Crop Production and Management Class 8 Important Questions and Answers
Important questions of Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management is given below. These important questions will help students while preparing for the exam. Practising these important questions will analyse their performance and work on their weak points. Score well in exam of Class 8 Science by going through these important questions. Students of Class 8 can download important questions of Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management PDF by clicking the link provided below.
Important Questions of Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
Here you can get Class 8 Important Questions Science based on NCERT Text book for Class 8. Science Class 8 Important Questions are very helpful to score high marks in board exams. Here we have covered Important Questions on Crop Production and Management for Class 8 Science subject.
Very Short Answer Questions
1. How green plants synthesize their own food?
Answer: Green plants synthesize their own food by the process of photosynthesis.
2. Where do animals get their own food?
Answer: Animals get their food from plants and other animals.
3. What do you mean by crop?
Answer: When plants of same kind are grown and cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called crop.
4. Name two broad cropping patterns.
Answer:
(a) Kharif crops
(b) Rabi crops
5. Mention the names of two kharif crops.
Answer:
(a) Paddy crops
(b) Maize crops
6. Write the names of two rabi crops.
Answer:
(a) Wheat crops
(b) Gram crops
7. What are agricultural practices?
Answer: The various steps to grow crops and storage of grains are collectively known as agricultural practices.
8. What do you mean by the tilling or ploughing?
Answer: The process of loosening and turning of the soil is called tilling or ploughing.
9. What is plough?
Answer: The device used for tilling or ploughing is called plough.
10. Name two materials used to make a plough.
Answer: Wood and iron.
11. What are crumbs?
Answer: The big pieces of soil are called crumbs.
12. Name some tools used in agriculture.
Answer: Plough, hoe, cultivator.
13. Write two uses of plough.
Answer:
(a) It is used for tilling of soil.
(b) It is used to remove the weeds.
14. Write two uses of hoe.
Answer:
(a) It is used to remove the weeds.
(b) It is used to loosen the soil.
15. What is traditional tool used for sowing?
Answer: The tool used traditionally for sowing is funnel-shaped tool.
16. What is manure?
Answer: Manure is an organic substance obtained from the decomposition of plant and animal wastes.
17. What do you mean by manuring?
Answer: The process of providing manure to replenish the soil with nutrients is called manuring.
18. What are fertilisers?
Answer: Fertilisers are the chemical substances which are rich in a particular nutrient.
19. Which is better to use manure or the fertilizers?
Answer: Manure is better than the fertilizers.
20. What do you mean by the term irrigation?
Answer: The supply of water to crops at different intervals is called irrigation.
21. Is the time and frequency of irrigation same for all the crops?
Answer: The time and frequency of irrigation varies from crop to crop.
22. Write some sources of irrigation.
Answer: Wells, tubewells, ponds, rivers and canals are the main sources of irrigation.
23. Mention traditional methods of irrigation.
Answer:
(a) Moat
(b) Chain pump
(c) Dhekli
(d) Rahat.
24. What is the use of pumps?
Answer: Pumps are commonly used for lifting water.
25. What are the modern methods of irrigation?
Answer:
(a) Sprinkler system
(b) Drip system.
26. What are weeds?
Answer: The unwanted plants growing naturally with the main crop are called weeds.
27. What is weeding?
Answer: The process of removal of weeds is called weeding.
28. What are weedicides?
Answer: The chemical substances which are used to control the weeds are called weedicides.
29. Name a weedicide which is commonly used by the farmers.
Answer: The weedicides commonly used by the farmers are 2, 4 D.
30. Define harvesting.
Answer: The cutting of crop after it is mature is called harvesting.
31. What is threshing?
Answer: The process by which grains are separated from the chaff is called threshing.
32. Name a machine which is combined harvester and thresher.
Answer: Combine.
33. What is winnowing?
Answer: It is a process of separation of grain and chaff.
34. Name some harvest festivals.
Answer: Pongal, Baishakhi, Nabanya, and Bihu are some harvest festivals.
35. What do you mean by storage?
Answer: The process to keep grains for a longer time by saving them from moisture, insects, rats and microorganisms is called storage.
