Class 6 Geography Chapter 2 Globe Latitudes and Longitudes Extra Questions and Answers
CBSE Class 6 Geography Chapter 2 Globe Latitudes and Longitudes Extra Questions and Answers is available here. Students can learn and download PDF of these questions for free. These extra questions and answers are prepared by our expert teachers as per the latest NCERT textbook and guidelines. Learning these extra questions will help you to score excellent marks in the final exams.
Class 6 Geography Chapter 2 Extra Questions and Answers
Very Short Answer Questions
1. Greenwich line passes through ______.
Answer: England.
2. Why the mid-day sun never shines overhead on any latitude beyond the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn?
Answer: The angle of the sun rays keep decreasing.
3. If it is 12 P.M. at Greenwich, then what will be the time at 15°W?
Answer: 11 A.M.
4. What are the total number of longitudes?
Answer: 360.
5. Torrid Zone lies between 00 to 23 ½° North and South of equator. True/False
Answer: True.
6. State the location of South Pole.
Answer: South Pole is in southern hemisphere at 90°S.
7. The 24 time zones of the Earth are of ______ each.
Answer: 1 hour.
8. India lies between 8°4′ N and 37°6′ N latitudes. True/False
Answer: True.
9. What is the time difference between the eastern most and western most parts of India if standard meridian is not adopted?
Answer: 1 hour 45 minutes.
10. State the location of Antarctic Circle.
Answer: Antarctic Circle lies south of equator at 66½°S.
11. What is the value of South Pole?
Answer: 90°S.
12. Where does North Temperate Zone lie?
Answer: 23½°N – 66½°N.
13. The angle of the sun rays, as it moves towards the poles increases/Decreases.
Answer: Decreases
14. Why is globe important?
Answer: A globe is useful when we want to study the earth as a whole as we can see
(i) The water bodies,
(ii) The axis,
(iii) The tilt and the location of the countries on the globe.
15. How can we find latitude of a place with the help of a pole star?
Answer: By measuring the angle of the pole star, one can find out the latitude of a place.
16. What type of climate is found in the Temperate Zone?
Answer: Moderate.
17. How many degrees are there in either of the Hemispheres?
Answer: There are 90 in either of the Hemispheres.
18. When does the equinox occurs?
Answer: An equinox occurs twice a year, when the tilt of the Earth’s axis is inclined neither away from nor towards the Sun, the centre of the Sun being in the same plane as the Earth’s equator.
19. Where do all the meridians meet?
Answer: At the poles.
20. When we move from the Equator towards the poles, the distance between the longitudes ______.
Answer: Decreases.
21. Where does Torrid Zone lie?
Answer: Torrid zone lies between 23 ½°N and 23 ½°S.
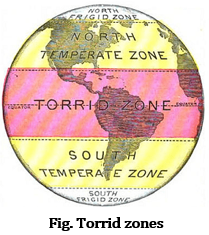
22. Name the area between the Tropic of Capricorn and Tropic of Cancer.
Answer: Torrid Zone.
23. Name the true model of the earth.
Answer: Globe.
24. At the poles, the sun rays are ______.
Answer: Slanting.
25. What is the importance of Equator?
Answer: The equator is an important reference point to locate places.
26. Define axis of a globe.
Answer: A needle is fixed through a globe in a tilted manner called axis of a globe.
27. Define latitudes.
Answer: The parallel circles from the equator up to the poles are called latitudes.
28. Name the heat zone that receives maximum heat.
Answer: Torrid Zone.
29. Why Frigid Zones are very cold?
Answer: In this zone, the sun does not rise much above the horizon so its rays are always slanting and provides less heat.
30. What is the value of Prime meridian?
Answer: 0° longitude.
31. If the time is 12 noon in Greenwich, then what is the time at 20° west?
Answer: 10:40 a.m.
32. What is the total number of standard time zones of Russia?
Answer: 11.
33. State the Total time zones in which the Earth has been divided.
Answer: 24.
34. Name the planet also known as the Earth’s twin.
Answer: Venus.
35. What does the term ‘Grid’ mean in Geography?
Answer: The network of the Parallels of Latitude and Meridians of Longitude on the Globe is known as Grid.
36. What is the true shape of the Earth?
Answer: The true shape of Earth is Geoid.
37. Name the different heat zones of the Earth?
Answer: There are mainly three heat zones of the earth:
(i) Torrid zone.
(ii) Temperate zone.
(iii) Frigid zone.
38. Name the two basic points of reference on the Earth’s surface?
Answer: North Pole & South Pole.
39. How can you locate a point on the globe?
Answer: Any point on the globe can be located by knowing its latitudes & longitudes.
40. What is the standard meridian of India?
Answer: The standard meridian of India is 82°30’E.
