Life Processes Class 10 Important Questions and Answers
Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes covers each topic of the chapter. These questions aim at providing a better understanding of the chapter to the students and can be downloaded in PDF format. These important question bank help students in clearing their doubts so that they can score well in the exam.
While preparing for exams, students should practise these important questions of Class 10 Science to understand the concepts better. Solving important questions of Class 10 Science Chapter 6 will teach students time management skills and enhance their problem-solving skills. Also, students may come across a few of these questions in the board exam.
Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 – PDF
1. How do autotrophs obtain CO2 and N2 to make their food?
Answer: Autotrophs have the ability to make their own food by the process of photosynthesis. Autotrophs are also known as producers. They obtain carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through the stomata. Nitrogen, an essential element in synthesis of proteins is taken up from the soil and is converted to N2 by root nodules.
2. Name the tissue which transports (a) Soluble products of photosynthesis in plants (b) Water and minerals in plants.
Answer: (a) Phloem vessels transports soluble products of photosynthesis i.e., sucrose to plant’s growing and storage regions.
(b) Xylem transports water and minerals in plants from roots up to the stem to the leaves.
3. Name the largest: (a) Artery (b) Vein in our body.
Answer: The largest artery in the body is Aorta that pumps blood into the body. The largest vein in the body is Vena Cava (Inferior/Superior) that returns blood to the heart.
4. What is the function of (a) Platelets (b) Haemoglobin in our body?
Answer: (a) Platelets- Platelets are cell fragments formed in the bone marrow. They are also called thrombocytes. Platelets carry blood coagulation factors on their surfaces, hence have a major role in initiating blood clotting. They are also involved in maintaining homeostasis.
(b) Haemoglobin– Haemoglobin is a special protein found in the red blood cells that imparts red colour to the blood. It picks up oxygen from lungs to form oxyhaemoglobin and delivers it to the tissues. It maintains blood pH to tolerable limits.
5. What will happen to a plant if its xylem is removed?
Answer: Xylem transports water and minerals in plants from roots up to the stem to the leaves. If Xylem is removed from a plant, the plant will not be able to transport water to leaves and stems and thus the plant will ultimately die.
6. Define transpiration. Give its role in the plants.
Answer: Transpiration is a process in which plants release water vapor. A part of water that plants get is used to prepare their food and store in different parts of the plant. The remaining amount of water is released by plants in the form of water vapor in air. This process of releasing water vapor by plants into the air is called transpiration.
Transpiration has the following roles in plants- it cools the plant, maintain water cycle, allows absorption of water and minerals from soil and its transport in plants, allows diffusion of carbon dioxide from air for photosynthesis.
7. What disadvantage (if any) would be there, if the human RBCs become biconvex instead of their normal biconcave shape?
Answer: If the human RBC’s become biconvex instead of their normal biconcave shape, the surface area of RBC’s will decrease and they will not be able to deliver the amount of oxygen they normally do because they will not accommodate enough haemoglobin to do so.
8. What is the function of pancreas in the human digestive system?
Answer: Pancreas secrete insulin, glucagon and pancreatic juice. Insulin and glucagon function to control the blood sugar levels of our body. The pancreatic enzymes help in digestion of protein, fat and carbohydrates present in the food.
9. Where does digestion of fat take place in our body?
Answer: Digestion of fat takes place in the small intestine. Bile emulsifies fats and breaks them into smaller fat globules. Lipase secreted from the pancreas split fat into fatty acids and glycerol.
10. What is the function of digestive enzymes?
Answer: The digestive enzymes assist in digestion and absorption of nutrients in the small intestine. In the process of digestion, the salivary gland produces saliva in the mouth which digests the starch in food to make food soluble and smooth. Pancreas secrete insulin, glucagon and pancreatic juice. The pancreatic enzymes help in digestion of protein, fat and carbohydrates present in the food. Liver produces bile salts which breakdown lipids to fatty acids.
11. What is meant by breathing? What happens to the rate of breathing during vigorous exercise and why?
Answer: Breathing is the act of moving air in and out of your lungs, as the diaphragm muscles moves up and down in the chest. Breathing in is called inhalation. Breathing out is called exhalation.
