NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Geography Chapter 2 Inside Our Earth
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Geography Chapter 2 Inside Our Earth contains the answers to the exercises given in the NCERT History book. These solutions are easy and accurate that help you to answer the questions asked in the examinations. NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Geography Chapter 2 are prepared by our subject experts in very easy language. Practice these solutions regularly to ensure excellent marks in the exams.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Geography Chapter 2
Question 1: Answer the following questions.
(i) What are the three layers of the earth?
Solution: the three layers of earth are:
- Crust
- Mantle
- Core
(ii) What is a rock?
Solution: Any natural mass of mineral matter that makes up the earth’s crust is called a rock. The earth’s crust is made up of various types of rocks of different texture, size and colour.
(iii) Name three types of rocks.
Solution: Three types of rocks are:
- Igneous Rocks
- Sedimentary Rocks
- Metamorphic Rocks
(iv) How are extrusive and intrusive rocks formed?
Solution: The molten lava comes out of volcanoes, reaches the earth’s surface and cools down rapidly to become a solid piece of rock. This is how extrusive rocks are formed. For example – basalt.
When the molten lava solidifies deep inside the earth’s crust, the rocks so formed are called intrusive rocks. For example – granite.
(v) What do you mean by a rock cycle?
Solution: The process of transformation of rocks from one type to another, due to changes in certain conditions in a cyclic manner, is called a rock cycle.
(vi) What are the uses of rocks?
Solution: Some of the uses of rocks are as follows:
(a) For building roads, houses and buildings
(b) For making jewellery
(c) For cutting and drilling purposes
(vii) What are metamorphic rocks?
Solution: Metamorphic rocks are the rocks that get formed under great heat and pressure. Igneous and sedimentary rocks, when subjected to heat and pressure, get transformed into metamorphic rocks.
Question 2: Tick the correct answer.
(i) The rock which is made up of molten magma is
(a) Igneous
(b) Sedimentary
(c) Metamorphic
Solution: (a) Igneous
(ii) The innermost layer of the earth is
(a) Crust
(b) Core
(c) Mantle
Solution: (b) Core
(iii) Gold, petroleum and coal are examples of
(a) Rocks
(b) Minerals
(c) Fossils
Solution: (b) Minerals
(iv) Rocks which contain fossils are
(a) Sedimentary rocks
(b) Metamorphic rocks
(c) Igneous rocks
Solution: (a) Sedimentary rocks
(v) The thinnest layer of the earth is
(a) Crust
(b) Mantle
(c) Core
Answer: (a) Crust
Question 3: Match the following.
| (i) Core | (a) Earth’s surface |
| (ii) Minerals | (b) Used for roads and buildings |
| (iii) Rocks | (c) Made of silicon and alumina |
| (iv) Clay | (d) Has definite chemical composition |
| (v) Sial | (e) Innermost layer |
| (f) Changes into slate | |
| (g) Process of transformation of the rock Rocks |
Solution:
| (i) Core | (e) Innermost layer |
| (ii) Minerals | (d) Has definite chemical composition |
| (iii) Rocks | (b) Used for roads and buildings |
| (iv) Clay | (f) Changes into slate |
| (v) Sial | (c) Made of silicon and alumina |
Question 4: Give reasons.
(i) We cannot go to the centre of the earth.
Solution: We cannot go to the centre of the earth because the temperature and pressure at the centre of the earth are very high and not just human beings, but even rocks melt at the centre of the Earth.
(ii) Sedimentary rocks are formed from sediments.
Solution: The small fragments of rock that hit each other and break to reach the ground are called sediments. These sediments are transported and deposited by wind, water, etc. and then are compressed and hardened to form a layer of rocks called the sedimentary rocks. This shows that sedimentary rocks are formed from sediments.
(iii) Limestone is changed into marble
Solution: Limestone is an example of a sedimentary rock. When it is subjected to conditions of extreme heat and pressure, it gets converted into marble, which is a metamorphic rock.
Extra Questions
Very Short Answer Questions
1. What are the main constituents of the continental mass?
Answer: The main mineral constituents of the continental mass are silica and alumina. It is thus called sial (si–silica and al–alumina).
2. What are the main constituents of the oceanic crust?
Answer: The oceanic crust mainly consists of silica and magnesium. It is therefore called sima (si–silica and ma–magnesium).
3. What is mantle?
Answer: Just below the crust is the mantle, which extends up to a depth of 2,900 km below the crust.
