CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflections
CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflections are given below. Our notes are designed by the subject experts and are as per the NCERT guidelines. These notes include all the important points of the chapter in detailed way, so you can refer to this whenever required. Study Path provides CBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 11 that are easy to understand and also free downloadable PDF format, so students can practice it for their studies and get good marks in their examinations.
Light Shadows and Reflections Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 11
Introduction
Light is a form of energy which helps us in seeing objects. When light falls on an object, some of the light gets reflected. The reflected light comes to our eyes and we are able to see an object.
Sources of Light
Objects that produce their own light are called Luminous Objects. Example, Sun, Fire
Objects that do not produce their own light but are visible when reflect light falling on them are called Non-Luminous Objects. Example – Table, planets.
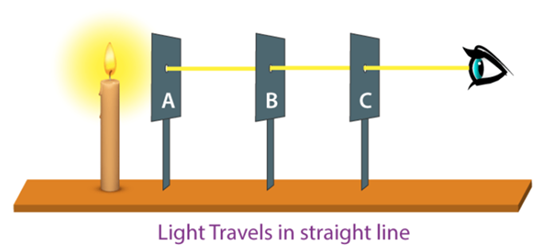
Rectilinear propagation of light
Light takes the quickest path between any two points. Therefore, light travels in a straight line. This is known as a rectilinear propagation of light.
Transparent, Opaque and Translucent Objects
Luminous & Non-luminous objects
- Objects that emit light and heat are known as luminous objects. E.g.: Sun and other stars
- Objects that do not produce their own light but reflect the light emitted by luminous objects are known as non-luminous objects. E.g.: Earth, trees
Objects can be classified based on their interaction with light.
- Transparent objects allow light to pass through them without getting scattered. E.g.: glass
- Translucent objects allow light to pass through them partially. E.g.: Butter paper
- Opaque objects do not allow any light to pass through them. E.g.: a table, a book, etc
Shadows are dark regions formed when an opaque object blocks the path of light. This formation is possible only because light only travels in a straight line.
Shadow formation
- A shadow is formed when an opaque object comes in the path of light.
- A shadow needs a screen where it is formed, for example, the ground, or walls of a room or even the surfaces of buildings.
- Shadows give us an idea about the shapes of different objects. Or, it can even mislead us about the shape of different objects. E.g. the shadow of a cone appears to be a triangle on the screen.

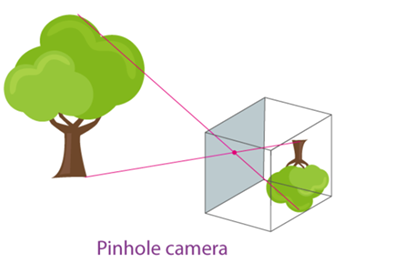
The Pinhole Camera
Formation of image by pinhole camera
- A pinhole camera is a simple camera that consists of a light-proof box, a thin film for a screen and a small aperture or hole to allow the passage of light rays.
- The light from outside enters through the small hole and forms an image on the screen that is inverted.
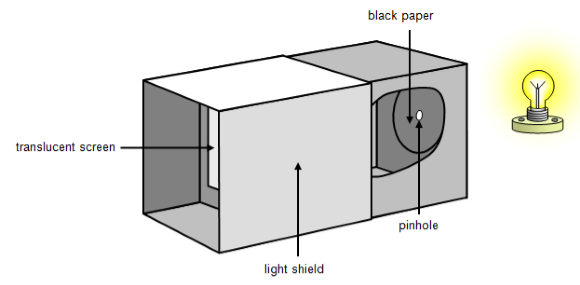
How to make a Pinhole Camera?
Step 1: Take two cardboard boxes one larger than the other such that one box slides into the other without any gap.
Step 2: Cut out open one side of each box. On the opposite side of the larger box cut a small hole in the centre.
Step 3: On the opposite side of the smaller box cut a square of about 5 cm and cover this open area with a tracing paper.
Step 4: Slide the smaller box inside the larger one such that the side with the tracing paper is on the inside.
Step 5: Cover the camera and your head with a black cloth and then get ready to observe the distant objects.
Natural Pin-hole Camera
When we pass under a tree covered with large number of leaves, we notice that small patches of sun light under it. These circular images are, in fact, pin hole images of the Sun. The gaps between the leaves, act as the pin holes. These gaps are all kinds of irregular shapes, but, we can see circular images of the Sun. This is called Natural Pin-Hole Camera
Mirrors and Reflection
Mirrors
A mirror is a surface usually consisting of a glass that reflects light incident on it to form clear erect images.
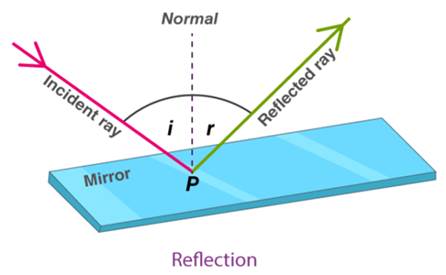
Reflection
When light is incident on a surface, it gets reflected or it bounces back. Any surface that is really well polished or shiny acts like a mirror. The phenomenon of light bouncing off surfaces is called reflection.
Characteristics of images
- Images have colour, unlike shadows. They are formed due to the converging rays of light that comes after reflecting from objects.
- A real image is formed by actual convergence of light rays. Real images always form on a screen.
- A virtual image is the apparent convergence of diverging light rays. Virtual images cannot be obtained on a screen.
Plane mirrors and images formed by them
A plane mirror changes the direction of light that falls on it.
This enables us to see images. Take the example of a comb placed in front of a mirror over a dark coloured paper. Let a beam of light pass through the comb on the mirror using a torch. Then an image is observed similar to the one given:
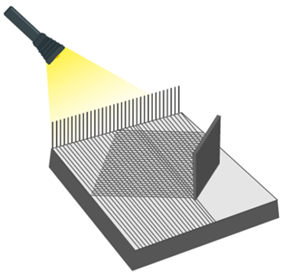
We observe that the light gets reflected from this mirror and it travels in straight lines.
Revision Notes for CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 11 – Free PDF Download
Our Class 6 Revision Notes will provide a quick glimpse of the chapter and improve the learning experience. We have made these revision notes keeping the convenience of students in mind so that it proves more effective. You can easily read these Class 6 notes just by clicking on the chapter names provided above.