During vigorous exercise the rate of breathing increases than the normal rate because more oxygen is needed for more energy and carbon dioxide produced in the respiratory cells of the muscles. The increased production of carbon dioxide increases the rate of breathing and thus oxygen is quickly supplied to the body cells and carbon dioxide is rapidly removed from lungs.
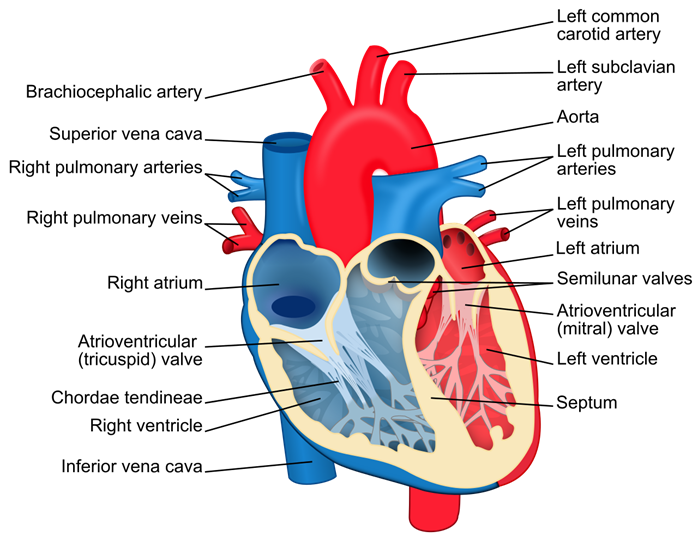
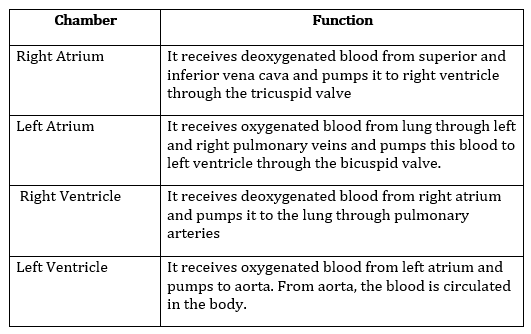
12. Name four chambers of human heart. State one function of each chamber in a tabular form.
Answer: The four chambers of heart are Right atrium, Left atrium, Right Ventricle and Left ventricle.
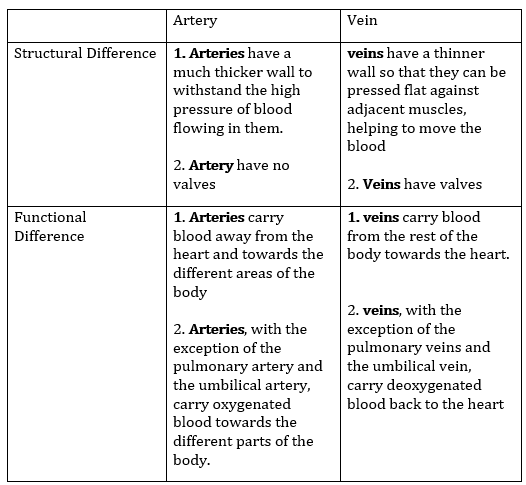
13. Give one structural and functional difference between an artery and a vein.
Answer:
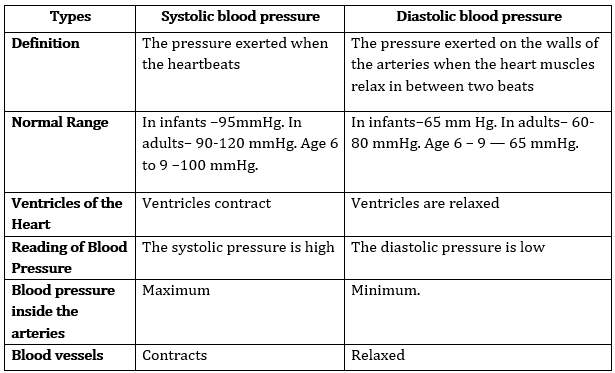
14. What is meant by blood pressure? How systolic pressure differs from diastolic pressure?
Answer: Blood pressure is the pressure exerted by blood against the wall of blood vessels while circulating. It is also called arterial blood pressure. Systolic and Diastolic pressure are the 2 parameters used to represent the blood pressure.
