NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Work and Energy
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science (physics) Chapter 11 Work and Energy are given below. In these solutions, we have answered all the intext and exercise questions provided in NCERT class 9 science textbook. Class 9 NCERT Solutions Science Chapter 11 provided in this article are strictly based on the CBSE syllabus and curriculum. Students can easily download these solutions in PDF format for free from our app.
Class 9 Science Chapter 11 Textbook Questions and Answers
INTEXT QUESTIONS
PAGE NO. 148
Question 1: A force of 7 N acts on an object. The displacement is, say 8 m, in the direction of the force. Let us take it that the force acts on the object through the displacement. What is the work done in this case?
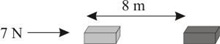
Answer: When a force F acts on an object to displace it through a distance S in its direction, then the work done W on the body by the force is given by:
Work done = Force × Displacement
⇒ W = F × S
Given,
F = 7 N
S = 8 m
Therefore, work done, W = 7 × 8
= 56 Nm
= 56 J
PAGE NO- 149
Question 1: When do we say that work is done?
Answer: Work is completed whenever the given conditions are satisfied:
(i) A force acts on the body.
(ii) There’s a displacement of the body caused by the applied force on the direction of the applied force.
Question 2: Write an expression for the work done when a force is acting on an object in the direction of its displacement.
Answer: When a force F displaces a body through a distance S in the direction of the applied force, then the work done W on the body is given by the expression:
Work done = Force × Displacement
⇒ W = F × s
Question 3: Define 1 J of work.
Answer: 1 J is the amount of work done by a force of 1 N on an object that displaces it through a distance of 1 m in the direction of the applied force.
Question 4: A pair of bullocks exerts a force of 140 N on a plough. The field being ploughed is 15 m long. How much work is done in ploughing the length of the field?
Answer: Work done by the bullocks is given by the expression:
Work done = Force × Displacement
⇒ W = F × s
Where,
Applied force, F = 140 N
Displacement, s = 15 m
∴ W = 140 × 15
= 2100 J
Hence, 2100 J of work is done in ploughing the length of the field.
PAGE NO- 152
Question 1: What is the kinetic energy of an object?
Answer: Kinetic energy is the energy possessed by a body by the virtue of its motion. Every moving object possesses kinetic energy. A body uses kinetic energy to do work. Kinetic energy of hammer is used in driving a nail into a log of wood, kinetic energy of air is used to run wind mills, etc.
Question 2: Write an expression for the kinetic energy of an object.
Answer: If a body mass m is moving with a velocity v, then its kinetic energy is given by the expression,
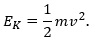
Its SI unit is Joule (J).
Question 3: The kinetic energy of an object of mass, m moving with a velocity of 5 m s−1 is 25 J. What will be its kinetic energy when its velocity is doubled? What will be its kinetic energy when its velocity is increased three times?

Where,
m = Mass of object
v = Velocity of the object in ms−1
Given that kinetic energy, EK = 25J
(i) If the velocity of an object is doubled, then v = 5 × 2 = 10 ms−1.
Therefore, its kinetic energy becomes 4 times its original value, because it is proportional to the square of the velocity.
Hence, kinetic energy = 25 × 4 = 100 J.
(ii) If velocity is increased three times, then its kinetic energy becomes 9 times its original value, because it is proportional to the square of the velocity. Hence, kinetic energy = 25 × 9 = 225 J.
PAGE NO-156
Question 1: What is power?
Answer: Power is the rate of doing work or the rate of transfer of energy. If W is the amount of work done in time t, then power is given by the expression,
Power = Work/Time
⇒ Power = Energy/Time
⇒ P = W/T
It is expressed in watt (W).
Question 2: Define 1 watt of power:
Answer: A body is said to have power of 1 watt if it does work at the rate of 1 joule in 1 s, i.e., 1W = 1J/1s
Question 3: A lamp consumes 1000 J of electrical energy in 10 s. What is its power?
Answer: Power is given by the expression,
Power = Work done /Time
Work done = Energy consumed by the lamp = 1000 J
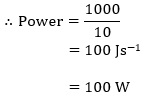
Question 4: Define average power.
Answer: A body can do different amount of work in different time intervals. Hence, it is better to find average power. Average power is obtained by dividing the total amount of work done in the total time taken to do this work.
Average Power =Total work done / Total time taken
EXERCISES
Question 1: Look at the activities listed below. Reason out whether or not work is done in the light of your understanding of the term ‘work’.
(a) Suma is swimming in a pond.
(b)A donkey is carrying a load on its back.
(c) A wind-mill is lifting water from a well.
(d) A green plant is carrying out photosynthesis.
(e) An engine is pulling a train.
(f) Food grains are getting dried in the sun.
(g) A sailboat is moving due to wind energy.
Answer: Work is done whenever the given two conditions are satisfied:
(i) A force acts on the body.
(ii) There is a displacement of the body by the application of force in or opposite to the direction of force.
(a) While swimming, Suma applies a force to push the water backwards. Therefore, Suma
swims in the forward direction caused by the forward reaction of water. Here, the force causes a displacement. Hence, work is done by Seema while swimming.
