NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science (biology) Chapter 6 Tissues are given below. In these solutions, we have answered all the intext and exercise questions provided in NCERT class 9 science textbook. Class 9 NCERT Solutions Science Chapter 6 provided in this article are strictly based on the CBSE syllabus and curriculum. Students can easily download these solutions in PDF format for free from our app.
Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Textbook Questions and Answers
INTEXT QUESTIONS
PAGE NO. 69
Question 1: What is a tissue?
Answer: Tissue is a group of cells that are similar in structure and are organised together to perform a specific task.
Question 2: What is the utility of tissues in multi-cellular organisms?
Answer: In multicellular organisms, the body system is based on the division of labour (like muscle cells form muscular tissue which helps in movement). It means the cells performing a specific function are grouped together to form a particular tissue. The different tissues are organized in a way to provide the highest efficiency in the functioning of the body.
PAGE NO. 74
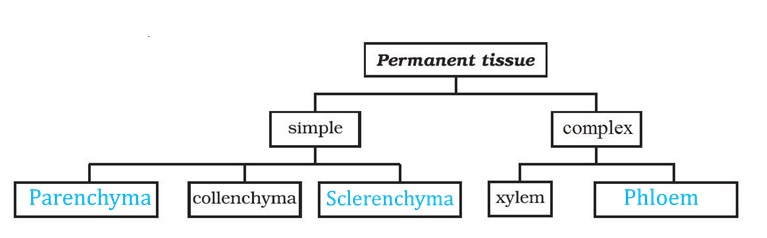
Question 1: Name types of simple tissues.
Answer: The types of simple tissues are as follows:
- Parenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
Question 2: Where is apical meristem found?
Answer: Apical meristem is present at the growing tips of stems and roots. Their main function is to initiate growth in new cells of seedlings, at the tip of roots, and shoots.
Question 3: Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
Answer: The husk of a coconut is made up of sclerenchyma tissue.
Question 4: What are the constituents of phloem?
Answer: Phloem is the food conducting tissue in plants. It is made up of four components:
- Sieve tubes
- Companion cells
- Phloem parenchyma
- Phloem fibres
PAGE NO. 77
Question 1: Name the tissue responsible for movement in our body.
Answer: The muscular tissue is responsible for movement in our body.
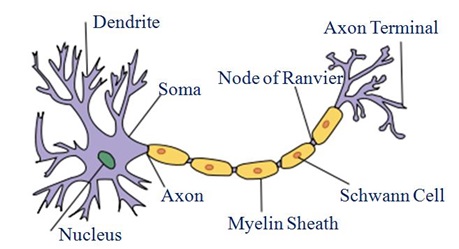
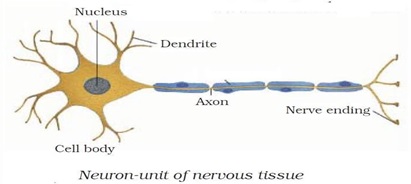
Question 2: What does a neuron look like?
Answer: A neuron consists of a cell body with a nucleus and cytoplasm, from which long thin hair like parts arise. Each neuron has a single long part called the axon, and many small, short branched parts called dendrite. An individual nerve cell is called neuron, it may be up to a metre long.
Question 3: Give three features of cardiac muscles.
Answer: Three features of cardiac muscles are:
Question 4: What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Answer: Functions of areolar tissue:
1. It fills the space inside the organs, thus acts as a packing tissue between the organs.
2. It supports many delicate organs in the body.
3. It plays role in repair of tissues.
EXERCISES
Question 1: Define the term ‘tissue’?
Answer: A tissue is defined as a cluster of cells which are similar in structure and work together to perform a particular function.
Question 2: How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
Answer: The following four types of elements make up xylem tissue:
- Tracheids.
- Vessels.
- Xylem parenchyma.
- Xylem fibres.
Question 3: How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
Answer: Simple tissues are made up of one type of cells which coordinate to perform a common function.
Complex tissues are made up of more than one type of cells. All these coordinate to perform a common function.
Or
| Simple tissue | Complex tissue |
| These tissues consist of only one type of cells. | These tissues are made up of more than one type of cells. |
| The cells are more or less similar in structure and perform similar functions. | Different types of cells perform different functions. For example, in the xylem tissue, tracheids help in water transport, whereas parenchyma stores food. |
| Three types of simple tissues in plants are parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma. | Two types of complex permanent tissues in plants are xylem and |
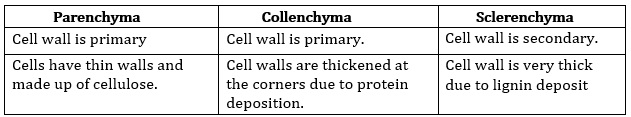
Question 4: Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma on the basis of their cell wall.
Answer: The differences between cell walls of parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma are given in the following table:
Question 5: What are the functions of Stomata?
Answer: Functions of Stomata are:
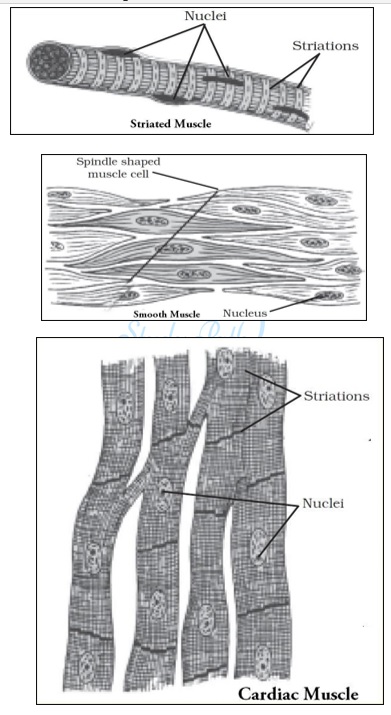
Question 6: Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle fibres.
