NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Motion and Time
NCERT Solutions for CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Motion and Time are given below. These solutions help students to clear their doubts and to obtain good marks in final exam. Class 7 Science NCERT questions and answers provided in this article are strictly based on the CBSE syllabus and curriculum.
Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Motion and Time NCERT Solutions
Class 7 NCERT Solutions for Science Chapter 13 includes all the intext and exercise questions. All these questions are solved by experts with a detailed explanation that will help students complete their assignments and homework.
Exercises
Question 1: Classify the following as motion along a straight line, circular or oscillatory motion:
(i) Motion of your hands while running.
(ii) Motion of a horse pulling a cart on a straight road.
(iii) Motion of a child in a merry-go-round.
(iv) Motion of a child on a see-saw.
(v) Motion of the hammer of an electric bell.
(vi) Motion of a train on a straight bridge.
Answer: (i) Oscillatory motion
(ii) Linear motion
(iii) Circular motion
(iv) Oscillatory motion
(v) Oscillatory motion
(vi) Linear motion
Question 2: Which of the following are not correct?
(i) The basic unit of time is second.
(ii) Every object moves with a constant speed.
(iii) Distances between two cities are measured in kilometres.
(iv) The time period of a given pendulum is not constant.
(v) The speed of a train is expressed in m/h
Answer: Incorrect statements are: (ii), (iv), (v)
Question 3: A simple pendulum takes 32s to complete 20 oscillations, what is the time period of the pendulum?

Question 4: The distance between two stations is 240 km. A train takes 4 hours to cover this distance. Calculate the speed of the train.

Question 5: The odometer of a car reads 57321.0 km when the clock shows the time 08:30 AM. What is the distance moved by the car, if at 08:50 AM, the odometer reading has changed to 57336.0 km? Calculate the speed of the car in km/min during this time. Express the speed in km/h also.
Answer: Initial reading of the odometer of the car = 57321.0 km
Final reading of the odometer of the car = 57336.0 km
Distance covered by the car = Final reading of the odometer of the car − Initial reading of the odometer of the car
= 57336.0 − 57321.0
= 15 km
The given car starts at 8:30 a.m. and stops at 8:50 a.m.
Therefore, time taken by the car to cover the distance is (8:50 − 8:30) min = 20 min

Question 6: Salma takes 15 minutes from her house to reach her school on a bicycle. If the bicycle has a speed of 2 m/s, calculate the distance between her house and the school.
Answer: Time taken by Salma to reach her school by bicycle = 15 mins = 15 × 60 = 90s
Speed of Salma’s bicycle= 2m/s

Question 7: Show the shape of the distance-time graph for the motion in the following cases:
(i) A car moving with a constant speed.
(ii) A car parked on a side road.
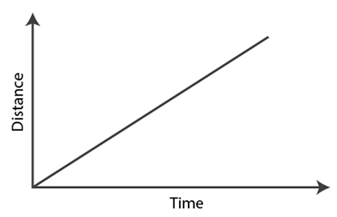
Answer: (i) A car moving with a constant speed covers equal distance in equal intervals of time. Such motion of car is represented in the given distance-time graph.
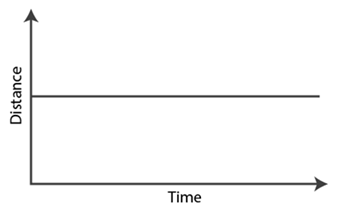
(ii) The distance-time graph of a car parked on a road side is such that with the increase in time, there is no change in distance, as shown in the given figure.
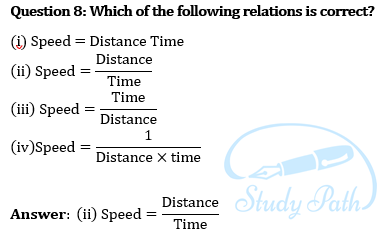
Question 9. The basic unit of speed is:
(i) km/min
(ii) m/min
(iii) km/h
(iv) m/s
Answer: (iv) m/s
The basic unit of distance is metre (m).
The basic unit of time is second (s).
Speed = Distance/Time
Therefore, the basic unit of speed is m/s.
Q.10.A car moves with a speed of 40 km/h for 15 minutes and then with a speed of 60 km/h for the next 15 minutes. The total distance covered by the car is:
(i) 100 km
(ii) 25 km
(iii) 15 km
(iv) 10 km
Answer: (ii) 25 km