(b) While carrying a load, the donkey has to apply a force in the upward direction. But, displacement of the load is in the forward direction. Since, displacement is perpendicular to force, the work done is zero.
(c) A wind mill works against the gravitational force to lift water. Hence, work is done by the wind mill in lifting water from the well.
(d) In this case, there is no displacement of the leaves of the plant. Therefore, the work done is zero.
(e) An engine applies force to pull the train. This allows the train to move in the direction of force. Therefore, there is a displacement in the train in the same direction. Hence, work is done by the engine on the train.
(f) Food grains do not move in the presence of solar energy. Hence, the work done is zero during the process of food grains getting dried in the Sun.
(g)Wind energy applies a force on the sailboat to push it in the forward direction. Therefore, there is a displacement in the boat in the direction of force. Hence, work is done by wind on the boat.
Question 2: An object thrown at a certain angle to the ground moves in a curved path and falls back to the ground. The initial and the final points of the path of the object lie on the same horizontal line. What is the work done by the force of gravity on the object?
Answer: Work done by the force of gravity on an object depends only on vertical displacement. Vertical displacement is given by the difference in the initial and final positions/heights of the object, which is zero.
Work done by gravity is given by the expression,
W = mgh
Where,
h = Vertical displacement = 0
∴ W = mg × 0 = 0 J
Therefore, the work done by gravity on the given object is zero joule.
Question 3: A battery lights a bulb. Describe the energy changes involved in the process.
Answer: Battery converts chemical energy into electrical energy. This electrical energy is further converted into light and heat energy.
Question 4: Certain force acting on a 20 kg mass changes its velocity from 5 m s–1 to 2 m s–1. Calculate the work done by the force.
Answer: Mass of the body = 20 kg
Initial velocity = 5 m/s
Final velocity = 2 m/s
We know that,
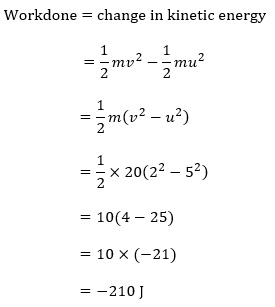
The negative sign indicates that the force is acting in the direction opposite to the motion of the object.
Question 5: A mass of 10 kg is at a point A on a table. It is moved to a point B. If the line joining A and B is horizontal, what is the work done on the object by the gravitational force? Explain your answer.
Answer: Work done by gravity depends solely on the vertical displacement of the body. It doesn’t rely on the trail of the body. Therefore, work done by gravity is given by the expression,
W= mgh
Where,
Vertical displacement, h = 0
∴ W= mg × 0 = 0
Therefore, the work done on the body by gravity is therefore zero.
Question 6: The potential energy of a freely falling object decreases progressively. Does this violate the law of conservation of energy? Why?
Answer: No. The process does not violate the law of conservation of energy. This is because when the body falls from a height, then its potential energy changes into kinetic energy progressively. A decrease in the potential energy is equal to an increase in the kinetic energy of the body. During the process, total mechanical energy of the body remains conserved. Therefore, the law of conservation of energy is not violated.
Question 7: What are the various energy transformations that occur when you are riding a bicycle?
Answer: While riding a bicycle, the muscular energy of the rider gets transferred into heat energy and kinetic energy of the bicycle. Heat energy heats the rider’s body. Kinetic energy provides a velocity to the bicycle. The transformation can be shown as: During the transformation, the total energy remains conserved.
Question 8: Does the transfer of energy take place when you push a huge rock with all your might and fail to move it? Where is the energy you spend going?
Answer: When we push the rock and fail to move it. Some of our energy is absorbed by the rock in the form of potential energy and the rest of our energy is goes to environment through our muscles and the surface between the rock and out hand.
Question 9: A certain household has consumed 250 units of energy during a month. How much energy is this in joules?
Answer: 1 unit of energy is equal to 1 kilowatt hour (kWh).
Energy consumed in one month = 250 unit
= 250 kWh
= 250 kW×h
= 250×1000W×3600s
= 900,000,000 J
= 9 × 108 J.
Question 10: An object of mass 40 kg is raised to a height of 5 m above the ground. What is its potential energy? If the object is allowed to fall, find its kinetic energy when it is half-way down.
Answer: We know that, potential energy = mgh
Where, m = 40 kg
g = 9.8 m/s2
h = 5 m
So, the potential energy = 40 × 9.8 × 5 J = 1960 J
According to law of conservation of energy, the total mechanical energy (Kinetic and potential energy) of an object remains constant.
Therefore, when the object is half-way down, its potential energy become half the original energy and remaining half converted into kinetic energy.
Hence, the kinetic energy = ½ (1960) J = 980 J
Question 11: What is the work done by the force of gravity on a satellite moving round the Earth? Justify your answer.
Answer: Work is done whenever the given two conditions are satisfied:
(i) A force acts on the body.
(ii) There is a displacement of the body by the application of force in or opposite to the direction of force.
