NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Geography Chapter 3 Our Changing Earth
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Geography Chapter 3 Our Changing Earth contains the answers to the exercises given in the NCERT History book. These solutions are easy and accurate that help you to answer the questions asked in the examinations. NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Geography Chapter 3 are prepared by our subject experts in very easy language. Practice these solutions regularly to ensure excellent marks in the exams.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Geography Chapter 3
Question 1: Answer the following questions.
(i) Why do the plates move?
Solution: The movement of molten magma inside the earth results in the movement of plates.
(ii) What are exogenic and endogenic forces?
Solution: The movement of the Earth is divided on the basis of the forces which cause them. So, the forces that act in the interior of the earth are called as Endogenic forces and the forces that work on the surface of the earth are called as Exogenic forces.
(iii) What is erosion?
Solution: Erosion is defined as the wearing away of the landscape by different agents like water, wind and ice. The process of erosion and deposition creates different land-forms on the surface of the earth.
(iv) How are flood plains formed?
Solution: When a river overflows its banks, it results in the flooding of the area surrounding it. When it floods, it deposits a layer of fine soil and other material called sediments. Thus, forming a fertile layer of soil called flood plains.
(v) What are sand dunes?
Solution: In deserts, when wind blows, it lifts and transports sand from one place to another. When it stops blowing, the sand particles fall and get deposited in low hill-like structures called sand dunes.
(vi) How are beaches formed?
Solution: The sea waves deposit sediments along the seashores. This results in the formation of beaches.
(vii) What are the ox-bow lakes?
Solution: When the river enters the plains, it twists and turns forming large bends known as meanders. In due course of time, the meander loops start to cut off the river and form cut off lakes, known as the ox-bow lakes.
Question 2: Tick the correct answer.
(i) Which is not an erosional feature of sea waves?
(a) Cliff
(b) Beach
(c) Sea cave
Solution: (a) Cliff
(ii) The depositional feature of a glacier is:
(a) Flood plain
(b) Beach
(c) Moraine
Solution: (c) Moraine
(iii) Which is caused by the sudden movements of the earth?
(a) Volcano
(b) Folding
(c) Flood plain
Solution: (a) Volcano
(iv) Mushroom rocks are found in:
(a) Deserts
(b) River valleys
(c) Glaciers
Solution: (a) Deserts
(v) Ox bow lakes are found in:
(a) Glaciers
(b) River valleys
(c) Deserts
Solution: (b) River valleys
Question 3: Match the following.
| (i) Glacier | (a) Sea shore |
| (ii) Meanders | (b) Mushroom rock |
| (iii) Beach | (c) River of ice |
| (iv) Sand dunes | (d) Rivers |
| (v) Waterfall | (e) Vibrations of earth |
| (vi) Earthquake | (f) Sea cliff |
| (g) Hard bedrock | |
| (h) Deserts |
Solution:
| (i) Glacier | (c) River of ice |
| (ii) Meanders | (g) Hard bedrock |
| (iii) Beach | (a) Sea shore |
| (iv) Sand dunes | (h) Deserts |
| (v) Waterfall | (d) Rivers |
| (vi) Earthquake | (e) Vibrations of earth |
Question 4: Give reasons.
(i) Some rocks have the shape of a mushroom.
Solution: In deserts, one can see rocks in the shape of a mushroom—with a narrower base and a wider top. These are known as mushroom rocks. Such rocks are formed when the winds erode the lower section of a rock more than the upper part.
(ii) Flood plains are very fertile.
Solution: Flood plains are formed as a result of the depositional activity of rivers. Rivers carry along with them eroded material like fine soil and sediments. When it overflows its banks, it deposits the eroded material and causes flood plains to be formed. The deposited material makes the land fertile.
(iii) Sea caves are turned into stacks.
Solution: When the cavities in the sea caves become bigger and bigger, only the roof of the caves are leftover, which forms sea arches. Further, due to erosion, the roof vanishes and only the walls stay intact, turning the sea caves into stacks.
(iv) Buildings collapse due to earthquakes.
Solution: When the lithospheric plates move, the surface of the earth vibrates and then these vibrations travel outwards from the epicentre in the form of waves, which leads to sudden movement and results in the collapse of buildings.
Question 5: Activity.
Observe the photographs given below. These are various features made by a river. Identify them and also tell whether they are erosional or depositional or landforms formed by both.