41. In which zone do the Poles fall?
Answer: Frigid Zone
42. In which unit are the Longitudes measured?
Answer: The distances between Longitude are measured in ‘degrees of longitude.’ Each degree is further divided into minutes, and minutes into seconds.
43. What happens to the Longitudes at the poles?
Answer: Longitudes are semicircles and the distance between them decreases steadily as they move towards the poles until it becomes zero at the poles, where all the meridians meet.
44. Where is British Royal Observatory is located?
Answer: Greenwich
45. If a day and night cricket match between India and England has started at 2 p.m. in London. So what will be the time in India?
Answer: If A day and night cricket match between India and England had started at 2 p.m. in London. This means that the match would begin at 7.30 p.m. in India and finish well into the night.
Short Answer Type Questions
1. Why is Frigid Zone very cold?
Answer: It lies close to poles. In this zone the sun does not rise much above horizon. Its rays are always slating and provide less heat. That is why this zone is very cold.
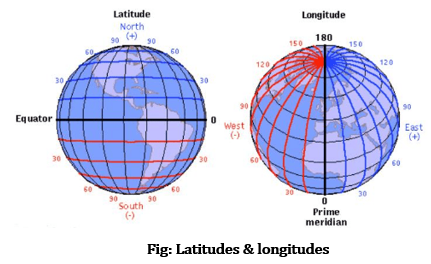
2. What are Latitudes & longitudes?
Answer: Parallels of latitudes: All parallel circles from the equator up to the poles are called parallels of latitudes.
Longitude is the invisible vertical line that runs around the Earth from North to South. The Prime Meridian is where its coordinates are 0°.
3. What is the difference between the local time and standard time of a place?
Answer: Local Time: Local time is the real time of a place according to its corresponding longitudes. Every place has its unique local time. Places having the same meridian of longitude have the same local time.
Standard Time: Standard time of a place is the time of that time zone in which that place lies. In countries with large east west extant variations in local time present; to overcome this problem standard time of specific time zone is taken as standard time of that place.
4. Why is it necessary to have standard time?
Answer: Standard time is necessary because:
(i) The different meridian’s having different time is likely to create problems for trains & flights.
(ii) To maintain uniformity in the country and the world.
5. If a person goes from west longitudes to east longitude he need to
(a) Increase time in his watch
(b) Decrease time in his watch
Answer: (b) Decrease time in his watch.
6. Suppose the time at 30° east is 2 p.m. then what is the time at Greenwich?
(a) 2 p.m.
(b) 12 p.m.
(c) 1 p.m.
(d) Cannot find
Answer: (b) 12 p.m
Solution: Earth moves 360° in 24 hours,
So 15° in an hour and 1° in four minutes
30° east means 30 × 4 = 120 minutes ahead of Greenwich
So where at 30° east time is 2 p.m.
So at Greenwich time = 2 pm – 2 hours = 12 p.m.
7. How have 90 latitude been calculated in each hemisphere?
Answer: The equator represents the zero degree latitude. Since the distance from the equator to either of the poles is one-fourth of a circle round the earth, it will measure 1/4th of 360 degrees, i.e., 90°.
8. Draw a diagram of a grid?
Answer:
9. Define a globe.
Answer: A globe is a true model of the earth.
Globe: A globe is a model of the Earth that shows the Earth’s shape, lands, oceans distances and directions as they relate to one another truly.
10. What is Prime Meridian?
Answer: The Meridian which passes through Greenwich, where the British Royal Observatory is located is called the Prime Meridian. Its value is 0o longitude.
11. What follows the value of the Latitude?
Answer: The value of Latitude is followed by N(for North) or S(for South).
12. Distinguish between parallels of latitude and meridians of longitude.
Answer:
| Latitudes | Longitudes |
| All parallel circles from the equator up to the poles are called parallels of latitudes. | All semi-circles running from North Pole to South Pole are called meridians o longitudes. |
| In total, there are 180° latitudes that is 90° in north and 90° in south. | In total, there are 360° longitudes that is 180° in east and 180° in west. |
| 0° latitude is known as equator. | 0° longitude is known as Prime Meridian. |
| The help to judge the climate of the places. | The help to find the time of the places. |
| They do not meet at the poles. | The meet at the poles. |
13. Why do places beyond Tropics have moderate temperature?
Answer: The mid–day sun never shines overhead on any latitude beyond the tropics. The angle of the sun rays goes on decreasing towards the poles. As a result, the places between tropics to Arctic Circle and to Antarctic Circle have moderate temperature.
14. How latitude and longitude is expressed?
Answer: Latitudes and longitudes are expressed in degrees. However, the increments of less than one degree can be expressed as a decimal or minutes and seconds. There are 60 minutes in a degree and 60 seconds in a minute. Longitudes can be written with an E or W for east or west. Latitudes have N or S for north or south.
