Acids, Bases and Salts Class 10 Important Questions and Answers
Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts covers each topic of the chapter. These questions aim at providing a better understanding of the chapter to the students and can be downloaded in PDF format. These important question bank help students in clearing their doubts so that they can score well in the exam.
While preparing for exams, students should practise these important questions of Class 10 Science to understand the concepts better. Solving important questions of Class 10 Science Chapter 2 will teach students time management skills and enhance their problem-solving skills. Also, students may come across a few of these questions in the board exam.
Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 – PDF
1. Which one of the following has a higher concentration of H+ ions? 1M HCl or 1M CH3COOH?
Answer: 1M HCl has a higher concentration of H+ ions because it is a comparatively strong acid whereas CH3COOH is a weak acid and contains lesser concentration of H+ ions.
2. Why CH3COOH is considered a weak acid whereas HCl is considered as a strong acid?
Answer: CH3COOH is considered a weak acid because when diluted it does not get completely dissociated to liberate the H+ ions i.e. CH3COOH upon dilution liberates a very small amount of H+ ions and considered a weak acid. HCl on the other hand upon dilution dissociates completely to generate the H+ ions and liberates a huge amount of H+ ions per unit volume and hence, considered a strong acid.
3. Which gas is evolved when dil. HCl reacts with metal bicarbonate? How is it recognized?
Answer: Carbon dioxide gas is evolved when dil. HCl reacts with metal bicarbonate.
It could be recognized by bringing a burning matchstick to the area where the gas is evolved. It would be observed the matchstick will stop burning.
4. What effect does an increase in concentration of H+ (aq) ions in a solution have on the pH of a solution?
Answer: The value of pH is inversely related with the concentration of hydrogen ions. Hence, when we increase the concentration of H+ (aq) ions in a solution the pH of the solution decreases.
5. Name the gas evolved when dil. HCl reacts with an active metal. How is it recognized?
Answer: When dil. HCl reacts with an active metal hydrogen gas is evolved.
It could be recognized by bringing a burning matchstick or candle towards the place from which the gas is being evolved, it would be observed that the matchstick would burn with a pop sound.
6. Why does tooth decay start when the pH of mouth is lower than 5.5?
Answer: When the pH of the mouth falls below 5.5 then our enamel which is composed of calcium phosphate gets corroded leading to tooth decay.
7. How is the pH of a solution of an acid influenced when it is diluted?
Answer: When a solution of an acid is diluted then, the concentration of H+ ions per unit volume in the solution reduces. Hence, any given sample of the solution now contains a lesser amount of H+ ions as it was present before dilution. Therefore, the pH of a solution of an acid upon dilution increases.
8. Fresh milk has a pH of 6. When it changes into curd (yoghurt), will its pH value increases or decreases? Why?
Answer: Fresh milk has a pH of 6. When it changes into curd its pH will decrease as curd contains lactic acid making the curd comparatively more acidic in nature than the fresh milk.
Q.9. Arrange the pH values of 0, 2, 4 and 6 in the increasing value of H+ (aq) ions conc.?
Answer: The smaller the pH the more the H+ (aq) ions concentration would be.
Hence, the pH values of 0, 2, 4 and 6 in the increasing value of H+ (aq) ions concentration is: 6 < 4 < 2 < 0
10. Why the flow of acid rainwater into a river make the survival of aquatic life in the river difficult?
Answer: The aquatic life survives in an optimum pH value. It is difficult for the aquatic life to maintain their metabolism in a pH value greater or less than the optimum pH value. When acid rainwater flows into a river it makes the river water acidic and disturbs the pH from its optimum value due to which the survival of aquatic life in the river becomes difficult.
11. Crystals of CuSO4 are heated in a test tube for some time.
(a) What is the colour of CuSO4 crystals:
(i) before heating, and
(ii) after heating?
(b) What is the source of liquid droplets seen on the inner upper side of the test tube during the heating process?
Answer: (a) (i) The colour of CuSO4 crystals before heating is blue.
(ii) after heating the colour of CuSO4 crystals changes to white.
(b) The source of liquid droplets seen on the inner upper side of the test tube during the heating process is the water of crystallization present in the formula unit of copper sulphate. These water of crystallization upon heating is removed from the formula unit and gets condensed on the inner upper side of the test tube during the heating process as liquid droplets.
12. (i) Name the products formed when NaHCO3 is heated.
(ii) Write the chemical equation for the reaction involved in the above.
Answer: (i) The products formed when NaHCO3 is heated are sodium carbonate water and carbon dioxide.
(ii) The chemical equation for the reaction involved above is:

13. Write the name and chemical formula of the calcium compound used for disinfecting drinking water. How is this compound manufactured?
Answer: The name and chemical formula of the calcium compound used for disinfecting drinking water is:
Chemical name – Calcium oxychloride
Formula – CaOCl2
This compound is manufactured by the action of chlorine on dry slaked lime as per the following reaction:
Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H2O
14. Show the decomposition of gypsum to P.O.P. and back interconversion of P.O.P. of gypsum.
Answer: The decomposition of gypsum to Plaster of Paris is as follows:
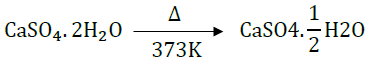
Plaster of Paris is prepared by decomposing gypsum at 373K.
Interconversion of Plaster of Paris into gypsum is as follows:
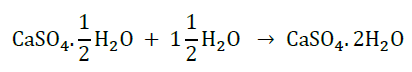
15. What happens when:
(a) CO2 is passed through lime water in a limited quantity?
(b) CO2 is passed through lime water in excess?