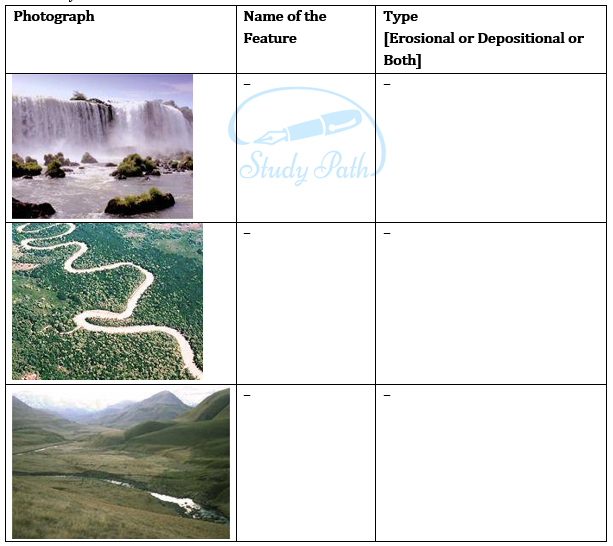
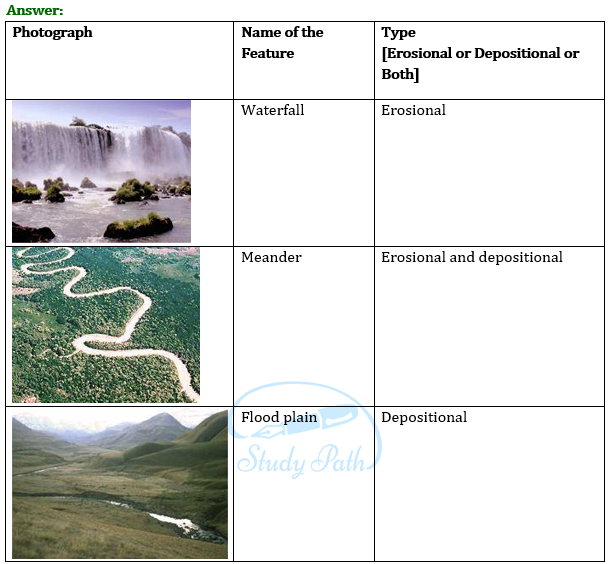
Question 6: For fun.
Solve the crossword puzzle with the help of given clues.
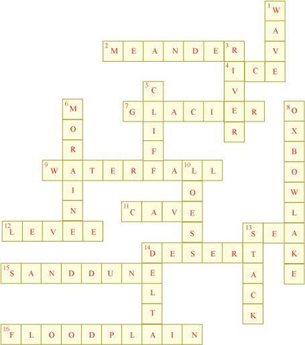
| Across | Down |
| 2. Loop like the bend of a river | 1. Rise and fall of water caused by friction of wind on water surface |
| 4. Solid form of water | 3. Flow of water in a channel |
| 7. Moving mass of ice | 5. Steep perpendicular face of a rock along sea coast |
| 9. Sudden descent of water in the bed of a river | 6. Debris of boulder and coarse material carried by glacier |
| 11. Natural cavity on weak rocks formed by action of waves | 8. Crescent-shaped lake formed by a meandering river |
| 12. Embankment on a river that keeps it in its channel | 10. Fine sand deposited by the action of the wind |
| 13. Large body of sea water | 13. Isolated mass of rising steep rock near a coastline |
| 14. Dry area where sand dunes are found | 14. Alluvial tracts of land formed by river deposits at mouth of the river |
| 15. Small hill of sand caused by the action of the wind | – |
| 16. Flat plain formed by river deposits during time of flood | – |
Answer:
Extra Questions
Very Short Answer Questions
1. What are lithosphere plates?
Answer: The earth’s crust consists of several large and several small rigid, irregularly shaped plates which carry continents and the ocean floor. The lithosphere is broken into a number of plates called lithospheric plates.
2. What is a volcano?
Answer: A volcano is a vent (opening) in the earth’s crust through which molten materials erupt suddenly.
3. What do endogenic forces produce?
Answer: Endogenic forces sometimes produce sudden movements and some other times produce slow movements. Sudden movements like earthquakes and volcanoes cause mass destruction over the surface of the earth.
