Chemical Reaction and Equations Class 10 Important Questions and Answers
Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reaction and Equations covers each topic of the chapter. These questions aim at providing a better understanding of the chapter to the students and can be downloaded in PDF format. These important question bank help students in clearing their doubts so that they can score well in the exam.
While preparing for exams, students should practise these important questions of Class 10 Science to understand the concepts better. Solving important questions of Class 10 Science Chapter 1 will teach students time management skills and enhance their problem-solving skills. Also, students may come across a few of these questions in the board exam.
Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 – PDF
1. What causes rancidity? Name an antioxidant which prevents rancidity.
Answer: When fats and oils are left open, they get oxidized in the presence of air, their smell and taste change. This means the oxidation is the main cause for rancidity in fats and oil. The substances which prevent oxidation of the food items are called antioxidants.
Example: Nitrogen is an inert gas and does not oxidize the food, thus is used as antioxidants by chips manufactures.
2. Balance the equation: S + HNO3 → H2SO4 + NO2 + H2O
Answer: Balanced equation: S + 6HNO3→ H2SO4 + 6NO2 + 2H2O
3. In electrolysis of water, why is the volume of gas collected over one electrode double that of gas collected over the other electrode?
Answer: In the electrolysis of water, the gas collected at cathode is hydrogen and the gas collected at anode is oxygen. The gas which is collected in double amount is hydrogen. This is because water contains two molecules as compared to one molecule of oxygen.
The reaction that takes place in the formation of water from H2 and O2 is:
2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
4. Why respiration and decomposition processes are considered to be an exothermic process?
Answer: Respiration and decomposition processes are exothermic process because:
- We all get energy from the food we eat.
- During digestion, food is broken down into simpler substances.
- For example, Carbohydrates (rice, potatoes, bread) are broken down to form glucose.
- This glucose combines with oxygen and provides energy to the whole body.
5. Identify the substance oxidised and reduced in the chemical reaction: 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
Answer: O2 is an oxidizing agent and Mg is reducing agent
2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
In the given reaction, O2 is reduced by losing oxygen atoms. Thus, O2 is an oxidizing agent as it undergoes reduction.
Mg is oxidized by gaining oxygen atoms. Thus, Mg is a reducing agent as it undergoes oxidation.
6. Why potato chips manufacturers fill the packet of chips with nitrogen gas?
Answer: Potato chips manufacturers fill the packet of chips with nitrogen gas to prevent the chips from getting oxidized. If the oxidation takes place, the chips can become rancid and their smell and taste will change. Hence, to prevent oxidation, the packet of chips are filled with nitrogen gas. Nitrogen gas is an antioxidant.
7. Identify the type of reaction:
Fe + CuSO4(aq) → FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
Answer: The type of reaction is displacement reaction. In the given reaction the iron metal being more reactive than copper displaces it, and forms a new compound that is FeSO4
8. Balance the given chemical equation:
Al(s) + CuCl2(aq) → AlCl3(aq) + Cu(s)
Answer: Balanced equation: 2Al + 3CuCl2→ 2AlCl3 + 3Cu
9. What happens chemically when quicklime is added to water?
Answer: When quicklime (calcium oxide- CaO) is added to water, it reacts vigorously with water to produce slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) and releases a large amount of heat.
The reaction that takes place is:
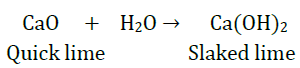
The above reaction is an example of combination reaction in which calcium oxide and water combined together to form a single product, calcium hydroxide.
10. On adding dilute HCl to CuO powder, the solution formed is blue green. Predict the new compound formed which imparts a blue-green colour to the solution.
Answer: When HCl is diluted with copper oxide, the following reaction takes place:
HCl + CuO → CuCl2 + H2O
The new compound formed is copper chloride (CuCl2) which imparts a blue-green colour to the solution. The above reaction is a type of double displacement reaction.
11. What happens when:
(a) Copper powder is heated in a china dish?
(b) Hydrogen gas is passed over hot copper (II) oxide?
Answer: (a) When copper powder is heated in the presence of air (oxygen), copper reacts with oxygen to form copper oxide. The copper oxide formed is black in colour. The black colour is formed due to the oxidation of copper takes place.
The chemical equation of the reaction that takes place is given below:
2Cu + O2→ 2CuO
(b) When hydrogen gas is passed over hot copper oxide, the black coating on the surface turns brown as the reverse reaction takes place and copper is obtained.
