Class 6 Science Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflection Extra Questions
CBSE Class 6 Science Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflection Extra Questions and Answers is available here. Students can learn and download the PDF of these questions for free. These extra questions and answers are prepared by our expert teachers as per the latest NCERT textbook and guidelines. Learning these extra questions will help you to score excellent marks in the final exams.
Light Shadows and Reflection Class 6 Science Extra Questions and Answers
Very Short Answer Questions
1. You have 3 opaque strips with very small holes of different shapes as shown in figure. If you obtain an image of the sun on a wall through these holes, will the image formed by these holes be the same or different?
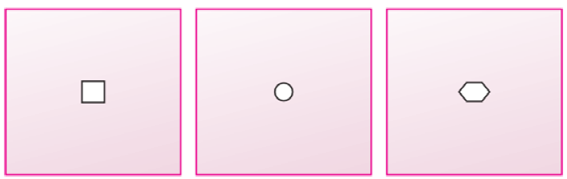
Answer: The image obtained will be the same in all the three cases.
2. Observe the picture given in figure. A sheet of some material is placed at position ‘P’, still the patch of light is obtained on the screen. What is the type of material of this sheet?
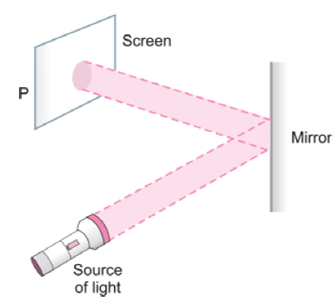
Answer: A sheet of transparent material is placed at ‘P’.
3. Three torches A, B and C shown in figure given below are switched on one by one. The light from which of the torches will not form a shadow of the ball on the screen?
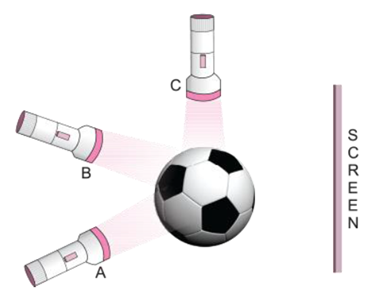
Answer: The light of torch at position C will not form a shadow of the ball on the screen.
4. Define eclipse.
Answer: Eclipse is a shadow formed in space that makes the sun or the moon invisible for some time.
5. Look at the figure.
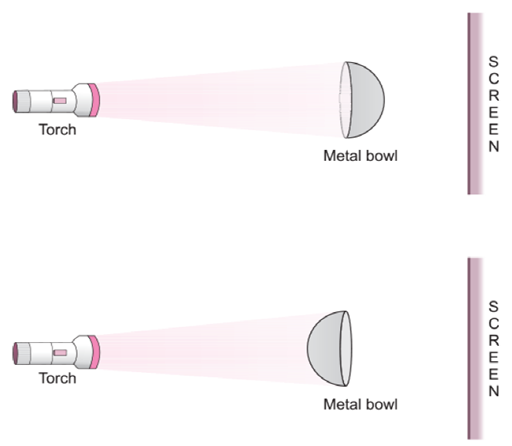
Will there be any difference in the shadow formed on the screen in A and B?
Answer: No
6. How can a transparent sheet be converted into a translucent sheet?
Answer: By greasing the paper with oil or fat.
7. What are the three things required for the formation of shadows?
Answer: Light, space and opaque object.
8. Moon is a non-luminous object. How does it shine at night?
Answer: Moon reflects the light of the sun at night.
9. Whether the moon is luminous or non-luminous body?
Answer: Moon is non-luminous body.
10. What is umbra?
Answer: Umbra is the dark region behind object facing light which does not receive light at all.
11. How does a light ray travel?
Answer: Light ray travels in a straight line.
12. Give one natural source of light.
Answer: Sun is a natural source of light.
13. What is shadow?
Answer: Shadow is the dark space behind an opaque object where light does not reach.
Short Answer Type Questions
1: What is the difference between transparent and translucent object?
Answer: If we are able to see clearly through an object, it is said to be transparent. Whereas there are some objects through which we can see but not clearly. Such objects are known as translucent objects. Transparent objects allow light to pass through them completely whereas translucent objects doesn’t allow light to pass through them completely.
2: What materials can be used to make a pinhole camera? How can it be used?
