Extra Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration In Organisms
Extra questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration In Organisms with answers is given below. Our subject expert prepared these solutions as per the latest NCERT textbook. These questions will be helpful to revise the all topics and concepts. CBSE Class 7 extra questions are the most simple and conceptual questions that are prepared by subject experts for the students to study well for the final exams. By solving these extra questions, students can be very efficient in their exam preparations.
Respiration In Organisms Class 7 Science Extra Questions and Answers
Very Short Extra Questions and Answers
1. Where does cellular respiration take place?
Answer: Cellular respiration takes place in the cells of all organisms.
2. What is aerobic respiration?
Answer: The process of breakdown of glucose with the use of oxygen is called aerobic respiration.
3. What are some common uses of Yeast?
Answer: Some common uses of Yeast are bread, wine and beer.
4. Name an organism that can survive in the absence of air.
Answer: Yeast can survive in the absence of air.
5. How do earthworms breathe?
Answer: Earthworms breathe through their skins.
6. What does a breath mean?
Answer: A breath means one inhalation plus one exhalation.
7. What is cell?
Answer: A cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of an organism.
8. What are all organisms made up of?
Answer: All organisms are made of small microscopic units called cells.
9. Name the respiratory organ of birds.
Answer: They have lungs in their chest cavities like the human beings.
10. What forms the floor of the chest cavity?
Answer: A large, muscular sheet called diaphragm forms the floor of the chest cavity.
11. What are the end products of anaerobic respiration?
Answer: The end products of anaerobic respiration are alcohol, carbon dioxide and energy.
12. What is produced during anaerobic respiration in muscles that causes cramps?
Answer: Lactic acid is produced during anaerobic respiration in muscles that causes cramps.
13. What is cellular respiration?
Answer: The process of breakdown of food in the cell with the release of energy is called cellular respiration.
14. What is breathing rate?
Answer: The number of times a person breathes in a minute is termed as the breathing rate.
15. Why smoking should be avoided?
Answer: Smoking damages lungs. Smoking is also linked to cancer. So, it must be avoided.
16. What are spiracles?
Answer: Insects have small openings on their body that allow them to breathe. These openings are called spiracles.
17. Why we should eat regularly?
Answer: We should eat regularly because food has stored energy, which is released during respiration.
18. What is a stomata and what is its function?
Answer: Leaves of the plants have tiny pores called stomata for exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
19. What is breathing?
Answer: Breathing means taking in air rich in oxygen and giving out air rich in carbon dioxide with the help of respiratory organs.
20. What is inhalation and exhalation?
Answer: The taking in of air rich in oxygen into the body is called inhalation and giving out of air rich in carbon dioxide is known as exhalation.
Short Extra Questions and Answers
1. How do frogs breathe?
Answer: Frogs have a pair of lungs like human beings to breathe air. They can also breathe through their skin, which is moist and slippery.
2. Name some animals that breathe through lungs.
Answer: Animals such as elephants, lions, cows, goats, frogs, lizards, snakes, birds, have lungs in their chest cavities like the human beings.
3. Why do mountaineers carry oxygen with them?
Answer: Mountaineers carry oxygen with them because the amount of air available to a person is less than that available on the ground.
4. Why should we cover our nose while sneezing?
Answer: When we sneeze, we should cover our nose so that the foreign particles we expel are not inhaled by other persons.
5. How does respiration occur in earthworms?
Answer: Earthworms breathe through their skins. The skin of an earthworm feels moist and slimy on touching. Gases can easily pass through them.
6. What role does hair present in the nasal cavity play in the process of respiration?
Answer: When we inhale, the particles get trapped in the hair present in our nasal cavity. Thus, the hairs present in the nasal cavity filters the air.
7. What is normal range of breathing rate per minute in an average adult person at rest?
Answer: On an average, an adult human being at rest breathes in and out 15ñ18 times in a minute.
8. Why do we get muscle cramps after heavy exercise?
Answer: The cramps occur when muscle cells respire anaerobically. The partial breakdown of glucose produces lactic acid. The accumulation of lactic acid causes muscle cramps.
9. What happens during exhalation?
Answer: During exhalation, ribs move down and inwards, while diaphragm moves up to its former position. This reduces the size of the chest cavity and air is pushed out of the lungs.
10. What happens during inhalation?
Answer: During inhalation, ribs move up and outwards and diaphragm moves down. This movement increases space in our chest cavity and air rushes into the lungs. The lungs get filled with air.
11. What happens to the air we breathe in?
Answer: The air we breathe in is transported to all parts of the body and ultimately to each cell. In the cells, oxygen in the air helps in the breakdown of food and energy is released.
