Heredity and Evolution Class 10 Important Questions and Answers
Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution covers each topic of the chapter. These questions aim at providing a better understanding of the chapter to the students and can be downloaded in PDF format. These important question bank help students in clearing their doubts so that they can score well in the exam.
While preparing for exams, students should practise these important questions of Class 10 Science to understand the concepts better. Solving important questions of Class 10 Science Chapter 9 will teach students time management skills and enhance their problem-solving skills. Also, students may come across a few of these questions in the board exam.
Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 – PDF
1. Why is sexual reproduction considered to be superior to asexual reproduction in terms of evolution?
Answer: Sexual reproduction, unlike asexual reproduction, provides room for a larger number of variations. In it, the intensity of variations maximises due to increased inaccuracies in the DNA copying mechanism because of involvement of two individuals in the reproductive process. Hence, greater diversity is observed in sexual reproduction, which favours evolution, and thus, it is considered superior to asexual reproduction.
2. Why the experiences of an individual during its lifetime cannot be passed on to its progeny and cannot direct evolution?
Answer: The experiences of an individual during its lifetime are acquired traits. These are changes in the non-reproductive tissue of the individual, and do not affect the DNA of the germ cell of that individual. As in reproduction, only the germ cells participate, the changes in non-reproductive tissues are not passed on to the next generation.
3. What is the information source for making proteins in the cell?
Answer: The source of information for making proteins is the DNA in the cells. The part of DNA which codes for a particular protein is the gene for that protein.
4. How will you define the gene of a particular protein?
Answer: The part of cellular DNA, which provides information regarding a particular protein, i.e. codes for that protein, is called the gene for that protein.
5. What forms the basis for evolutionary processes?
Answer: Genetic mutations and natural selection for the basis of evolution.
6. Why a child bears all the basic features of a human being but it does not look exactly like its parents?
Answer: The DNA copying mechanism of sexual reproduction are precise, but they are not completely accurate. This allows for a good extent of variations to take place. But, the variations are not so large to change the basic structure of the human being. Thus, the child bears all basic features but doesn’t look exactly like its parents.
7. How does the creation of variations in a species promote survival?
Answer: The frequency of inherited traits, or the genes carrying those traits increases over generations. The variations that provide better adaptive advantage over others are promoted, or say, naturally selected over others. Thus, creation of variations in a species promotes their survival.
8. What control characteristics or traits? How they control those characteristics?
Answer: The genes present in the DNA control characteristics or traits. The phenotypic or physical expression of a character depends upon the genotypic constitution. The expressed traits are a result of the specific genotypic combination of the alleles, which are a pair of genes themselves. Also, particular genes code for specific proteins that determine the physical characteristics of an individual. This is how genes control the traits.
9 What will be the genotype for homozygous dominant black hair colour and homozygous recessive brown hair colour?
Answer: Considering, B to stand for black hair, and b to stand for brown hair, Homozygous dominant black hair = BB
Homozygous recessive brown hair= bb.
10. What is the essence of the idea of evolution?
Answer: The essence of the idea of evolution is that the frequency of certain genes that control traits, changes in a population over generations. This, in turn, changes the frequency of inherited traits or characters and some rare variations, become a common character in population.
11. How do Mendel’s experiments show that traits may be dominant or recessive?
Answer: Mendel used pea plants to conduct experiments demonstrating the inheritance of characters like height, colour, etc. When a tall plant was crossed with a dwarf plant, the progeny or first generation showed all tall plants. When two of these plants were crossed, the progeny showed three tall and one dwarf plant.
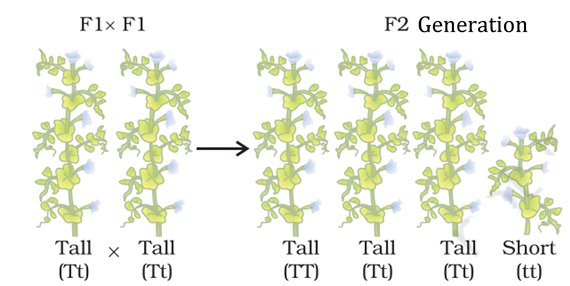
The above crosses show that only one T is enough to make the plant tall, that is, it dominates the inheritance of height. Thus, it is called the dominant trait. To make a plant dwarf, both the alleles must be t. Thus, it is the recessive trait.
12. What is meant by genetic drift? What is the notion of genetic drift?
Answer: Genetic drift is a phenomenon that occurs in small populations. Here, there is a change in frequency of a gene or genes, due to a random event or chance when there is disappearance of certain part of population, or when reproduction does not take place.
The notion of genetic drift is that certain accidents can alter the frequency of some genes on a small population, even if they don’t provide any survival advantage.