Answer: (a) When CO2 is passed through lime water in a limited quantity than calcium carbonate gets precipitated as a white colour mass at the bottom of the test tube according to the following reaction:
Ca (OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O
(b) When CO2 is passed through lime water in excess then the white precipitate initially formed gets dissolved forming Ca(HCO3)2 which is soluble in water as per the following reaction:
CaCO3 + H2O + CO2 → Ca (HCO3)2
16. Give a reason to explain why:
(a) bleaching powder smell strongly of chlorine?
(b) bleaching powder does not dissolve completely in water?
Answer: (a) Bleaching powder is produced by the action of chlorine on dry slaked lime according to the following reaction:
Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H2O
Hence, bleaching powder smell strongly of chlorine.
(b) Bleaching powder does not dissolve completely in water because bleaching powder is actually a quite complex molecule. It contains various other heavy calcium salts in it like calcium chloride, calcium hydroxide and calcium hypochlorite. These salts are insoluble in water. Hence, bleaching powder does not dissolve completely in water.
17. What is the chemical formula for washing soda? How can it be obtained from baking soda? Describe two applications of washing soda.
Answer: The chemical formula for washing soda is – Na2CO3.10H2O
It is prepared by heating baking soda and then recrystallizing the product so obtained.
The equations related to the above reaction are:

Two applications of washing soda are:
- It is used in glass, soap and paper industries
- It is used for removing permanent hardness of water.
18. What is the difference between litmus solution indicator and universal indicator solution? How synthetic indicators differ from natural indicators?
Answer: Litmus solution indicator just shows us whether the given sample is acidic or basic and tells us nothing about the strength of the acid or the base. Blue litmus solution turns red under acidic conditions; red litmus solution turns blue under basic /alkaline conditions.
On the other hand, universal indicator solution tells us or depicts through its colour exactly how much strong an acid or a base is. It has different colours as reference for different pH values from 0 to 14 indicating the strength of the acid or the base.
Natural indicators- The indicators which are prepared from natural substances are known as natural indicator.
Example – litmus, turmeric indicator.
Synthetic indicators – The artificial indicators which are prepared in the lab are known as synthetic indicators.
Example – Phenolphthalein, methyl orange etc.
19. What happens when:
(a) zinc reacts with NaOH
(b) zinc reacts with HCl?
Answer: (a) When zinc reacts with NaOH the following reaction takes place: –
2NaOH + Zn → Na2ZnO2 + H2
Hydrogen gas is evolved with the formation of the corresponding salt.
(b) When zinc reacts with HCl the following reaction takes place: –
2HCl + Zn → ZnCl2 + H2
Hydrogen gas is evolved with the formation of the corresponding salt.
Q.20. Give two characteristics each of acids and bases.
Answer: Two characteristics of acids:
- Acids are sour in taste.
- They produce H+ ions upon dilution.
Two characteristics of bases:
- Bases are bitter in taste.
- They produce OH- ions upon dilution.
21. Explain chlor-alkali process. Why is it called so?
Answer: When electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of sodium chloride, it decomposes to form sodium hydroxide. This process is called chlor-alkali process.
It is called so because the products formed in the reaction are chlorine and sodium hydroxide. Here chlor stands for chlorine and alkali is for sodium hydroxide.
22. Give reason why:
(a) water should not be added to concentrated acid?
(b) antacids are required when there is pain or irritation in the stomach?
(c) Baking soda should be rubbed on bee-stung area?
Answer: (a) Water should not be added to concentrated acid because the process of dissolving an acid or a base in water is a highly exothermic one. If water is added to an acid then the heat generated may cause the acid to splash out and cause burns.
(b) Pain or irritation is caused in our stomach when there is production of an excess amount of acid in our body. Antacids are basic in nature. Hence antacids are required when there is pain or irritation in the stomach to neutralize the effect of the excess acid.
(c) Bee-stung injects acid in our body. Baking soda is a base. Hence, baking soda should be rubbed on bee-stung area to neutralize the effect of the acid.
23. What is meant by water of crystallisation? Name four such salts which contain water of crystallisation in them. Why P.O.P. is written as CaSO4. ½H2O?
Answer: Water of crystallization is the fixed number of water molecules present in one formula unit of a substance
Four salts which contain water of crystallization are – copper sulphate, gypsum, Plaster of Paris, washing soda.
P.O.P. is written as CaSO4. ½ H2O because two formula unit of CaSO4 shares one molecule of water.
24. Why NaHCO3 is used in soda-acid fire extinguisher as well as for making baking powder.
Answer: When NaHCO3 is heated or mixed with water a reaction takes place which leads to the evolution of carbon dioxide gas. Now carbon dioxide extinguishes fire very well hence, it is used in soda-acid fire extinguisher and also the carbon dioxide produced during the reaction causes the bread or cake to rise making them soft and spongy. Hence, NaHCO3 is used for making baking powder.
25. Give reason why:
(a) tartaric acid is added while making banking powder?
(b) bleaching powder is used for disinfecting drinking water?
(c) strong acid and concentrated acid do not mean the same thing?
Answer: (a) While making baking powder tartaric acid id being added to it because when this mixture is heated or mixed with water carbon dioxide gas is evolved which causes the bread or cake to rise making them spongy and soft.
(b) Bleaching powder is used for disinfecting drinking water because bleaching powder is an oxidizing agent and helps in removing or killing the germs.
(c) Strong acid means those acids which gives a very high H+ ion concentration upon dilution or those which are able to generate a greater volume of H+ ions per unit quantity whereas concentrated acid means how many moles of the acid is present in a given quantity of a solvent. Higher concentration means greater amount of the acid per unit of the solvent.