12. How does respiration work in yeast?
Answer: Yeasts are single-celled organisms. They get energy through anaerobic respiration. In the absence of oxygen, glucose breaks down into alcohol and carbon dioxide.
13. Why are yeasts used to make wine and beer?
Answer: Yeasts are single-celled organisms. They respire anaerobically and during this process yield alcohol. They are, therefore, used to make wine and beer.
14. What is the function of gills in fish?
Answer: Gills in fish help them to use oxygen dissolved in water. Gills are projections of the skin and are well supplied with blood vessels for exchange of gases.
15. How do plant roots respire?
Answer: Like all other living cells of the plants, the root cells also need oxygen to generate energy. Roots take up air from the air spaces present between the soils particles.
Long Extra Questions and Answers
1. Why do we feel hungry after a physical activity?
Answer: When we need extra energy, we breathe faster. As a result more oxygen is supplied to our cells. It speeds up the breakdown of food and more energy is released. Due to rapid breakdown of food we feel hungry.
2. What is anaerobic respiration?
Answer: Food can also be broken down, without using oxygen. This is called anaerobic respiration. Breakdown of food releases energy.
3. Do the plants also respire?
Answer: Like other living organisms, plants also respire for their survival. They also take in oxygen from the air and give out carbon dioxide. In the cells oxygen is used to break down glucose into carbon dioxide and water as in other organisms.
4. When we release our breath after holding it for some time, we had to breathe heavily. Why it was so?
Answer: This is so, because whenever we need extra energy, we breathe faster. As a result more oxygen is supplied to our cells. It speeds up the breakdown of food and more energy is released.
5. How does exchange of gases take place in insects?
Or
Explain respiration in insects.
Answer: Insects have a network of air tubes called tracheae for gas exchange.
Oxygen rich air rushes through spiracles into the tracheal tubes, diffuses into the body tissue, and reaches every cell of the body. Similarly, carbon dioxide from the cells goes into the tracheal tubes and moves out through spiracles.
6. When and where does anaerobic respiration occur in humans?
Answer: During heavy exercise, fast running, cycling, walking for many hours or heavy weight lifting, the demand for energy is high. But the supply of oxygen to produce the energy is limited. Then anaerobic respiration takes places in the muscle cells to fulfill the demand of energy.
7. What is the percentage of oxygen and carbon dioxide in inhaled and exhaled air?
Answer: When we exhale, we breathe out less oxygen but more carbon dioxide than we inhale.
Inhaled air: Oxygen 21% and Carbon dioxide 0.04%
Exhaled air: Oxygen 16.4 % and Carbon dioxide 4.4%
8. Why do we get relief from cramps after a hot water bath or a massage?
Answer: Hot water bath or massage improves circulation of blood. As a result, the supply of oxygen to the muscle cells increases. The increase in the supply of oxygen results in the complete breakdown of lactic acid into carbon dioxide and water. Thus, we get relief from cramps after a hot water bath or a massage.
9. Why do we often sneeze when we inhale a lot of dust-laden air?
Answer: When we inhale a lot of dust-laden air, the particles get trapped in the hair present in our nasal cavity. However, sometimes these particles may get past the hair in the nasal cavity. Then they irritate the lining of the cavity, as a result of which we sneeze. Sneezing expels these foreign particles from the inhaled air and a dust free, clean air enters our body.
10. How does respiration occur in plants?
Or
How do the plants breathe in oxygen?
Answer: In plants each part can independently take in oxygen from the air and give out carbon dioxide. Roots take in air present in the soil. Leaves have tiny pores called stomata through which they exchange gases. The breakdown of glucose in the plant cells is similar to that in other living beings.
11. What parts of the human body are involved in respiration?
Answer: We take in air through our nostrils. When we inhale air, it passes through our nostrils into the nasal cavity. From the nasal cavity, the air reaches our lungs through the windpipe. Lungs are present in the chest cavity. This cavity is surrounded by ribs on the sides. A large, muscular sheet called diaphragm forms the floor of the chest cavity. Breathing involves the movement of the diaphragm and the rib cage.
12. How do the cockroaches breathe?
Answer: A cockroach has small openings on the sides of its body. These openings are called spiracles. They have a network of air tubes called tracheae for gas exchange. Oxygen rich air rushes through spiracles into the tracheal tubes, diffuses into the body tissue, and reaches every cell of the body. Similarly, carbon dioxide from the cells goes into the tracheal tubes and moves out through spiracles.
13. Why does an athlete breathe faster and deeper than usual after finishing the race?
Answer: During fast running the demand for energy is high. But the supply of oxygen to produce the energy is limited. Our muscle cells can also respire anaerobically, but only for a short time, when there is a temporary deficiency of oxygen. Thus, an athlete breathes faster and deeper than usual after finishing the race so that more oxygen is supplied to the cells. This speed up the breakdown of food and more energy is released.