13. What are homologous organs? Give examples.
Answer: The organs of different species, which are similar in structure, but are modified to perform different functions are called homologous organs.
For example: Limbs of a human, frog, lizard and a bird.
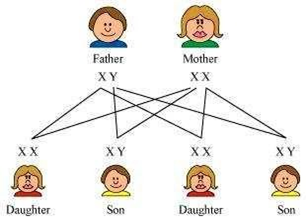
14. How is the sex of the child determined in human beings?
Answer: The sex of a child in human beings in genetically determined. The humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, out of which 22 are a perfect pair of one paternal and one maternal copy. The last pair of chromosomes also called the sex chromosomes, is different for males and females. Females have a pair of X chromosomes, whereas males have XY chromosomal pair. The inheritance of these sex chromosomes that determine the gender of an individual is as follows:
15. What are Analogous organs? Give examples.
Answer: The organs of different species, which are similar in function, but have different structural framework are called analogous organs.
For example: wings of a bat, and wings of a bird.
16. How do Mendel’s experiments show that traits are inherited independently?
Answer: In Mendel’s experiments, when pea plants with two characters such as colour of seed and shape of seed were bred together, plants with Yellow coloured Round seeds were crossed with plants having Green coloured wrinkled seeds. The F1 progeny showed all plants with Yellow coloured Round seeds, showing that these were the dominant characters. However, when self-pollinated for second generation, certain progeny plants also exhibited new combinations like Yellow coloured Wrinkled seeds, or Green coloured Round seeds. This shows that both the characters were inherited independently.
17. What are the different ways in which individuals with a particular trait may increase in a population?
Answer: There are two ways in which individuals with a particular trait can increase in a population. They are:
1. Natural selection: Here the organisms which have a particular trait that enhances the survival rate or provides a survival benefit are selected naturally over others.
2. Genetic drift: This occurs in a small population where an accident or a chance event can change the frequency of genes, thus increasing a particular trait in a population, even if it provides no survival advantage.
18. Will geographical isolation be a major factor in the speciation of a self-pollinating plant species? Why or why not?
Answer: No, geographical isolation will not be a factor in speciation of self-pollinated plants. Self – pollinating plants are those which have both the male and the female reproductive organs in one [d1] plant themselves. Thus, they don’t require any other plant for reproduction. Hence, geographical isolation of such species will not change its genetic constitution.
19. Give an example of characteristics being used to determine how close two species are in evolutionary terms.
Answer: The relative closeness of two species can be determined using characters called the homologous characteristics. These are similar in different species, because of their inheritance from a common ancestor. For example, the limbs of human, frog, lizard and bird are similar in structure, though they perform different functions, suggesting their evolutionary relationship.
20. Will geographical isolation be a major factor in the speciation of an organism that reproduces asexually? Why or Why not?
Answer: No. Organisms which reproduce asexually, do not require mating or a partner for reproductive process. The reproduction process requires a single parent, that is the organism itself. Thus, geographical isolation does not affect the speciation process.
21. What factors could lead to the rise of a new species?
Answer: The factors that can lead to rise of new species are:
- Variations inherited from one generation to the other
- Natural selection
- Genetic drift
- Genetic mutations
- Geographical isolation
- Environmental factors acting on geographically isolated species.
- Reproductive isolation for a longer time.
22. What are four different ways in which individuals with a particular trait may increase in population?
Answer: The four ways in which individuals with a particular trait may increase in population are:
- Natural selection
- Genetic drift
- Geographical isolation
- Reproductive isolation or migration.
23. What are fossils? What do they tell us about the process of evolution?
Answer: Sometimes when an organism dies, it’s body, or a part of it ends up in an environment which does not let it decompose. Thus, the impressions of body structures of these organisms are preserved. These preserved traces of organisms are called fossils.
Fossil dating helps in determining the order of appearance of organisms in the evolutionary process. There are two ways of fossil dating. They are:
1. Digging of fossils from Earth
2. By detecting the ratio of different isotopes of same element in fossil material.
24. Distinguish between acquired and inherited traits giving one example of each. Why are traits acquired during the lifetime of an individual not inherited?
Answer: The changes in germ cells of reproductive tissue of a sexually reproducing organism, which can be passed on to the next generation are called inherited trait. For example: colour of the eye.
The changes in non -reproductive tissue of an organism, which cannot be passed on to the progeny, because they do not involve any change in the DNA of germ cells, are called acquired traits. For example: reduction in weight due to starvation. These are the traits acquired during lifetime of an individual and are not inherited because of lack of change in germ cells that participate in reproduction process.
25. Why are human beings who look so different from each other in terms of size, colour and look said to belongs to the same species?
Answer. Human beings though different in size, colour and looks, belong to the same species because:
- They have similarities in the DNA sequences
- They have descended from the same ancestor
- They can reproduce among themselves.