questions
1. What is global warming?
Answer: When greenhouse gas level increases due to factory smoke or car fumes, the heat retained increases the temperature of the earth. This is called global warming.
2. Distinguish between weather and climate.
Answer: Weather is hour-to-hour, day-to-day condition of the atmosphere. On the other hand, the average weather condition of a place for a longer period of time represents the climate of a place.
3. What is temperature?
Answer: The degree of hotness and coldness of the air is called temperature.
4. What is insolation?
Answer: Insolation is the incoming solar energy intercepted by the earth.
5. What is water vapour?
Answer: When water evaporates from land and different water bodies, it becomes water vapour.
6. What is humidity?
Answer: Moisture in the air at any time is called humidity.
7. What is rain?
Answer: Precipitation that comes down to the earth in liquid form is called rain.
8. What is wind?
Answer: The movement of air from high-pressure area to low-pressure area is called wind.
Short Answer Questions
1. What are the effects of global warming?
Answer: (i) The rise in temperature causes the snow in the coldest parts of the world to melt.
(ii) Due to this, sea level rises causing floods in the coastal areas.
(iii) There may be drastic changes in the climate of a plate leading to extinction of some plants and animals in the long run.
2. How is nitrogen a constituent of the atmosphere?
Answer: (i) Nitrogen is the most plentiful gas in the air.
(ii) When we inhale, we take some amount of nitrogen into our lungs and exhale it.
(iii) But plants need nitrogen for their survival.
(iv) They cannot take nitrogen directly from the air.
(v) Bacteria, which live in the soil and roots of some plants, take nitrogen from the air and change its form so that plants can use it.
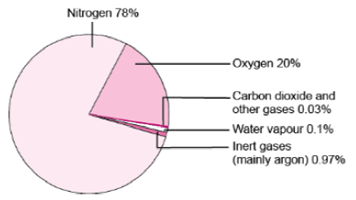
3. Describe the composition of the atmosphere.
Answer: (i) Nitrogen and oxygen are two gases which make up the bulk of the atmosphere.
(ii) Carbon dioxide, helium, ozone, argon and hydrogen are found in lesser quantities.
(iii) Apart from these gases, tiny dust particles are also present in the air. The composition of atmosphere is as follows:
4. How is oxygen a constituent of the atmosphere?
Answer: (i) Oxygen is the second most plentiful gas in the air.
(ii) Humans and animals take oxygen from the air as they breathe.
(iii) Green plants produce oxygen during photosynthesis.
(iv) In this way, oxygen content in the air remains constant.
(v) If we cut trees, this balance gets disturbed.
5. How does humidity affect us?
Answer: (i) When the air is full of water vapour, we call it a humid day.
(ii) As the air gets warmer, its capacity to hold the water vapour increases and so it becomes more and more humid.
(iii) On a humid day, clothes take longer to dry, and sweat from human body does not evaporate easily, making us feel uncomfortable.
6. How does water vapour lead to precipitation?
Answer: (i) When the water vapour rises, it starts cooling.
(ii) The water vapour condenses, causing the formation of droplets of water.
(iii) When these droplets of water become too heavy to float in air, they come down as precipitation.
7. How did cyclone affect Odisha in October 1999?
Answer: (i) The cyclone in Odisha in October 1999 affected 13 million people, uprooted trees and damaged the houses.
(ii) A large number of livestock were killed. Standing crops of paddy, vegetables and fruits were heavily damaged.
(iii) Due to salinisation caused by tidal surge, large tract of agricultural land became infertile.
(iv) Large number of mangrove forests vanished.
Long Answer Questions
1. How is carbon dioxide useful?
Answer: (i) Green plants use carbon dioxide to make their food and release oxygen.
(ii) Humans or animals release carbon dioxide.
(iii) The amount of carbon dioxide released by humans or animals seems to be equal to the amount used by the plants which make a perfect balance.
(iv) However, the balance is upset by burning of fuels, like coal and oil. All this affects earth’s weather and climate.
2. How does air pressure get affected due to layers of atmosphere?
Answer:
- The pressure falls rapidly as we go up the layers of the atmosphere.
- The air pressure is highest at the sea level and decreases with height.
- Horizontally, the distribution of air pressure is influenced by temperature of air at a given place.
- In areas where temperature is high, the air gets heated and thus rises.
- This creates a low-pressure area, which leads to cloudy skies and wet weather.
- In areas with low temperature, air is cold and pressure is heavy.
- Heavy air sinks and creates a high-pressure area.
- High pressure is associated with clear and sunny skies.
- Air moves from high-pressure to low pressure areas.
3. How are winds classified?
Answer: Winds are classified into three types:
(i) Permanent winds: It consists of trade winds, westerlies and easterlies. These blow constantly throughout the year in a particular direction.
(ii) Seasonal winds: These winds change their direction in different seasons, like monsoons in India.
(iii) Local winds: These blow only during a particular part of the day or year in one area or the whole area; for examples, land and sea breeze or winds in North India.
Hots (Higher Order Thinking Skills)
1. How does insolation affect temperature?
Answer: (i) The amount of insolation decreases from the equator towards the poles.
(ii) Therefore, the temperature decreases in the same manner.
(iii) If the earth’s temperature rises too high, it would become too warm for some crops to grow.
(iv) Temperature in cities is much higher than that of villages.
(v) The concrete and metals in buildings and the asaphalt of roads get heated up during the day.
(vi) This heat is released during the night.
(vii)Further, the crowded high-rise buildings of the cities trap the warm air and thus raise the temperature of the cities.
2. Examine the structure of the atmosphere.
Answer: The structure of atmosphere is divided into five layers. These include:
(i) Troposphere: Its average height is 13 km and all weather phenomena like rainfall, fog and hailstorm occur here. The air we breathe is found here.
(ii) Stratosphere: It extends up to a height of 50 km. It is free from weather conditions and clouds making it ideal for flying aeroplanes. It even contains ozone layer, which protects us from the harmful sun rays.
(iii) Mesosphere: It extends up to a height of 80 km. Meteorites burn up in this layer on entering from the space.
(iv) Thermosphere: In this, the temperature rises with increasing height. Ionosphere is a part of this layer. It extends 80–400 km. It even helps in radio transmission. Radio waves transmitted from the earth are reflected back to the earth by this layer.
(v) Exosphere: It is the upper most layer and has very thin air. Light gases like helium and hydrogen float into the space from here.
Class 7 Geography Chapter 4 NCERT Questions and Answers
CBSE Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Geography Chapter 4 Air are given above. All our solutions are updated as per the latest CBSE Syllabus and Guidelines. Download these NCERT solutions for free from our app and use offline.