14. Why do we respire?
Answer: All organisms are made of small microscopic units called cells. A cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of an organism. Each cell of an organism performs certain functions such as nutrition, transport, excretion and reproduction. To perform these functions, the cell needs energy. Even when we are eating, sleeping or reading we require energy. The food has stored energy, which is released during respiration. Therefore, we respire to get energy from food.
15. List the similarities and differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Answer: Similarities
- Both aerobic and anaerobic respirations are types of cellular respiration.
- Both generate energy by breaking down glucose and produces byproducts.
Differences
| Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic respiration |
| 1. It occurs in the presence of oxygen. | 1. It occurs in the absence of oxygen. |
| 2. Large amount of energy is released. | 2. Small amount of energy is released. |
| 3. Glucose breaks down into water and carbon dioxide. | 3. Glucose breaks down into alcohol and carbon dioxide. |
| 4. It is a slow process. | 4. It is a fast process. |
| 5. It occurs in most of the plants and animals. | 5. It occurs in human muscles cells, yeast, bacteria etc. |
16. How do we breathe?
Answer: Normally we take in air through our nostrils. When we inhale air, it passes through our nostrils into the nasal cavity. From the nasal cavity, the air reaches our lungs through the windpipe. Lungs are present in the chest cavity. This cavity is surrounded by ribs on the sides. A large, muscular sheet called diaphragm forms the floor of the chest cavity. Breathing involves the movement of the diaphragm and the rib cage. During inhalation, ribs move up and outwards and diaphragm moves down. This movement increases space in our chest cavity and air rushes into the lungs. The lungs get filled with air. During exhalation, ribs move down and inwards, while diaphragm moves up to its former position. This reduces the size of the chest cavity and air is pushed out of the lungs.
17. Take three test-tubes. Fill ¾ th of each with water. Label them A, B and C. Keep a snail in test-tube A, a water plant in test-tube B and in C, keep snail and plant both. Which test-tube would have the highest concentration of CO2?
Answer: Snail breathes in oxygen and breathes out carbon dioxide. Hence concentration of CO2 increases in the test tube. Therefore, test tube A will have high concentration of carbon dioxide.
In test tube B water plant uses carbon dioxide for synthesizing food and hence there will be less concentration of carbon dioxide compared to test tube A.
In test tube C, carbon dioxide produced by snail is utilized by plant for synthesis of food and oxygen released by plant is utilized by snail for respiration. Hence, concentration of carbon dioxide is least in test tube C.
18. Whales and dolphins often come up to the water surface. They even release a fountain of water sometimes while moving upwards. Why do they do so?
Answer: Whales and dolphins are mammals and breathe air into their lungs, just like we do. They cannot breathe under water like fish can as they do not have gills. They breathe through a nostril, called a blowhole, located right on top of their heads. This allows them to take breaths by exposing just the top of their heads to the air while they are swimming or resting under the water. After each breath, the blowhole is sealed tightly by strong muscles that surround it, so that water cannot get into the dolphin’s lungs.
When they surfaces for air, they breathes out (exhales) first and then breathes in (inhales) fresh air. The water spray is not coming from theirs lungs; it is just water sitting on top of their head around the blowhole being blown away before they inhale.
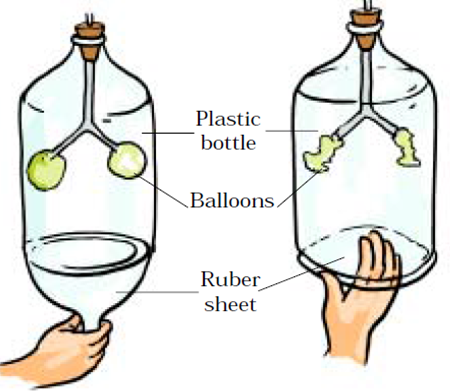
19. Explain the mechanism of breathing with the help of an activity.
Answer: Take a wide plastic bottle. Remove the bottom. Get a Y-shaped glass or plastic tube. Make a hole in the lid so that the tube may pass through it. To the forked end of the tube fix two deflated balloons. Introduce the tube into the bottle. Now cap the bottle. Seal it to make it airtight. To the open base of the bottle tie a thin rubber or plastic sheet using a large rubber band. To understand the expansion of the lungs, pull the rubber sheet from the base downwards. The volume of the cavity increases. This causes the pressure to decrease. Air rushes in to equalize the pressure, causing the balloons to inflate. Next, push the rubber/plastic sheet up. The volume of the cavity decreases. This causes an increase in pressure within the bottle, the air rushes out of the balloons causing them to deflate.