Extra Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 17 Forests Our Lifeline
Extra questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 17 Forests Our Lifeline with answers is given below. Our subject expert prepared these solutions as per the latest NCERT textbook. These questions will be helpful to revise the all topics and concepts. CBSE Class 7 extra questions are the most simple and conceptual questions that are prepared by subject experts for the students to study well for the final exams. By solving these extra questions, students can be very efficient in their exam preparations.
Forests Our Lifeline Class 7 Science Extra Questions and Answers
Very Short Extra Questions and Answer
1. Define carnivores.
Answer: The organisms which eat flesh and are dependent on other animals for food are called carnivores.
2. Define herbivores.
Answer: The organisms which depend on plants or plant products for their food are called herbivores.
3. What happens if an animal dies in the forest?
Answer: Dead animals become food for vultures, crows, jackals and insects.
4. What is known as the crown of the tree?
Answer: Branchy part of a tree above the stem is known as the crown of the tree.
5. What is canopy?
Answer: Branches of the tall trees look like a roof over the other plants in the forest. This is called a canopy.
6. List five products we get from forests.
Answer: Gum, oils, spices, fodder for animals and medicinal plants are some of the products which we get from the forest.
Short Extra Questions and Answers
1. What are known as understoreys in forest?
Answer: Trees have crowns of different types and sizes. These create different horizontal layers in the forest. These are known as understoreys.
2. What is the effect of deforestation on soil?
Answer: Roots of trees normally bind the soil together, but in their absence the soil is washed away or eroded.
3. In which layer of the soil would you find humus? What is its importance to the soil?
Answer: Humus is found in the top, organic layer of soil. Humus provides many useful nutrients to the soil.
4. Why does the forest floor seem to be dark-coloured?
Answer: The forest floor seem to be dark coloured as it is covered with a layer of dead and decaying leaves, fruits, seeds, twigs and small herbs. The decaying matter was moist and warm.
5. Who would have planted trees in forest?
Answer: In nature trees produce enough seeds. The forest floor provides favourable conditions for them to germinate and develop into seedlings and saplings. Some grow up into trees.
6. Why even after heavy rainfall water do not stagnate in the forest?
Answer: Forest acts as a natural absorber of rainwater and allows it to seep. It helps maintain the water table throughout the year. Forests not only help in controlling floods but also help maintain the flow of water in the streams so that we get a steady supply of water.
7. Why forests are called green lungs?
Answer: Plants release oxygen through the process of photosynthesis. The plants help to provide oxygen for animal respiration. They also maintain the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. That is why forests are called lungs.
8. Why raindrops do not hit the forest floor directly?
Answer: The uppermost layer of the forest canopy intercept the flow of raindrops and most of the water come down through the branches and the stems of the trees. From the leaves it drips slowly over branches of the shrubs and herbs. Thus, raindrops do not hit the forest floor directly.
9. Why are forests disappearing?
Answer: Forests are disappearing due to:
- Construction of roads, buildings, industrial development and increasing demand of wood.
- Overgrazing of animals and indiscriminate felling of trees for agricultural land.
10. Explain the importance of forest.
Or
Why is it important to conserve forest?
Answer: Forests are very important to us. They provide us with oxygen. They protect soil and provide habitat to a large number of animals. They help in bringing good rainfall in neighbouring areas. They are a source of medicinal plants, timber and many other useful products.
Long Extra Questions and Answers
1. What are decomposers? Name any two of them. What do they do in the forest?
Answer: The micro-organisms which convert the dead plants and animals to humus are known as decomposers. Decomposers break down dead plant and animal matter so the nutrients in them are recycled back into the ecosystem to be used again. Examples of decomposers include bacteria, fungi etc.
2. Explain the role of forest in maintaining the balance between oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Answer: Plants release oxygen through the process of photosynthesis. The plants help to provide oxygen for animal respiration. Plants use carbon dioxide released by animals. Thus, they maintain the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
3. Why does deforestation increase carbon dioxide in the atmosphere?
Answer: Plants release oxygen through the process of photosynthesis. The plants help to provide oxygen for animal respiration. Plants use carbon dioxide released by animals. Thus, they maintain the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. If forests disappear, the amount of carbon dioxide in air will increase, resulting in the increase of earth’s temperature.
4. Explain why there is no waste in a forest.
Answer: The decomposers convert dead plants and animals to humus. The presence of humus ensures that the nutrients of the dead plants and animals are released into the soil. From there, these nutrients are again absorbed by the roots of the living plants. The dead animals become food for vultures, crows, jackals and insects. In this way, the nutrients are cycled. So, nothing goes waste in a forest.