The reaction that takes place is:
CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O
12. A student has found black coating on his silver coins and green coating on his copper coins. Which chemical phenomenon is responsible for this? Write chemical name of these coatings.
Answer: The chemical phenomenon which is responsible is corrosion.
When a metal is attacked by substances around it such as moisture, acids, etc. it is said to corrode and this process is called corrosion.
After corrosion, the colour of:
Silver changes to → black
Copper changes to → green
Hence, the chemical name of coatings are silver coating and copper coating.
13. Give differences between Oxidation and Reduction.
Answer: Differences between oxidation and reduction are:
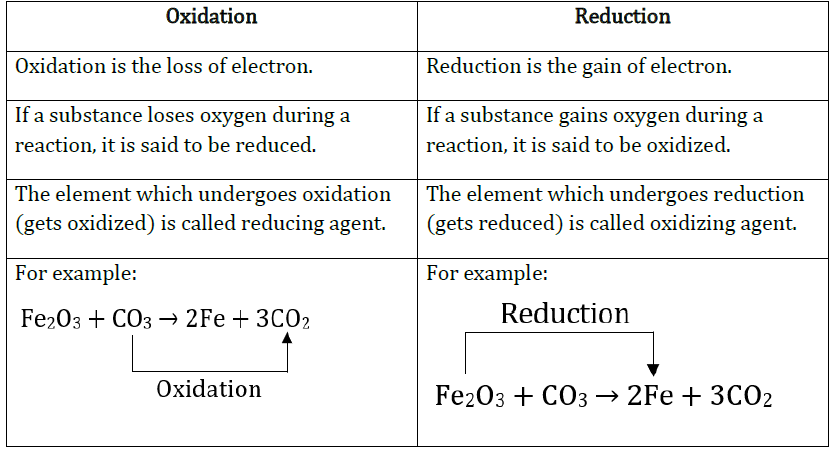
14. How combination reaction differs from decomposition reaction?
Answer: Differences between combination reaction and decomposition reaction are:
| Combination Reaction | Decomposition Reaction |
| When two or more reactants combine together to a single compound, the reaction is call combination reaction. | The reaction in which a single reactant breaks down to give simpler products is called decomposition reaction. |
15. Differentiate between displacement and double displacement reactions.
Answer: Difference between displacement and double displacement reactions:
| Displacement Reaction | Double Displacement Reaction |
| Displacement reaction is a reaction in which one element displaces the other element from its compound and takes its place therein. | Those reactions in which two compounds react by an exchange of ions to form two new compounds are called double displacement reactions. |
| A displacement reaction is represented by the general equation. A + BC → AC + B | A double displacement reaction is represented by the general equation. AB + CD → AD + CB |
| For Example: Fe + CuSO4 → FeSO4 + Cu | For Example: Fe2O3 + 6HCl → 2FeCl3 + 3H2O |
16. What is observed when:
(i) Potassium iodide is added to aqueous lead nitrate?
(ii) Identify the type of reaction.
(iii) Give a balanced chemical equation for this.
Answer: (i) When potassium iodide is added to aqueous lead nitrate, it forms potassium nitrate and a precipitate of lead iodide which is yellow in colour.
The reaction that takes place is:
Pb(NO3)2 + 2KI → 2PbI + 2KNO3
Note: The insoluble substance formed is known as precipitate. Precipitate settles down at the bottom of the test tube.
(ii) The type of reaction is double displacement reaction or precipitation reaction. Any reaction that produces a produces a precipitate can be called a precipitation reaction.
(iii) The balanced chemical equation is:
Pb(NO3)2 + 2KI → 2PbI + 2KNO3
17. Define oxidizing and reducing agents by giving suitable example.
Answer: Oxidizing agent: An oxidizing agent is an element that gains electrons. Since the oxidizing agent means to gain electrons; it is said to have been reduced.
The element which undergoes reduction (gets reduced) is called oxidizing agent.
For example: 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
In the given reaction, O2 is reduced by losing oxygen atoms. Thus, O2 is an oxidizing agent as it undergoes reduction.
Reducing agent: A reducing agent is an element that loses electrons. The reducing agent means to lose electrons; it is said to have been oxidized.
The element which undergoes oxidation (gets oxidized) is called reducing agent.
For example: 4NH3 + 5O2→ 4NO + 6H2O
In the given reaction, nitrogen is oxidized to NO by gaining oxygen atom. Thus, NH3 is reducing agent as it undergoes oxidation.
18. What is meant by rancidity? How it can be prevented?
Answer: When fats and oils are oxidized in the presence of air, they become rancid and their smell and taste change. This phenomenon is called rancidity. Rancidity can be prevented using antioxidants:
Using antioxidants- substances which prevent oxidation are called antioxidants. They are added to foods containing fats and oil.
For example: Nitrogen gas is filled in the packets of chips to prevent them from oxidation.
19. Give reason why:
(a) Magnesium ribbon should be cleaned before burning at air.
(b) Iron should be protected from moist air.
Answer: (a) Magnesium ribbon should be cleaned before burning at air because:
- Magnesium is a very reactive metal.
- When it is stored, it forms a layer of magnesium oxide (MgO) by reacting with oxygen.
- This layer of MgO stops the further reaction of magnesium with oxygen.
- Thus, magnesium ribbon should be cleaned to before burning to air to remove this layer
(b) Iron should be protected from the moist air because:
- When iron (a metal) is attacked by moist air (moisture), it is said to corrode.
- This process is called corrosion or rusting of iron.
- Rusting of iron causes damage to car bodies, bridges, iron railings to all objects made of iron.
- Every year a big amount of money is spent to replace damaged iron.
- Hence, we should protect iron from moist air.
20. What happens when:
(i) Lead nitrate is heated
(ii) crystals of FeSO4 are heated?
Answer: (i) When lead nitrate [Pb(NO3)2] is heated, it forms lead oxide. The emission of brown fumes is also observed. These brown fumes are of nitrogen dioxide (NO2).
The reaction that takes place is:
Pb(NO3)2 + heat → 2PbO + 4NO2 + O2
The above reaction is an example of decomposition reaction in which single reactant breaks down to give simpler products.
(ii) When green crystals of ferrous sulphate [FeSO4] are heated, the crystals lose water and the colour of the crystals changes. It then decomposes to ferric oxide [Fe2O3], sulphur dioxide, and Sulphur dioxide.
The reaction that takes place is:
FeSO4 + heat → Fe2O3 + SO2 + SO3
The above reaction is also an example of decomposition reaction.
21. Give two examples each of:
A. Double displacement reactions.
Answer: The reaction in which there is an exchange of ions between the reactant takes place is called double displacement reaction.
For examples:
Na2SO4 + BaCl2→ BaSO4 + 2NaCl
AgNO3 + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO3
B. Combination reactions.
Answer: Combination reaction is a reaction in which two or more reactants combined together to form a single product.
For examples: When nitrogen gas is treated with hydrogen gas in the presence of a catalyst at 773K to form ammonia gas. The following reaction takes place:
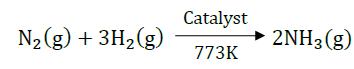
Formation of water from H2 and O2:
2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
22. Differentiate between exothermic and endothermic reactions by giving one example of each.
Answer:
| Exothermic Reactions | Endothermic Reactions |
| Reaction in which heat is released along with the formation of products are called exothermic reactions. | Reaction in which heat energy is absorbed is known as endothermic reactions. |
| Products have less energy than reactants. | Products have more energy than reactants. |
| Example: CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2 + heat | Example: 2AgBr + Sunlight → 2Ag + Br2 |
23. Give reason why:
A) Na acts as a reducing agent while chlorine acts as an oxidizing agent in reaction:
2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2NaCl(s)
Answer: 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) → 2NaCl(s)
In the above reaction, sodium (Na) loses electrons and produces Na+ Ions and thus Na acts as a reducing agent as it undergoes oxidation. On the other hand, chlorine gains electrons and forms chloride ions and thus chlorine acts as an oxidizing agent as it undergoes reduction.
B) White coloured AgCl turns grey when kept in sunlight.
Answer: White silver chloride turns grey in sunlight due to the decomposition of silver chloride into silver and chlorine by light.
The reaction that takes place is:
2AgCl + sunlight → 2Ag + Cl2
The above reaction is an endothermic reaction.
C) Colour of the solution changes when iron nail is dipped in copper sulphate solution.
Answer: Iron nails when left dipped in blue copper sulphate solution become brownish in colour and the blue colour of copper sulphate fades away.
Fe + CuSO4 → FeSO4 + Cu
The above reaction is a type of displacement reaction in which one element displaces another element from its compound and takes its place therein. In the reaction, Fe replaces Cu and form a new compound.