If the direction of force is perpendicular to displacement, then the work done is zero. When a satellite moves around the Earth, then the direction of force of gravity on the satellite is perpendicular to its displacement. Hence, the work done on the satellite by the Earth is zero.
Question 12: Can there be displacement of an object in the absence of any force acting on it? Think. Discuss this question with your friends and teacher.
Answer: Yes, it is true. There may be displacement in the absence of force.
We know that,
F = ma,
In the absence of force,
F = 0, then ma = 0
If a = 0, the object is either at rest or in a state of uniform motion in a straight line. In case the object is moving in a straight line, there must be displacement. So, in the absence of force, there may be displacement in the object.
Question 13: A person holds a bundle of hay over his head for 30 minutes and gets tired. Has he done some work or not? Justify your answer.
Answer: Work is done whenever the given two conditions are satisfied:
(i) A force acts on the body.
(ii) There is a displacement of the body by the application of force in or opposite to the direction of force.
When a person holds a bundle of hay over his head, then there is no displacement in the bundle of hay. Although, force of gravity is acting on the bundle, the person is not applying any force on it. Hence, in the absence of force, work done by the person on the bundle is zero.
Question 14: An electric heater is rated 1500 W. How much energy does it use in 10 hours?
Answer: We know that, Energy = Power × time
Here, Power = 1500 W
Time = 10 hours = 10 × 60 × 60 seconds = 36000 seconds
Therefore,
The energy used by heater = Power × time
= 1500 × 36000 J
= 54000000 J
= 5.4 × 107 J
Question 15: Illustrate the law of conservation of energy by discussing the energy changes which occur when we draw a pendulum bob to one side and allow it to oscillate. Why does the bob eventually come to rest? What happens to its energy eventually? Is it a violation of the law of conservation of energy?
Answer: In the given pendulum, there are three cases of points to be discussed.
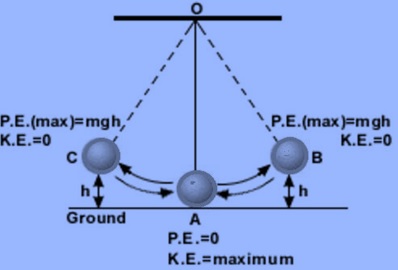
At the points B and C, the pendulum bob is at its maximum height, so its potential energy is maximum and kinetic energy is zero. In this way the total mechanical energy remains constant. At the point A, the pendulum bob is at its lowest point, total potential energy is converted into kinetic energy. Now the kinetic energy is maximum and potential energy is zero. Once again the total mechanical energy remains constant
Question 16: An object of mass, is moving with a constant velocity, . How much work should be done on the object in order to bring the object to rest?

Question 17: Calculate the work required to be done to stop a car of 1500 kg moving at a velocity of 60 km/h?

Question 18: In each of the following a force, F is acting on an object of mass, m. The direction of displacement is from west to east shown by the longer arrow. Observe the diagrams carefully and state whether the work done by the force is negative, positive or zero.
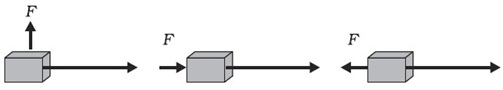
Answer: In the first case, the force and displacement are perpendicular to each other, so work done is zero.
In the second case, the force and displacement are in the same direction, so the work done is positive.
In the third case, the force and displacement are in the opposite direction, so the work done is negative.
Question 19: Soni says that the acceleration in an object could be zero even when several forces are acting on it. Do you agree with her? Why?
Answer: Acceleration in an object could be zero even when several forces are acting on it. This happens when all the forces cancel out each other i.e., the net force acting on the object is zero. For a uniformly moving object, the net force acting on the object is zero. Hence, the acceleration of the object is zero. Hence, Soni is right.
Question 20: Find the energy in kW h consumed in 10 hours by four devices of power 500 W each.
Answer: The power of four devices = 4 × 500 W = 2000 W
Time = 10 hours
Therefore, the energy consumed = power × time
= 2000 × 10 Wh
= 20000 Wh
= 20 kWh
= 20 units [1 unit = 1 kWh]
Question 21: A freely falling object eventually stops on reaching the ground. What happens to its kinetic energy?
Answer: When a freely falling body eventually stops on reaching the ground, its kinetic energy gets converted into heat energy (as the body and ground become warm due to collision), sound energy and into potential energy (due to change of shape or deformation).
Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 11 Work and Energy
CBSE Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 11 helps students to clear their doubts and to score good marks in the board exam. All the questions are solved by experts with a detailed explanation that will help students complete their assignments & homework. Having a good grasp over CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science will further help the students in their preparation for board exams and other competitive exams such as NTSE, Olympiad, etc.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 11 PDF
Below we have listed the topics discussed in NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 11. The list gives you a quick look at the different topics and subtopics of this chapter.
| Section in NCERT Book | Topics Discussed |
|---|---|
| 11.1 | Work |
| 11.2 | Energy |
| 11.2.2 | Kinetic Energy |
| 11.2.3 | Potential Energy |
| 11.3 | Rate of Doing Work |