5. Explain why forest is called “the dynamic living entity”?
Answer: By harbouring greater variety of plants, the forest provides greater opportunities for food and habitat for the herbivores. Larger number of herbivores means increased availability of food for a variety of carnivores. The wide variety of animals helps the forest to regenerate and grow. Decomposers help in maintaining the supply of nutrients to the growing plants in the forest. Therefore, the forest is a ‘dynamic living entity’ — full of life and vitality.”
6. Explain how forests prevent floods.
Answer: Forest also acts as a natural absorber of rainwater and allows it to seep. It helps maintain the water table throughout the year. Forests not only help in controlling floods but also help maintain the flow of water in the streams so that we get a steady supply of water. On the other hand, if trees are not present, rain hits the ground directly and may flood the area around it. Heavy rain may also damage the soil. Roots of trees normally bind the soil together, but in their absence the soil is washed away or eroded.
7. Explain how forest affects our food chain.
Or
Every part of the forest is dependent on the other parts. Comment
Or
What difference will it make if we cut trees for a factory?
Answer: All animals whether herbivores or carnivores, depend ultimately on plants for food. Organisms which feed on plants often get eaten by other organisms, and so on. For example, grass is eaten by insects, which in turn, is taken by the frog. The frog is consumed by snakes. This is said to form a food chain: Grass→ insects→ frog→ snake→ eagle. Many food chains can be found in the forest. All food chains are linked. If anyone food chain is disturbed, it affects other food chains. Every part of the forest is dependent on the other parts.
8. Why should we worry about the conditions and issues related to forests far from us?
Or
What would happen if forests disappear?
Answer: We should worry about the conditions and issues related to forests far from us because:
- If forests disappear, the amount of carbon dioxide in air will increase, resulting in the increase of earth’s temperature.
- In the absence of trees and plants, the animals will not get food and shelter.
- In the absence of trees, the soil will not hold water, which will cause floods.
- Deforestation will endanger our life and environment.
9. Explain why there is a need of variety of animals and plants in a forest.
Answer: There is a need of variety of animals and plants in a forest because
- The micro-organisms convert the dead plants and animals to humus. Humus provides nutrients to the plants. The decaying animal dung also provides nutrients to the seedlings to grow.
- The insects, butterflies, honeybees and birds help flowering plants in pollination.
- By harbouring greater variety of plants, the forest provides greater opportunities for food and habitat for the herbivores. Larger number of herbivores means increased availability of food for a variety of carnivores. The wide variety of animals helps the forest to regenerate and grow.
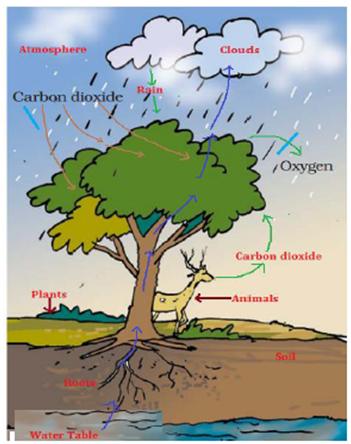
10. In Fig., the artist has forgotten to put the labels and directions on the arrows. Mark the directions on the arrows and label the diagram using the following labels: clouds, rain, atmosphere, carbon dioxide, oxygen, plants, animals, soil, roots, water table.
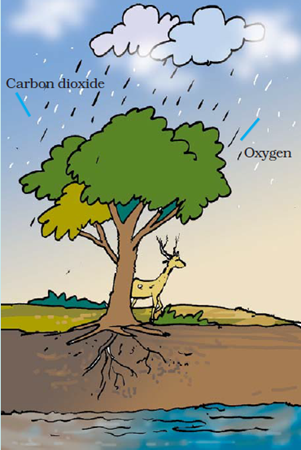
Answer:
11. Explain how animals dwelling in the forest help it grow and regenerate.
Answer: Animals dwelling in the forest help it grow and regenerate in the following ways:
- The micro-organisms convert the dead plants and animals to humus. Humus provides nutrients to the plants. The decaying animal dung also provides nutrients to the seedlings to grow.
- The insects, butterflies, honeybees and birds help flowering plants in pollination.
- By harbouring greater variety of plants, the forest provides greater opportunities for food and habitat for the herbivores. Larger number of herbivores means increased availability of food for a variety of carnivores. The wide variety of animals helps the forest to regenerate and grow.