Question 11. Suppose the two photographs, shown in fig. 13.1 and fig. 13.2 of NCERT had been taken at an interval of 10 seconds. If a distance of 100 metres is shown by 1 cm in these photographs, calculate the speed of the blue car.
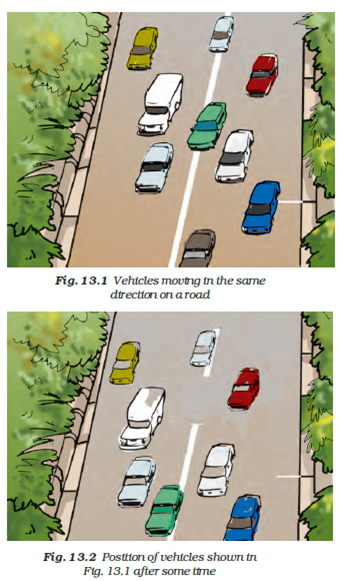
Answer: The distance covered by the blue car (as evident from the photograph) from one horizontal white strip to another, which is measured by scale is 1.2 cm.
It is given that 1 cm is equivalent to 100 m.
Therefore, 1.2 cm is equivalent to 120 m.
Distance travelled by the car = 120 m
Time taken to cover this distance = Time interval between the two photographs = 10 s

12. Fig. 13.15 shows the distance-time graph for the motion of two vehicles A and B. Which one of them is moving faster?
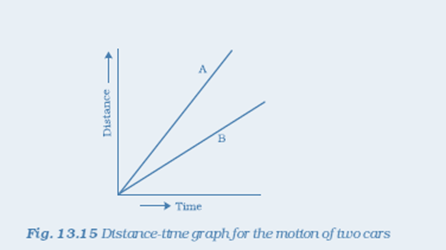
Solution: Vehicle A is moving faster than vehicle B.
Reason: Speed is given by the relation

This relation shows that speed of a vehicle is greater if it covers maximum distance in a given interval of time. To compare the distance, draw a line perpendicular to the time-axis, as shown in the following distance-time graph.
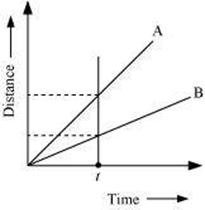
From the graph, it is evident that for a given time t, the distance covered by vehicle A is more than vehicle B. Hence, vehicle A is moving faster than vehicle B.
13. Which of the following distance-time graphs shows a truck moving with speed which is not constant?
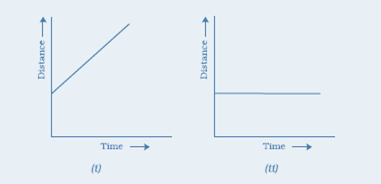
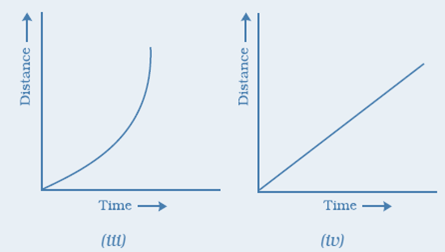
Answer: (iii)
Reason: In a distance-time graph, the constant speed of a truck will be represented by a straight line.
In a distance-time graph, a straight line parallel to the time axis indicates that the truck is not moving.
A curved line on the distance-time graph indicates that the truck is moving with a speed which is not constant.