16. In the given diagram mark the important parallels of Latitudes.
(a) Equator
(b) Tropic of Cancer
(c) Tropic of Capricorn
(d) Arctic Circle
(e) Antarctic Circle
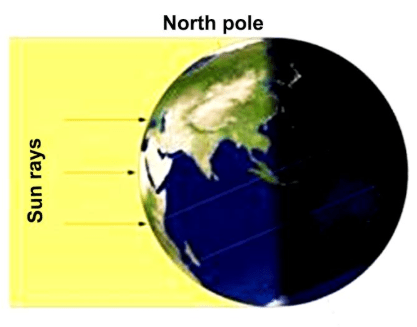
Answer:
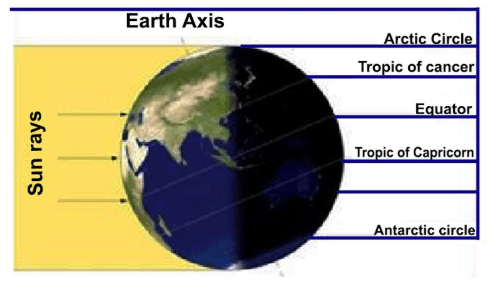
Long Answer Type Questions
1. Why is it necessary to have standard time? Also define Indian Standard Time (IST).
Answer: It is necessary to have a standard time because:
(a) Different meridians have different time, which makes it difficult to prepare a time table for trains and flights.
(b) It helps to maintain uniformity of time in the country and the world.
Indian Standard Time: In India, the longitude of 82o 30’E is treated as the standard meridian and the local time at this meridian is taken as the standard time for the whole country. It is known as Indian Standard Time (IST).
2. Which meridian is taken as a standard meridian for India and why?
Answer: This is because India is a vast country and has a great difference in sunrise timing along West in Gujarat and East in Arunachal Pradesh. There is a time difference of 1 hour and 45 minutes. Hence, it is necessary to have a specific time all over the India which is done by taking Standard Meridian of India at 82.30º East at the Tropic of Cancer passing through the middle of India. To avoid such confusion and to have same time all over the country, we have taken a standard meridian.
3. What are the advantages of a Globe?
Answer: Advantages of the Globe are:
- It shows the exact shape of the Earth
- It helps us to understand how day and night occur and seasons are caused.
- It gives the ideas of tilt of the Earth’s axis.
- It shows us the exact position and areas of the continents and the oceans.
4. How we can calculate time using longitudes?
Answer:
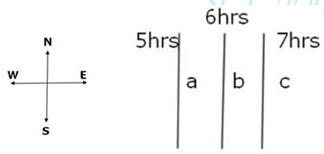
- In the figure, three places namely a, b and c are marked.
- Let us assume that time difference between ‘a’ ‘b’ and ‘c’ is 1 hour each.
- If the time at a place ‘b’ is 6 in the morning
- then the time at ‘a’ would be 5 in the morning
- time at ‘c’ would be 7 in the morning.
- The time at place ‘a’ is 1 hour less because it is to the west of ‘b’
- and time at ‘c’ is 1 hour more because it is to the east of ‘b’.
- It is because Earth rotates from west to east.
- As the sun rises in the east so place ‘c’ has 7 am,
- place ‘b’ has 6 am and
- place ‘a’ has 5 am.
- This shows that time increases as we go towards east and it decreases as we go to west.
5. Why is latitude and longitude useful?
Answer: Usefulness of Longitude and Latitude
- The Earth is divided into degrees of longitude and latitude which helps us measure location and time using a single standard.
- When used together, longitude and latitude define a specific location through geographical coordinates. These coordinates are what the Global Position System or GPS uses to provide an accurate locational relay.
- Longitude and latitude lines measure the distance from the Earth’s Equator or central axis – running east to west – and the Prime Meridian in Greenwich, England – running north to south.
- They have been useful to navigators, geographers, cartographers and surveyors for a long time. Latitude and longitude are useful on a daily basis for a great number of people for global positioning system, GPS and computerized mapping.
- Using latitude and longitude, it is possible to calculate all sorts of things such as calculate the distances from city to city, calculate the distance from any point on earth to any other point.
Example: we can calculate the distance from your house to school.
6. Which longitude is taken as International Date Line and why?
Answer: The International Date Line (IDL) is an imaginary line on the surface of the Earth opposite the Prime Meridian, where the date changes as one travels across east or west.
- Roughly along 180° longitude, it almost corresponds to the time zone boundary separating -12 and +12 hours Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
- Crossing the IDL, travelling east results in a day or 24 hours being added and crossing west results in a day being subtracted.
- The exact number of hours depends on the time zones.