Short Answer Questions
1. How do earth movements cause changes on the earth’s crust?
Answer: (i) The movements of lithospheric plates cause changes on the surface of the earth.
(ii) The earth movements are divided on the basis of forces which cause them.
(iii) The forces which act on the interior of the earth are called endogenic force.
(iv) The forces that work on the surface of the earth are called exogenic forces.
2. Examine the movements of earthquake.
Answer: (i) When lithosphere plates move, the surface of the earth vibrates. This vibration is called earthquake.
(ii) The place in the crust where the movement starts is called the focus.
(iii) Vibration travels outside towards epicentre as waves.
(vi) The place on the surface above the focus is called the epicentre.
(v) The strength of earthquake decreases away from the centre.
3. Examine the preparedness required during an earthquake.
Answer: During earthquake we should take the following measures:
- Safe spot: We should take shelter under a kitchen counter, table or desk, against an inside corner or wall.
- Stay away from: Fire places, areas around chimney and windows that it may include mirrors and picture frames.
- Be prepared: Spread awareness, amongst your friends and family members to face any disasters confidently.
4. How is the landscape worn away?
Answer: The landscapes are being continuously worn away by two processes:
- Weathering: It is the breaking up of the rocks on the earth’s surface.
- Erosion: It is the wearing away of the landscape by different agents like water, wind and ice.
5. Examine the work of ice.
Answer: (i) Glaciers are rivers of ice which too erode the landscape by bulldozing soil and stones to expose the solid rocks below.
(ii) They carve out deep hollows.
(iii) As the ice melts, they get filled up with water to form beautiful lakes in the mountains.
(iv) The material carried by the glaciers like big and small rocks, sand and silt gets deposited.
(v) These deposits form glacial moraines.
Long Answer Questions
1. Examine the features formed due to the work of a river.
Answer: The work of a river creates the following features:
- Waterfall: The running water in the river erodes the landscape. When the river tumbles at a steep angle over hard rocks or down a steep valleyside, it forms a waterfall.
- Meanders: If the river enters the plain, it twists and turns, forming large bends called meanders.
- Oxbow lake: Due to continuous erosion and deposition along the sides of the meander, the ends of the meander loop come closer and closer. In due course of time, the meander loop cuts off from the river and forms a cut-off lake called ox-bow lake.
- Floodplain: When the river overflows its banks, it leads to flooding of the neighbouring area. As it floods, it deposits layers of fine soil and sediments along its banks. They form a fertile plain called floodplain.
- Levees: The raised banks along the river are called levees.
- Distributaries: When the river approaches the sea, the speed of the flowing water decreases and the river begins to break up into a number of streams called distributaries.
- Delta: The river becomes so slow that it begins to deposit its load. Each distributary forms its own mouth. The collection of sediments from all the mouths forms a delta.
2. Examine the features of the work of a wind.
Answer: The features of work of wind are as follows:
- Mushroom rocks: An active agent of erosion and deposition in the deserts is wind. The rocks in the shape of a mushroom seen in desert are called mushroom rocks.
- Sand dunes: When the wind blows, it lifts and transports sand from one place to another. When it stops blowing, the sand falls and gets deposited in low, hill-like structures. These are called sand dunes.
- Loess: When the grains of sand are very fine and light, the wind can carry it over very long distances. When such sand is deposited in large areas, it is called loess.
Hots (Higher Order Thinking Skills)
1. Examine the features formed due to work of sea waves.
Answer: The features formed due to the formation of sea waves are:
(i) Sea caves: The erosion and deposition of sea waves gives rise to coastal landforms. Sea waves continuously strike at the rocks. Cracks develop over time and they become larger and wider. Thus, hollow-like caves are formed on the rocks. They are called sea caves.
(ii) Arches: Deposition of sea waves form cavities which become bigger and bigger. Gradually only the roof of the cave remains, leading to the formation of sea arches.
(iii) Stacks: Erosion breaks the roof and only walls are left. These wall-like features are called stacks.
(iv) Sea cliff: The steep rocky coast rising almost vertically above sea water is called sea cliff.
Class 7 Geography Chapter 3 NCERT Questions and Answers
CBSE Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Geography Chapter 3 Our Changing Earth are given above. All our solutions are updated as per the latest CBSE Syllabus and Guidelines. Download these NCERT solutions for free from our app and use offline.