36. Why is it necessary to dry grains before storage?
Answer: The grains are properly dried in the sun to reduce the moisture in them. This prevents the attack by insects, pests, fungi and bacteria.
37. Name two devices which are used to store grains at large scale.
Answer:
(a) Silos
(b) Granaries
38. Name some animals which provide food.
Answer: Cow, buffalo, hen, pig and fish, etc.
39. Name two milk yielding animals.
Answer:
(a) Cow
(b) Buffalo
40. Mention the name of three animals which provide meat.
Answer: Goat, pig and fish.
41. What do you mean by animal husbandry?
Answer: Animal husbandry is the process to provide proper food, shelter and care to animals at large scale.
42. Name a vitamin which is found in cod liver oil.
Answer: Vitamin D.
43. Name any two fertilizers.
Answer: NPK, Diammonium phosphate.
44. What is combine?
Answer: Combine is a machine which is used for harvesting as well as threshing of crops or simply we can say combine is a combined harvester and thresher.
45. Name some crop plants.
Answer: Some of the crop plants are wheat, rice, maize, sugarcane, cotton, vegetables, fruits etc.
46. Name the following shown traditional methods of irrigation:
Answer: Moat Dhekli, Sprinkler system, Drip system
47. Name three natural methods of adding nutrients to soil?
Answer: Field fallow, crop rotation and mixed cropping
Short Answer Type Questions
1. Define crop along with examples
Answer: Plants of same kind that are grown and cultivated at one place on large scale are called a crop. Some of the crop plants are wheat, rice, maize, sugarcane, cotton, vegetables, fruits etc.
2. Differentiate between kharif and rabi crops
Answer:
| Kharif Crops | Rabi Crops |
| Kharif crops are the crops which are sown at the beginning of the rainy season, e.g. between April and May. | Rabi crops are the crops that are sown at the end of monsoon or at the beginning of winter season, e.g. between September and October. |
| These crops are known as monsoon crops. | These crops are also known as winter or spring crops. |
| These crops depend on the rainfall patterns. | These crops are not affected by the rainfall. |
| Major Kharif crops are rice, maize, cotton, jowar, bajra etc. | Major Rabi crops are wheat, gram, peas, barley etc. |
| It requires a lot of water and hot weather to grow. | A warm climate is required for seed germination and cold climate for the growth of crops. |
| Flowering requires shorter day length. | Flowering requires longer day length. |
| Harvesting months from September to October. | Harvesting months from March to April. |
3. What do you mean by preparation of soil?
Answer: Preparation of soil is a very important step in agriculture before cultivation of crops. It includes loosening of soil, removing weeds from the soil and levelling of soil before sowing of seeds. Loosening of soil improves the air circulation in soil and enhances the water retaining capacity of the soil.
4. Why loosened soil is important for cultivation of crops?
Answer: It is necessary to turn and loosen the soil because only loose soil allows the roots to penetrate freely deeper into soil. The roots can breathe easily in loose soil. The deep roots hold the plants more firmly. The water also can reach easily up to more depth in loose soils. Microbes and worms can also grow in loose soil.
5. Write a paragraph in your own word on each of the following:
(a) Tilling
(b) Weeds
Answer:
(a) Tilling: The process of loosening and turning of the soil is called tilling or ploughing and is carried on by using a plough. Ploughs are made by wood or iron material, it is being used since ancient time for different purposes like tilling the soil, adding fertilisers to crops, removing weeds etc. this implement is drawn by a pair of bulls or other animals like camels, horses etc.
(b) Weeds: Weeds are unwanted plants that grow along with crop plants and compete with them for water, nutrients, space and light, thus they affect growth of crop plants. Some of the weeds are poisonous for animals and human beings and they interfere even in harvesting of crop plants and the removal of weeds is called weeding.
6. Write shorts notes on:
(a) Sowing of seeds
(b) Threshing
Answer:
(a) Sowing of seeds: One of the important part of crop production is sowing. Good quality seeds are selected and are sown in prepared soil with the help of various tools like traditional tools and seed drill.
(i) Traditional tools: The shape of this tool is like a funnel which is filled by seeds, then the seeds are passed down through two or three pipes having sharp ends and these ends pierce into the soil and place seeds there.
(ii) Seed drill: This tool is used for sowing with the help of tractors and it sows the seeds uniformly and at proper distances and depth, it also ensures covering of the seeds from soil after sowing, so that seeds could not get damaged by birds and by other organisms. Sowing by using a seed drill saves time and labour. In order to avoid overcrowding of plants it is very important to leave some space between two seeds. This also allows plants to get sufficient sunlight, nutrients and water from the soil.
(b) Threshing: Threshing is the process of separating the grains from the straw and chaff. This is carried out with the help of a machine called combine which works as harvester and thresher both.
7. What are the advantages of a cultivator over plough for the purpose of ploughing?
Answer: Ploughing by cultivators save time and labour as cultivator is driven by tractors whereas plough is driven by pair of bull.
8. How could you separate good and healthy seeds from the damaged ones?
Answer: Take a beaker half filled with water and put some seeds into it and stir well, wait for some time. You will observe some seeds sink in water while some seeds float in water, damaged seeds become hollow and lighter and thus they float on water.
9. Write a short notes on tools used for sowing seeds.
Answer: Tools used for sowing of seeds are:
(a) Traditional tools: The shape of this tool is like a funnel which is filled by seeds, then the seeds are passed down through two or three pipes having sharp ends and these ends pierce into the soil and place seeds there.
(b) Seed drill: This tool is used for sowing with the help of tractors and it sows the seeds uniformly and at proper distances and depth, it also ensures covering of the seeds from soil after sowing, so that seeds could not get damaged by birds and by other organisms. Sowing by using a seed drill saves time and labour. In order to avoid overcrowding of plants it is very important to leave some space between two seeds. This also allows plants to get sufficient sunlight, nutrients and water from the soil.
10. What are the advantages of a seed drill used for sowing?
Answer: Advantages of seed drill are as follows:
(a) This sows the seeds uniformly at equal distance and depth.
(b) It ensures that seeds get covered by the soil after sowing.
(c) This protects seeds from being eaten by birds.
(d) Sowing by using a seed drill saves time and labour.
11. How could we supply nutrients to the soil?
Answer: We can supply nutrients to the soil by adding manure and fertilisers. Manures are organic substances obtained from the decomposition of plants and animal wastes which provides lot of humus to the soil. It is very important for the healthy growth of plants, and Fertilisers are chemical substances which are rich in particular nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, they are produced in factories. Examples: Urea, NPK, Ammonium sulphate etc.
12. Differentiate between manure and fertilizers.
Answer:
| Fertiliser | Manure |
| It may be an artificial or natural substance. | It is a natural substance. |
| These are chemicals that are added to the soil to increase its fertility and productivity. | These are obtained from dead and decaying plants and animals. |
| Prepared in factories. | Prepared in fields. |
| Does not provide humus to the soil. | Provides humus to the soil. |
| Rich in plant nutrients. | Less rich in plant nutrients. |
| Absorbed by plants quickly. | Absorbed by plants slowly. |
| Costly | Comparatively cheaper and cost-effective |
| It harms the organisms present in the soil and also causes health issues in people consuming the crop. | It causes no harm to the organisms and improves soil quality. |
13. What do you understand by manuring and what are the harmful effects of improper or insufficient manuring?
Answer: Farmers add manure to the fields to replenish the soil with nutrients and to increase their crop production, this process of adding manures to the field is called manuring. Improper manuring results in poor development of crop plants and unhealthy crops.
14. How could we prepare organic manure?
Answer: Organic manure can be prepared in fields. Dump plant and animal wastes in pits at open places and allow it to decompose by some of the microorganisms; the decomposed matter is used as manure.
15. What are the harmful effects of fertilisers?
Answer: Harmful effects of fertilisers are as follows:
(a) The excessive use of fertilisers makes soil less fertile.
(b) It is also considered as one of the source of water pollution
16. What is crop rotation? How it helps in replenishment of the soil?
Answer: Crop rotation involves growing two or more crops alternatively on the same piece of land. For example: after growing wheat for a season, farmers prefer to grow crop of legume family such as peas, gram and groundnut. These leguminous plants have nitrogen fixing bacteria on their root nodules. These bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen into compound that can be used by plants. This makes the soil rich in nitrogen which is good for crops.
17. State advantages of manure
Answer: Advantages of manure:
(a) Water holding capacity of soil is increased by adding manure to the soil
(b) It increases the total number of friendly microbes in soil and thus increases soil fertility
(c) By adding manure soil become more porous so that the exchange of gases becomes easy
(d) It improves the texture of the soil.
18. What is irrigation and its importance?
Answer: Irrigation is the process of applying water to the crops artificially to fulfil their water requirements. The various sources of water for irrigation are wells, ponds, lakes, canals, tube-wells, and even dams. Water is very important for proper growth and development of flowers, fruits and seeds of plants, it plays important role in
(a) Germination of seeds
(b) Transportation of nutrients in different parts of plants
(c) Protects crops from both frost and hot air currents
(d) It maintains the moisture of soil
19. Why we should supply more water to crops during summer season?
Answer: Because of the increased rate of evaporation of water from the soil and the leaves it is important to increase the frequency of watering in summer season.
20. Explain modern methods of irrigation.
Answer: Modern method of irrigation help us to use water economically, it involves following methods:
Sprinkler system: In this system the perpendicular pipes with rotating nozzles on top are joined to the main pipeline at regular intervals when water is allowed to flow through the main pipe under pressure with the help of pump, it escape from the rotating nozzles, it gets sprinkled on the crop as if it is raining, sprinkler is very useful for sandy soil.
Drip system: In this system water falls drop by drop just at the position of the roots. So it is called drip system. It is the best technique for watering plants, trees and garden. This system provides water to plants drop by drop, and water is not wasted at all
21. Why do we have to eat food?
Answer: Food provides us energy. The energy provided by food is utilised by the organisms for carrying out their various body functions, such as digestion, respiration and excretion. We get our food from plants and animals.
22. Explain various types of crops.
Answer: Crops are of two types:
(a) Kharif crops: The crops which are grown in the rainy season are called kharif crops (June to September). Paddy, maize, soyabean, groundnut, cotton are some of the major kharif crops.
(b) Rabi crops: The crops sown in the winter season are called rabi crops (October to March). Wheat, gram, pea, mustard and linseed are some of the major rabi crops.
23. List various agricultural practices.
Answer: The agricultural practices are listed below:
(a) Preparation of soil
(b) Sowing
(c) Adding manure and fertilizers
(d) Irrigation
(e) Protecting from weeds
(f) Harvesting
(g) Storage
24. What is plough?
Answer: This implement is made of wood and iron. It is drawn by a pair of bulls or other animals. It contains a strong triangular iron strip called ploughshare. The main part of the plough is a long log of wood which is called ploughshaft. The plough is used for tilling the soil, adding fertilizers to the crop, removing the weeds and scraping of soil.

25. What is hoe? What is its use?
Answer: Hoe is a simple tool which is used for removing weeds and for loosening the soil. It has a long rod of wood or the iron. A strong broad and bent plate of iron is fixed to one of its ends and works like a blade. It is also pulled by animals.
26. Explain the preparation of manure by the farmers.
Answer: Manure is an organic substance obtained from decomposition of plant or animal wastes. Farmers dump plant and animal wastes in pits at open places and allow it to decompose. The decomposition is caused by some microorganisms. The decomposed matter is used as organic manure.
27. What are fertilizers? How do they differ from manure on the basis of their formation?
Answer: Fertilizers are the chemical substances which are rich in a particular nutrient. Fertilizers are produced in the factories while manure can be made by farmers themselves in the fields. Some fertilizers are urea, ammonium sulphate, super‑phosphate, potash, N.P.K. (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium). Fertilizers are used to get better yield of crops.