15. Differentiate between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Answer:
| Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic Respiration |
| Oxygen is present when this form of respiration takes place. | Oxygen is absent when this form of respiration takes place. |
| Gases are exchanged in this form of respiration. | Gases are not exchanged in this form of respiration. |
| It can be found in the cytoplasm and the mitochondria. | It can be found only in the cytoplasm. |
| Glucose breaks down into carbon dioxide and water. | Glucose breaks down into ethyl alcohol, carbon dioxide and energy. |
| All higher organisms such as mammals have this type of respiration. | Lower organisms such as bacteria and yeast use this type. In other organisms, it occurs during heavy activities. |
16. Name the end products formed during:
(i) Oxidation of glucose in the muscles
(ii) Oxidation of glucose in body cells
(iii) Breakdown of glucose anaerobically.
Answer: (a) Oxidation of glucose in the muscles occur in the absence of oxygen. The end products formed are lactic acid and ATP.
(b) Oxidation of glucose in body cells occur in the mitochondria in presence of oxygen. The end products are carbon dioxide, water and ATP.
(c) Breakdown of glucose anaerobically in yeast produces Ethanol, carbon dioxide and ATP.
17. Give only the function of the following
(a) Stomatal pore (b) Guard cell.
Answer: (a) Stomatal pore- It allows carbon dioxide to diffuse into leaf for photosynthesis. Water vapour and oxygen leave the leaf through the stomatal pores.
(b) Guard cell- Guard cell facilitate gas exchange into and out of the plant by closing and opening the stomatal pore.
18. What is the role of: (a) Bile (b) Lipase (c) Salivary amylase (d) Trypsin?
Answer: (a) Bile- bile which is produced by liver helps in breaking down lipids to fatty acids (in small intestine).
(b) Lipase-Lipase breaks down dietary fats to fatty acids and glycerol. It is secreted by pancreas in our digestive tract.
(c) Salivary amylase- It is secreted by the salivary gland and it acts on starch present in the food and breaks it down into smaller carbohydrate molecules.
(d) Trypsin-Trypsin secreted by the pancreas, hydrolyses more protein present in food that isn’t broken down by pepsin earlier.
19. What would be the consequences of a deficiency of haemoglobin in our bodies?
Answer: Haemoglobin picks up oxygen from lungs to form oxyhaemoglobin and delivers it to the body tissues. Its deficiency in our bodies will lead to anaemia. This is because the body cells will not receive sufficient oxygen due to deficiency of haemoglobin and thus the body will suffer with anaemia, facing nausea, dizziness, headache, fatigue etc.
20. What are the necessary conditions for autotrophic nutrition? What are its by-products?
Answer: Autotrophs are producers that make their own food by the process of photosynthesis. The necessary conditions for autotrophic nutrition, i.e., to make food are the presence of chlorophyll, carbon dioxide, water and sunlight. Glucose produced during photosynthesis is converted to starch and stored as food. The by-products of photosynthesis are oxygen and water.
21. Describe double circulation in human beings. Why is it necessary?
Answer: Double circulation is the process of blood flow through heart twice. Deoxygenated blood from body is returned to heart from where it is pumped to lungs. Lungs purify the blood and the oxygenated blood from the lungs return back to heart and is pumped to the body via aorta.
Double circulation is necessary because it separates the oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, makes the circulatory system more efficient, maintains constant body temperature, increased pressure of blood flow, quick supply of oxygen etc.
22. What are the differences between the transport of materials in xylem and phloem?
Answer: Xylem transports water and minerals in plants from roots up to the stem to the leaves. Phloem vessels transports soluble products of photosynthesis i.e., sucrose to plant’s growing and storage regions.
23. Draw a labelled diagram of sectional view of human heart of human digestive system.
Answer: