Periodic Classification of Elements Class 10 Important Questions and Answers
Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements covers each topic of the chapter. These questions aim at providing a better understanding of the chapter to the students and can be downloaded in PDF format. These important question bank help students in clearing their doubts so that they can score well in the exam.
While preparing for exams, students should practise these important questions of Class 10 Science to understand the concepts better. Solving important questions of Class 10 Science Chapter 5 will teach students time management skills and enhance their problem-solving skills. Also, students may come across a few of these questions in the board exam.
Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 – PDF
1. Name a group of elements which was not known when Mendeleev formulated his periodic table.
Answer: Noble gases were not known when Mendeleev formulated his periodic table. This is because the noble gases such as He, are etc. where not discovered at that time.
2. Element M is in the first group of the periodic table. Write the formula of its oxide.
Answer: First group of the periodic table is mainly known as alkali metals and they have valency = 1 and oxide with the valency = 2 so the formula of oxide would be M2O.
3. Why do you think the noble gases are placed in a separate group?
Answer: The noble gases are placed in a separate group because these are unreactive and present in a very low concentration in the atmosphere and their properties do not resemble with any other group so they are placed in a separate group.
4. An element belongs to the 3rd period and 2nd group of the periodic table. Find out the valence electrons and valency of this element.
Answer: The valency of an atom refers to the number of electrons present in the outermost shell. The element in the 3rd period and 2nd group is Magnesium (Mg). Its configuration is 2, 8, 2 which shows that its outermost shell has 2 valence electrons and its valency is 2.
5. Name two elements which will be chemically similar to aluminium. What is the basis of your choice?
Answer: In periodic table elements of the same group have the same chemical properties so aluminium will have same chemical properties are Gallium (Ga) and Indium (In). All these elements belong to the same group so they have similar chemical properties.
6. Amongst elements with atomic number 11 and 14, which has a bigger atomic size?
Answer: Both the elements with atomic number 11 and 14 lie in the same group so when we move from right to left in a period atomic size decreases. So, an element with atomic number 11 will be in bigger in size.
7. Element X with atomic number 12 and Y atomic number 17 reacts with hydrogen to form hydrides. Which of them is expected to have a high melting point?
Answer: The element with atomic number 12 is Magnesium (Mg) and element with atomic number 17 is Chlorine (Cl). When Mg reacts with hydrogen it forms MgH2 and chlorine forms HCl. MgH2 is solid and HCl is liquid so MgH2 has a higher melting point.
8. An element X has E.C. = 2, 8, 8, 1 while Y has 2, 8, 7. Which of these is a metal?
Answer: ‘X’ has 1 valence electron and it belongs to a 4th period so it is Potassium (K) and the ‘Y’ is of the 3rd period and it has 7 electrons in an outermost cell with atomic number 17 so it is Chlorine (Cl). We know that poopt5assium is a metal.
9. Name the most reactive element present in group 17.
Answer: Fluorine is a most reactive element in group 17 because of its small size and high electronegativity by which it accepts electron easily and forms a bond with another element.
10. Give the formula of oxide formed by a metal if it belongs to the 3rd period and 13th group.
Answer: 13th group consists of the following elements:
Boron (B), Aluminium (Al), Gallium (Ga), Indium (In), Thallium (Ti).
‘Al’ lies in the 3rd period so; the formula of oxide of Aluminium is ‘Al2O3’.
11. What similarity do you observe in:
(i) Elements belonging to the same period.
(ii) Elements belonging to the same group.
Answer: (i) Elements belonging to the same period have the same number of shells.
Example: Every element in the first period (top row) has one orbital for its electrons. All the elements in the second period (the second row) have two orbitals for their electrons.
(ii) Elements belonging to the same group have same number of valence electrons.
12. How is the valency of an element related to its electronic configuration? Explain giving suitable example.
Answer: The valency of an atom refers to the number of electrons present in the outermost shell. The number of valence electrons in the atom will determine the last number of the atom’s electron configuration.
For example, Sodium has an electron configuration of 2,8,1, so it has 2 valence electrons.
13. Why is the atomic number of the element more important to a chemist than its atomic mass?
Answer: Atomic number represents the number of electrons in the element and also in electronic configuration and physical and chemical properties.
14. What is the similarity between elements Li, Be, B, C, N, O, F and Ne belonging to the second period?
Answer: These all elements (Li, Be, B, C, N, O) belong to the same period i.e. Period 2. One similarity between them is they have the same number of shells.
15. Chlorine and bromine are kept in the same group in the periodic table. Why?
Answer: As Chlorine and Bromine consists of the same number of valence electrons in the outermost shell so they are kept in the same group of the periodic table.
16. Which amongst the following elements whose atomic number is given below belong to the same period?
Give reason. 17, 10, 20, 12, 19, 15.
Answer: We will first write the electronic configuration of all the elements mentioned:
17: – 2,8,7
10: – 2,8
20: – 2,8,8,2
12: – 2,8,2
19: – 2,8,8,1
15: – 2,8,5
So, the elements with atomic number 17, 12, 15 belong to the same period as they have the same number of the shell.
20, 19 belong to the same period as they have the same number of the shell.
17. What were the achievements of Mendeleev’s periodic table? What was the basis of the classification of elements in it?
Answer: The achievements by Mendeleev were:
(i) Mendeleev kept some blank spaces in the periodic table for the elements that were yet to be discovered.
E.g.: Eka-aluminium, Eka-boron, Eka-silicon.
(ii) He also predicted properties of some elements which were yet to be discovered.
E.g.: The properties of Eka-aluminium predicted by Mendeleev and those of element gallium were almost the same.
(iii) When noble gases were discovered, they could be placed in a new group without disturbing the order. The formula of the hydrides and oxides formed by an element were treated as one of the basic the properties of an element for its classification.
18. How does the electronic configuration of an atom relate to its position in the modern periodic table?
Answer: The modern periodic table contains of groups and periods.
(i) The atoms with identical outer shell electronic cell electronic configuration are in the same groups.
(ii) The atoms with same number of shells are in same period.
19. The elements of the second period of the periodic table are given along:
Li Be B C N O F
(a) Give a reason to explain why atomic radii decrease from Li to F.
(b) Identify the most:
(i) Metallic
(ii) Non-metallic elements.
Answer: (a) The atomic radii decrease from Li to F because of increase in nuclear charge which tends to pull electrons closer to nucleus and reduces the size of an atom.
(b) (i) As we go down the group metallic character increases and decreases along the period. So, the most metallic element is Li (Lithium)
(ii) As the metallic character decreases along the period, the non-metallic character increases. The most non-metallic element is F (fluorine).
20. The elements of the 3rd period of the periodic table are given along:
Na Mg Al Si P S Cl
(a) Which is more non-metallic S or Cl?
Na Mg Al Si P S Cl
(b) Which has a higher atomic mass: Al or Cl?
Answer: (a) Along the group non-metallic character increases so; Cl (Chlorine) is more non-metallic.
(b) As we see the trend as the atomic no. increases atomic mass also increases (other than few exceptions). So, Cl has a higher atomic mass than Al.
21. What physical and chemical properties of elements were used by Mendeleev in creating his Periodic Table? List two observations which posed a challenge to Mendeleev’s Periodic Law.
Answer: “The physical and chemical properties of the elements are the periodic functions of their atomic weights”.
According to Mendeleev periodic law, the characteristic property of the elements is based on their atomic weights. In this periodic table, elements are arranged in increasing order of their atomic weight.
Two observations which posed a challenge to Mendeleev’s periodic Law are:
- Isotopes of all elements posed a challenge to Mendeleev’s periodic law.
- The atomic masses do not increase in a regular manner in going from element to another so, it was not possible to predict how many elements could be discovered between 2 elements.
22. Study the Periodic Table and answer the following questions:
(i) Na has physical and chemical properties similar to which element(s) and why?
(ii) Write the electronic configuration of N and P. Which one of these will be more electronegative and why?