Answer: Pinhole camera can be made with simple material like cardboard, tracing paper etc. It can be used to image the sun and brightly lit objects.
3: Why is shadow formed when an opaque object comes in path of light?
Answer: Light travels in a straight line and when opaque object obstructs it, shadow is formed.
4: What is reflection?
Answer: When any surface reflects light without absorbing it, it is known as reflection.
5: Classify the objects as opaque, transparent and translucent-
Fog, glass, wood, plastic box, smoke, water
Answer: Transparent-glass and water.
Opaque-wood and plastic box
Translucent- fog and smoke
6: Why we cannot see our image in the mirror in complete dark room?
Answer: We cannot see our image in the mirror in complete dark room because there is no light to reflect.
7: Classify the following as luminous and non luminous object:
Sun, moon, table, chair, stars
Answer: Luminous –sun, stars
Non luminous-moon, table, chair
8: What is the difference between luminous and non-luminous objects?
Answer: Objects that give out or emit light of their own are known as luminous objects. For example candle, sun etc. Objects that cannot give out or emit light of their own are known as non- luminous objects. Such as chair, book etc.
9: Why we cannot see objects through T shaped or N shaped pipe?
Answer: We cannot see objects through T shaped or N shaped pipe because light travels through straight line.
10: What do we need to see an object?
Answer: To see an object, we need source of light, eyes and object. When light emitted by luminous body falls on an object, it is reflected back and received by our eyes. Then we see that object.
11: Give example of an object which is a) opaque and luminous b) translucent and luminous.
Answer: A) Sun b) flame of gas burner.
12: If moon is non luminous, how it appears bright in night?
Answer: Moon appears bright in night because it reflects sun light that falls on it.
13: What type of objects does not cast shadow and why is that?
Answer: Transparent and some translucent objects do not cast shadow because light passes through them.
14: Why polished surface cause glares in our eyes?
Answer: Polished surface cause glares in our eyes because they produce regular reflection of light.
15: Give two examples of each:
a) Transparent and non-luminous object
b) Translucent and non-luminous object.
Answer: a) Air and water b) polythene and smoke.
16: Which of these objects can cast shadow:
Paper, air, rock, glass, sun
Answer: Paper, rock and sun.
17: How is shadow formed?
Answer: When an object is placed in path of light, a dark portion is formed on the opposite side of object. This dark portion is shadow.
18: What is periscope?
Answer: Optical object by which we can see objects located above our line of sight.
19. Suggest a situation where we obtain more than one shadow of an object at a time.
Answer: We can obtain more than one shadow of an object if light from more than one source falls on it. For example, during a match being played in a stadium, multiple shadows of players are seen.
20. On a sunny day, does a bird or an aeroplane flying high in the sky cast its shadow on the ground? Under what circumstances can we see their shadow on the ground?
Answer: No. Shadow of the bird can only be seen when the bird is flying very low, close to the ground.
21. You are given a transparent glass sheet. Suggest any two ways to make it translucent without breaking it.
Answer: i. By applying oil, grease, butter on it or pasting a butter paper on it.
ii. Grinding (rubbing) the surface of the glass by any abrasive material.
22. A student covered a torch with red cellophane sheet to obtain red light. Using the red light she obtains a shadow of an opaque object. She repeats this activity with green and blue light. Will the colour of the light affect the shadow? Explain.
Answer: The colour of light will not affect the shadow, because shadow is the dark patch formed when an object obstructs the path of light and hence no light reaches in the shadow region.
23. Is air around us always transparent? Discuss.
Answer: Air around us is transparent but when thick smoke, thick clouds, etc. are present in the air it does not remain transparent.
24. Three identical towels of red, blue and green colour are hanging on a clothes line in the sun. What would be the colour of shadows of these towels?
Answer: The colour of shadows of all three towels will be the same. This is because shadows are always black in colour.
25. Using a pin hole camera a student observes the image of two of his friends, standing in sunlight, wearing yellow and red shirt respectively. What will be the colours of the shirts in the image?
Answer: The colours of the image of the shirts will be the same as the colour of the shirt. This is because a pin hole camera has only a small aperture through which light passes and forms the image.
26. In the figure given below, a flower made of thick coloured paper has been pasted on the transparent glass sheet. What will be the shape and colour of shadow seen on the screen?