28. What is the role of water in the production of crops?
Answer: Water is essential for plants. It helps in the germination of seeds because seeds cannot germinate under dry conditions. Nutrients dissolved in water get transported to each part of the plant. It protects the crop from frost and hot air currents. Water is important for proper growth and development of flowers, fruits and seeds of plants. Along with water minerals and fertilizers are also absorbed. Plants contain nearly 90% water. The time and frequency of irrigation varies from crop to crop, soil to soil and season to season.
29. Explain traditional methods of irrigation.
Answer: The water available in wells, lakes and canals is lifted up by different methods in different regions, for taking it to the fields. Cattle or human labour is used in these methods. These methods are cheaper but less efficient. The various traditional ways are:
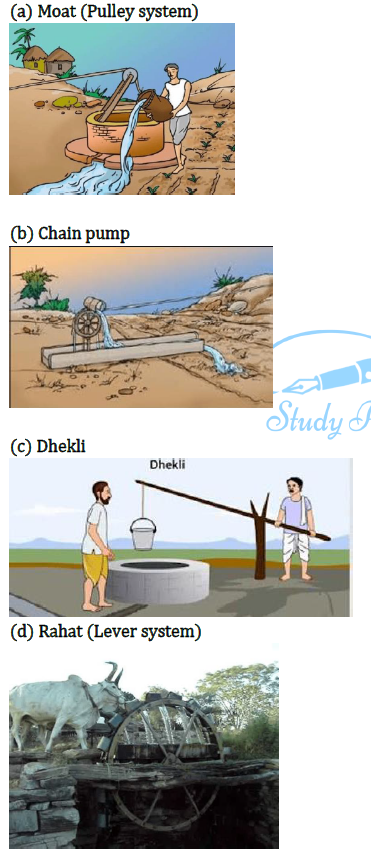
30. What is weeding? Why is it necessary?
Answer: The process of removal of weeds is called weeding. Weeding is necessary since weeds compete with crop plants for water, nutrients, space and sunlight. Thus they affect the growth of crop. Some weeds interfere even in harvesting and may be poisonous for animals and human beings.
31. Explain the various methods of weeding.
Answer: Farmers use many ways to remove weeds and control their growth. Tilling before sowing of crops helps in uprooting and killing weeds, which may then dry up and get mixed with the soil. The best time for the removal of weeds is before they produce flowers and seeds. The khurpi is used to remove weeds by uprooting or cutting them from time to time. A seed drill is also used to uproot weeds. Weeds are also controlled by using weedicides like 2, 4‑D.
32. Explain various methods of harvesting in our country.
Answer: There are mainly two methods which are used to harvest the mature crops:
(a) Manual: A device called sickle is used to harvest mature crops manually.
(b) By Machine: A machine called harvester is also used to harvest crops. A machine called combine which is in fact, a combined harvester and thresher. This machine does both the functions of harvesting and threshing at the same time.
33. What do you know about Harvest Festival?
Answer: After three or four months of hard work there comes the day of harvest. The sight of golden fields of standing crops, laden with grains fills the hearts of farmers with joy and a sense of well being. Men and women celebrate this period with great enthusiasm. This period of joy is called Harvest Festival. Pongal, Baishakhi, Holi, Diwali, Nabanya and Bihu are such Harvest Festivals.
34. How do the grains stored and preserved?
Answer: Farmers store the grains in jute bags or metallic bins. However, large scale storage of grains is done in silos and granaries, to protect them from pests like rats and insects. Dried neem leaves are used for storing food grains at home. For storing large quantities of grains in big godowns, specific chemical treatments are required to protect them from pests and microorganisms.
Long Answer Type Questions
1. Describe various methods of agricultural practices involved in crop production and management.
Answer: Various methods of agricultural practices involved in crop production and management are:
- Preparation of soil by tilling and leveling.
- Sowing of seeds into prepared soil.
- Adding manure and fertilizers for replenishment and enrichment of soil and healthy growth of crops.
- The supply of water to crops at appropriate interval called as irrigation.
- Protecting from weeds by using weedicides.
- Harvesting of crops by machines.
- Proper storage to protect them from harmful effects of pests and microorganisms.