4. What are igneous rocks?
Answer: When the molten magma cools down, it becomes solid. Rocks formed over here are called igneous rocks. They are also called primary rocks.
5. What are sediments?
Answer: Rocks roll down, crack and hit each other and are broken into small fragments. These smaller particles are called sediments.
Short Answer Questions
1. What is the crust?
Answer: (i) The uppermost layer over the earth’s surface is called the crust.
(ii) It is the thinnest of all the layers.
(iii) It is about 35 km on the continental masses and only 5 km on the ocean floors.
2. What is core?
Answer: The innermost layer of the earth is core with a radius of 3,500 km. It is mainly made of nickel and iron and is called nife. (ni–nickel and fe–ferrum, i.e., iron). The central core has a very high temperature and pressure.
3. What are minerals?
Answer: The naturally occurring substances which have certain physical properties and definite chemical composition are called minerals, e.g., uranium, gold, coal, natural gas.
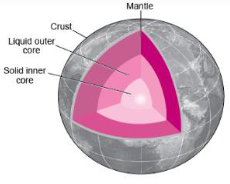
4. Draw a structure of the interior of the earth.
Answer:
5. Into how many types are igneous rocks divided?
Answer: Igneous rocks are of two types:
(i) Extrusive igneous rocks
(ii) Intrusive igneous rocks.
6. What are extrusive igneous rocks? Give an example.
Answer: When the molten lava comes on the earth’s surface, it rapidly cools down and becomes solid. Rocks formed in such a way on the crust are called extrusive igneous rocks. The example is Basalt rock found in Deccan plateau.
7. What are intrusive igneous rocks? Give an example.
Answer: Sometimes the molten magma cools down deep inside the earth’s crust, leading to the formation of solid rocks. These are called intrusive igneous rocks. For example, granite rocks which are used to prepare grinding stone for preparing spice powder.
8. What are the uses of minerals?
Answer: Minerals are very important to mankind. Some are used as fuels. Some minerals, such as coal, natural gas and petroleum, iron, aluminium, gold, uranium, etc. are also used in industries. Further they are even used in medicines and in making fertilisers.
9. What are fossils?
Answer: The remains of the dead plants and animals trapped in the layers of rocks are called fossils.
Long Answer Questions
1. Give a brief description of three layers of the earth.
Answer: (i) Crust:
- It is almost 35 km on the continental masses and 5 km on the ocean floors.
- The main mineral constituents of the continental masses are silica and aluminium soil.
(ii) Mantle: Just beneath the crust is the mantle which extends up to 2,900 km below the crust.
(iii) Core:
- The innermost layer is the core with a radius of 3,500 km.
- It is made of nickel and iron, i.e. knife.
2. What is a rock? Classify igneous rocks.
Answer: (i) Any natural mass of mineral material that makes up the earth’s crust is called a rock. The earth’s crust is made of various types of rocks. Rocks can be of different sizes, textures, shapes, colours, etc.
(ii) Extrusive rocks: When the molten lava comes on the earth’s surface, it rapidly cools down and becomes a solid. They thus, form extrusive igneous rocks; for example, basalt.
(iii) Intrusive Igneous rocks: Sometimes, the molten magma cools down deep inside the earth’s crust. Solid rocks so formed are called intrusive igneous rocks. For example, granite.
3. What are sedimentary rocks? Give an example.
Answer: (i) Sediments formed due to roll down of rocks are transported and deposited by wind, water, etc.
(ii) These loose sediments are compressed and hardened to form layers of rocks.
(iii) These types of rocks are called sedimentary rocks. For example, sandstone made from grains of sand.
(iv) These rocks may even contain fossils of plants, animals and other microorganisms that lived once on them.
Hots (Higher Order Thinking Skills)
1. Explain the uses of rocks in our lives.
Answer: The uses of rocks are:
(i) Hard rocks are used for making roads, houses and buildings.
(ii) Rocks are made of different minerals which are important for mankind; for example, coal, petroleum and natural gas.
(iii) Rocks like aluminium, gold, uranium, etc. are also used in industries such as medicines, fertilisers, etc.
Class 7 Geography Chapter 2 NCERT Questions and Answers
CBSE Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Geography Chapter 2 Inside Our Earth are given above. All our solutions are updated as per the latest CBSE Syllabus and Guidelines. Download these NCERT solutions for free from our app and use offline.