Answer:
Question 7: What is the specific function of cardiac muscle?
Answer: Cardiac muscles facilitate contraction and relaxation of heart; which results in pumping action of the heart.
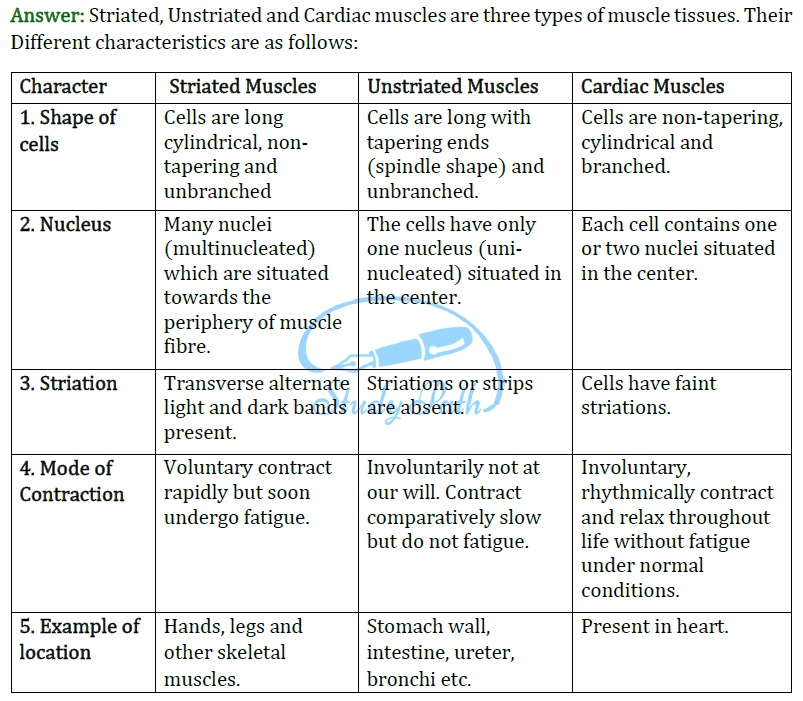
Question 8: Differentiate between striated, unstriated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site / location in the body.
Answer: Striated, Unstriated and Cardiac muscles are three types of muscle tissues. Their Different characteristics are as follows:
Question 9: Draw a labelled diagram of neuron.
Answer:
Question 10: Name the following:
(a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth.
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans.
(c) Tissue that transports food in plants.
(d) Tissue that stores fat in our body.
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix.
(f) Tissue present in the brain.
Answer: (a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth → Epithelial tissue
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans → Dense regular connective tissue (tendons)
(c) Tissue that transports food in plants → Phloem
(d) Tissue that stores fat in our body → Adipose tissue
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix → Blood
(f) Tissue present in the brain → Nervous tissue
Question 11: Identify the type of tissue in the following: Skin, bark of tree, bone, lining of kidney tubule, vascular bundle.
Answer: Skin: Stratified squamous epithelial tissue
Bark of tree: Simple permanent tissue
Bone: Connective tissue
Lining of kidney tubule: Cuboidal epithelial tissue
Vascular bundle: Complex permanent tissue
Question 12: Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
Answer: Parenchyma is a simple permanent tissue of angiospermic plants. It is present in cortex and pith of stem and roots. It is also present in mesophyll of leaves. When it contains chlorophyll, it is called Chlorenchyma, found in green leaves.
Question 13: What is the role of epidermis in plants?
Answer: The epidermis in plants forms an uninterrupted and continuous layer that has no intercellular spaces. It provides protection.
or
Epidermis is a protective tissue of angiospermic plants. It provides protections to underlying tissues. Epidermis forms outer covering of various plant organs such as roots, stem, leaves, and flowers and remains in direct contact with the environment. Any substance whether solid, liquid or gas can enter into the plant or move outside only after passing through this layer. Epidermis helps in absorption, secretion, gaseous exchange and transpiration. It helps in preventing the entry of pathogens.
Question 14: How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
Answer: The outer protective layer or bark of a tree is known as the cork. It is made up of dead cells. Therefore, it protects the plant against mechanical injury, temperature extremes, etc. It also prevents the loss of water by evaporation.
Question 15: Complete the table:
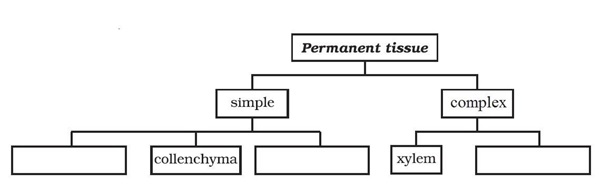
Answer:
Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 6 Tissues
CBSE Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 6 helps students to clear their doubts and to score good marks in the board exam. All the questions are solved by experts with a detailed explanation that will help students complete their assignments & homework. Having a good grasp over CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science will further help the students in their preparation for board exams and other competitive exams such as NTSE, Olympiad, etc.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 PDF
Below we have listed the topics discussed in NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6. The list gives you a quick look at the different topics and subtopics of this chapter.
| Section in NCERT Book | Topics Discussed |
|---|---|
| 6.2 | Plant Tissues |
| 6.3 | Animal Tissues |
| 6.3.1 | Epithelial Tissue |
| 6.3.2 | Connective Tissue |
| 6.3.3 | Muscle Tissue |
| 6.3.4 | Nervous Tissue |