Answer: The shadow formed will be dark or black in colour and of the shape of the flower along with the stalk.
27. How is a shadow formed?
Answer: When a beam of light shines on an opaque object, some light rays are stopped and some pass by the edges. The region without light formed behind the object is called shadow.
28. State difference between a luminous and a non-luminous body.
Answer: The bodies which emit light are called luminous bodies. Example: sun, stars, burning candle etc. The bodies which does not emit light are called non-luminous bodies. Example: moon, earth, blackboard.
29. Why is the moon not considered as a luminous body?
Answer: Moon is non-luminous body because it shines by reflecting the sunlight falling on it.
30. What is an incandescent body? Give example.
Answer: The bodies which emit light when heated to a very high temperature are called incandescent bodies. Example: electric bulb.
31. When does a shadow form?
Answer: Shadow is formed when light does not reach behind the opaque object kept in the path of light
32. What are the essential conditions for the formation of shadow?
Answer: (i) There should be an opaque material.
(ii) There should be a source of light and screen.
The object must be placed in the path of light. Then shadow is formed on the screen.
33. Define reflection of light.
Answer: When light rays after striking the smooth and shiny surface return to same medium, this phenomenon is called reflection of light.
34. How will you convert a glass sheet into a translucent sheet?
Answer: There are following two methods to convert glass sheet into a translucent sheet:
(i) By smearing a thin layer of oil on glass sheet.
(ii) By covering a side of sheet by butter paper.
36. What is shadow? How does the colour of an opaque object affects the colour of the shadow?
Answer: A dark outline or patch formed by an opaque object that blocks light coming from a source of light is called shadow. The colour of an opaque object does not affect the colour of the shadow.
37. What do we need in order to see a shadow?
Answer: We need: (i) A source of light (ii) a screen (in) an opaque object.
38. What do you mean by scattering of light?
Answer: When a beam of light falls on a rough surface it is turned back in different directions. It is called scattering of light.
39. Have you ever seen an ambulance? It is written in the form of mirror image on vehicles. Explain why it is done so and give the mirror image of AMBULANCE.
Answer: It is written so on the vehicles for the people to see in their rear view mirrors, read it correctly and immediately give way to the vehicle as it carries patients who need urgent medication.
Long Answer Type Questions
1. Explain that light has the property of rectilinear propagation.
Answer: We take three pieces of cardboard. Place them one on the top of one another and make a hole in the middle of each cardboard by using a thick nail. Erect these cards up on the table at a short distance away from each other. Take a candle which is of the same height as the holes in the cards. Light the candle and place it in front of the cards. We see that the light of candle is visible only when the holes on cards lie in a straight line. If we disturb them the light of candle disappears. This experiment shows that light propagates in a straight line.
2: Why can we see our image in the mirror?
Answer: Light rays reflected from parts of our body fall on mirror and are reflected back. When these reflected rays reach our eyes (reflected on our retina), we can see the image. Mirror has one surface painted so when we see the mirror light rays which reflect from our body not get pass through mirror.
3. Write difference between shadow and image.
Answer:
| Image | Shadow |
| It is formed by intersection of reflected rays. | Shadow is formed when light does not reach behind the object. |
| Image is seen when reflected rays approach to the observer’s eyes. | No light enters the observer’s eyes. |
| Image gives more information such as colour, structure etc. | Shadow does not provide such information. |
| Image can be straight or inverted. | Shadow is never inverted. |
4: What are transparent, translucent and opaque objects? Explain with example.
Answer: If we are able to see clearly through an object, it is said to be transparent.
Example- Glass and water. There are some objects through which we can see but not clearly. Such objects are known as translucent objects. Example- tracing paper. If we cannot see through an object at all, it is an opaque object. Example -wood, plastic box etc
5. You have to cost the shadow of your pencil on the wall with the help of candle in a dark room. How can you obtain the shadow of same size, small size and big size of the same pencil?
Answer: (a) The shadow of the pencil will be small when the pencil is taken close to the wall and away from the candle.
(b) The shadow will be big in size when the pencil is taken closer to the candle.
(c) To get the same sized shadow as the pencil is, adjust the distance between the wall, pencil and candle at equal distances.