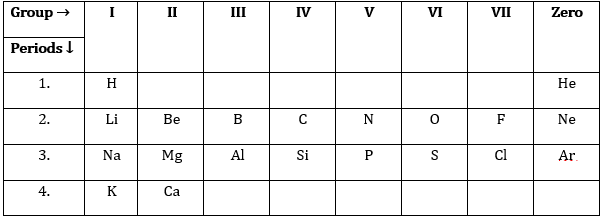
Answer: (i) Na has similar properties as of the same group members as K, Rb, Cs. They contain 1 valence in the outermost shell so all of them are reactive.
(ii) Nitrogen:- 2,5
Phosphorus:- 2,8,5
Electronegativity is a measure of how strongly atoms attract bonding electrons to themselves.
Nitrogen is more electronegative because in nitrogen outermost shell is nearer to nucleus and nucleus will attract electrons easily.
23. Using the above periodic table Explain why:
(i) Li and Na are considered as active metals.
(ii) Atomic size of Mg is less than that of the Na.
(iii) F is more reactive than Cl.
Answer: (i) Li and Na have a single electron in the outermost shell. They can easily lose 1 electron and produce cation which causes chemical reactions which are explosive in nature.
(ii) Na and Mg both lie in the same period so along the period atomic size decreases. So, the size of Mg is smaller than Na.
(iii) Electronegativity of F is more than Cl i.e. F has more affinity to attract electrons because of its small size due to this F is more reactive than Cl.
24. Explain giving a reason, why:
(i) Metallic character decreases in a period.
(ii) Atomic size increases in a group.
(iii) Chemical reactivity first decreases and then increases in a period.
Answer: (i) As the effective nuclear charge acting on the valence shell increases across the period, the tendency to lose electrons decreases due to this metallic character decreases.
(ii) Atomic size increases in a group because new shells are being added as we go down the group. This increases the distance between the outermost shell and nucleus.
(iii) The reactivity of element depend upon their tendency to lose or gain electrons to complete their outermost shell, greater is the tendency to lose/gain electron greater is the reactivity
So, in a period first tendency to lose electron decreases so reactivity decreases and the tendency to gain electron increases so the reactivity increases.
25. The position of three elements A, B and C in the Periodic table is given above. Giving a reason, explain the following:
(i) Element A is a non-metal.
(ii) An atom of element C has a larger size than an atom of element A.
(iii) Element B has a valency of 1.
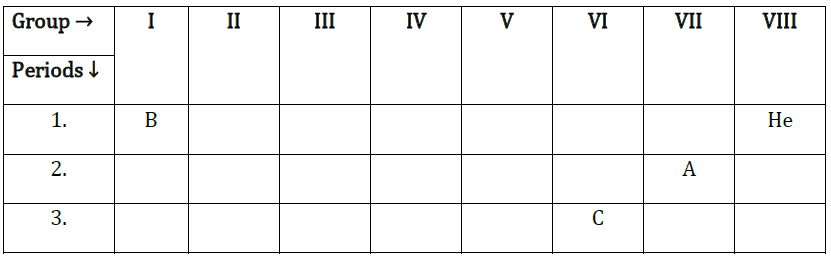
Answer: (i) Element A is closer to noble gas and is on the right side of the period and in the periodic table, non-metals are on the right side.
(ii) As we go down in periodic table atomic size increases, so the size of element C is greater than element A.
(iii) Element B is in the first group and it consists of elements having 1 electron in the outermost shell so it has valency 1.
26. Define the following:
(i) Ionisation energy
(ii) Electron affinity
(iii) Atomic radii
(iv) Modern periodic law
Answer: (i) Ionisation energy: It is the amount of energy required to remove an electron from an isolated gaseous atom.
(ii) Electron affinity: Electron affinity is the energy which is released when an extra electron is added to an isolated gaseous atom in its outermost shell.
(iii) Atomic radii: The distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost shell is defined as atomic radii.
(iv) Modern periodic law: Properties of the element are a periodic function of their atomic number.