2. Define irrigation and its various methods and explain its two methods which conserve water.
Answer: Irrigation is the artificial application of water to crops at different intervals. The time and frequency of irrigation varies from crop to crop, soil to soil and season to season.
Two methods of irrigation are
1. Traditional method of irrigation involves cattle or human labour and thus are cheaper than modern methods of irrigation, various traditional ways of irrigation are:
(a) Moat (pulley system)
(b) Chain pump
(c) Dhekli
(d) Rahat (Lever system)
2. Modern methods of irrigation helps us to use water economically, it involves following methods:
Sprinkler system: In this system, perpendicular pipes, having rotating nozzles on top, are joined to the main pipeline at regular intervals. When water is allowed to flow through the main pipe under pressure with the help of a pump, it sprinkles from the rotating nozzles. It gets sprinkled on the crop as if it is raining.
Example: It is used mostly on uneven land.

Drip system: In this system water falls drop by drop just at the position of the roots. So it is called drip system. It is the best technique for watering plants, trees and garden. This system provides water to plants drop by drop, and water is not wasted at all.
Example: watering fruit plants, gardens and trees.

3. Describe the importance of weedicides, manures and fertilizers in good agricultural practice.
Answer: Weeds: Weeds are unwanted plants that grow along with crop plants and compete with them for water, nutrients, space and light, thus they affect growth of crop plants. Some of the weeds are poisonous for animals and human beings and they interfere even in harvesting of crop plants.
Example: Wild oat, grass.
Weedicides: are chemical that are sprayed in the fields to kill the weeds, they do not damage the crops. Weedicides are diluted with water and are sprayed in the field by sprayer to kill the weeds.
Example: 2,4-D
Manure and fertilizers are added to the soil to replenish it with nutrients to ensure healthy growth of plants. Manures like animal waste, plant residues and fertilizers like urea, NPK are used for this purpose.
4. Explain harvest festivals.
Answer: A Harvest Festival is an annual celebration that occurs around the time of the main harvest of a given region. The efforts of the farmer of past season borne fruit in the form of crop, laden with grain, at this point they celebrate harvest festival to express their joy and happiness. Special festivals associated with the harvest season are Pongal, Baisakhi, Holi, Diwali, Nabanya and Bihu.
5. Explain how continuous plantation of crops in a field affects the quality of soil.
Answer: Crop rotation is the practice of growing a series of different types of crops in the same area in sequential seasons. Growing the same type of in the same place for many years in a row disproportionately depletes the soil of certain nutrients. With rotation, a crop that leaches the soil of one kind of nutrient is followed during the next growing season by a dissimilar crop that returns that nutrient to the soil or draws a different ratio of nutrients. For example, rice followed by cotton.
6. Differentiate between mixed cultivation and crop rotation
Answer: In mixed cultivation, two or more different types of crops are sown in a particular field at the same time.
For example, pea plants can be grown in the same field along with a cereal like wheat.
Crop rotation is a practice of growing two or more dissimilar crops in the same field one after the other. The nutrient requirements of a particular crop are kept in mind when crops are grown on a rotational basis.
For example, it is a known fact that paddy uses up a lot of nitrogen from the soil. When planning for the subsequent crop to be sown, this fact is kept in mind. So leguminous plants like soya bean or pea are purposely sown so that this loss of nitrogen can be replaced naturally by them.
7. Write a brief note on ‘Animal Husbandry’.
Answer: Animal husbandry is the management and care of farm animals by humans for profit. In animal husbandry, genetic qualities and behavior are considered to be advantageous to humans for further development. Animal husbandry has been practiced for thousands of years since the first domestication of animals. Humans are dependent on animals in many ways. The animals are domesticated by humans for many purposes. Depending on the usefulness of domestic animals they are categorized as:
- Meat and Egg yielding animals like pig, sheep, fish, poultry, goat and duck.
- Milk-yielding animals or dairy animals like cow, buffalo and goat.
- Wool and skin yielding animals like sheep, goat, camel, buffaloes and cow. Skins are used as leather for different articles.